Strategies for Improving Wildlife Habitat
- February 11, 2025
- 0 comment
Wildlife habitat management plays a crucial role in preserving the rich biodiversity of our planet. As human activities continue to expand and encroach upon natural environments, the delicate balance of ecosystems is increasingly threatened. Effective strategies are needed to ensure that wildlife can thrive in their natural habitats, despite the pressures of development, climate change, and other challenges.

By focusing on restoring and maintaining these habitats, we can support the diverse species that depend on them and promote a healthier, more resilient environment. Understanding and implementing key approaches to habitat management is essential for the long-term conservation of wildlife and the ecosystems they inhabit.
Habitat Restoration and Rehabilitation
One of the most effective strategies for improving wildlife habitat management is habitat restoration and rehabilitation. This involves returning a degraded or altered habitat to its original condition or improving it to support a broader range of wildlife species. Restoration efforts can include planting native vegetation, removing invasive species, re-establishing wetlands, and reconstructing natural waterways.

- Restoration of Vegetation: Replanting native plants that are well-suited to the local environment can help restore the natural balance of ecosystems. Native plants provide essential food, shelter, and breeding sites for wildlife, making them a cornerstone of habitat restoration projects.
- Removal of Invasive Species: Invasive species often outcompete native plants and animals, leading to habitat degradation. Effective management includes the removal or control of these invasive species to allow native species to recover.
- Wetland Reconstruction: Wetlands are among the most productive ecosystems in the world, providing crucial habitat for a variety of species. Reconstructing drained or altered wetlands can significantly improve the habitat for waterfowl, amphibians, and many other species.
Habitat Connectivity and Corridor Development
Fragmentation of habitats due to urbanization, agriculture, and infrastructure development is a major threat to wildlife populations. To counteract this, creating habitat corridors and enhancing connectivity between fragmented habitats is vital.

- Wildlife Corridors: These are strips of natural habitat that connect isolated patches of ecosystems. Corridors allow animals to move safely between different areas, promoting genetic diversity and reducing the risk of inbreeding.
- Underpasses and Overpasses: In regions where highways or railways disrupt animal movement, building underpasses or overpasses specifically designed for wildlife can help reduce roadkill and connect fragmented habitats.
- Buffer Zones: Establishing buffer zones around critical habitats can protect wildlife from the adverse effects of human activities. These zones can serve as transitional areas where human activities are gradually minimized to allow for more natural conditions closer to the core habitats.
Sustainable Land Use Practices
Integrating sustainable land use practices into agricultural and forestry activities is crucial for wildlife habitat management. These practices aim to minimize the impact of human activities on wildlife while ensuring that land remains productive for human use.

- Agroforestry: This practice combines agriculture and forestry to create a more diverse and sustainable land-use system. Agroforestry can provide habitat for wildlife while also offering economic benefits for farmers.
- Conservation Tillage: Reducing tillage in agriculture can help preserve soil structure, reduce erosion, and maintain habitat for ground-dwelling species. It also promotes healthier soil ecosystems, which in turn supports a diverse range of wildlife.
- Sustainable Forestry: Implementing selective logging and maintaining old-growth forests can ensure that forestry activities do not completely disrupt wildlife habitats. Sustainable forestry practices help maintain habitat continuity and preserve critical areas for wildlife.
Protection of Key Habitats
Some habitats are more critical than others for the survival of certain species. Identifying and protecting these key habitats is essential for effective wildlife habitat management.

- Critical Habitats: These are areas essential for the survival of endangered or threatened species. Protecting critical habitats from development and degradation is a legal requirement in many regions, but it also requires active management to maintain their ecological integrity.
- Seasonal Habitats: Many species depend on different habitats at different times of the year, such as breeding grounds, wintering areas, or migration stopovers. Protecting these seasonal habitats is crucial for the life cycle of many species.
- Aquatic Habitats: Rivers, lakes, and coastal areas are vital for many wildlife species, including fish, birds, and mammals. Protecting these aquatic habitats from pollution, overfishing, and development is essential for maintaining biodiversity.
Adaptive Management and Monitoring
Wildlife habitat management is not a static process; it requires continuous monitoring and adaptive management to respond to changing conditions and new information.

- Adaptive Management: This is a dynamic approach that involves constantly evaluating the effectiveness of management strategies and making adjustments as needed. Adaptive management allows wildlife managers to respond to unforeseen challenges and opportunities effectively.
- Regular Monitoring: Implementing long-term monitoring programs helps track the health of ecosystems and the success of management strategies. Monitoring provides valuable data that can inform future management decisions and ensure that strategies are working as intended.
- Community Involvement: Engaging local communities in monitoring and management efforts can enhance the effectiveness of wildlife habitat management. Community members often have valuable knowledge of local ecosystems and can play a crucial role in protecting and restoring habitats.
Integrating Technology in Wildlife Habitat Management
The use of technology can greatly enhance the effectiveness of wildlife habitat management. From satellite imagery to drones, various technological tools are available to monitor, protect, and restore habitats.
GIS Mapping
Geographic Information Systems (GIS) can be used to map habitats, track changes over time, and identify areas in need of protection or restoration. GIS data can also help managers plan more effective strategies by providing a comprehensive view of the landscape.
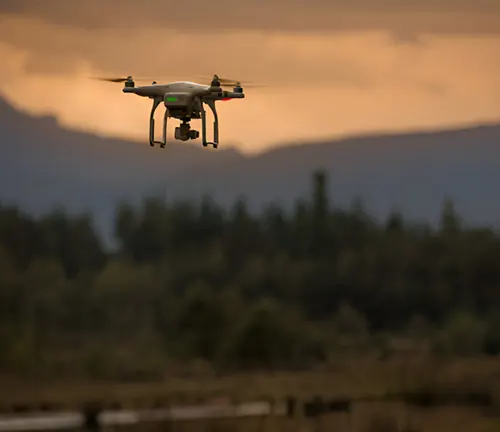
Remote Sensing
Satellites and drones equipped with cameras and sensors can monitor large areas of habitat with high precision. Remote sensing can detect changes in vegetation, water levels, and other key indicators of habitat health.
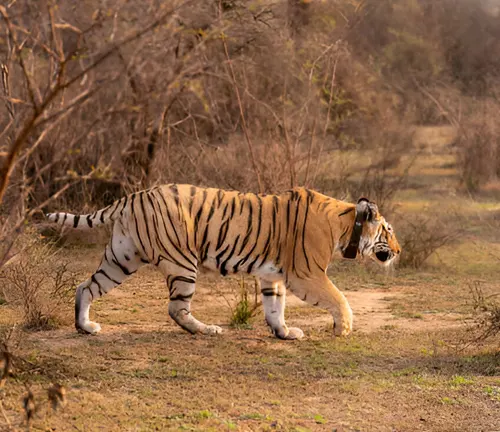


Wildlife Tracking
GPS collars and tags can be used to track the movements of wildlife, providing valuable data on habitat use and migration patterns. This information can inform the creation of wildlife corridors and other management strategies.
Policy and Legislation
Effective wildlife habitat management often requires strong policy and legal frameworks. Governments play a critical role in establishing and enforcing laws that protect habitats and regulate activities that impact wildlife.

- Protected Areas: Establishing national parks, wildlife reserves, and other protected areas is a fundamental strategy for habitat conservation. These areas provide safe havens for wildlife and help preserve biodiversity.
- Environmental Regulations: Governments can enforce regulations that limit habitat destruction and pollution, such as restrictions on land development, logging, and industrial activities. Strong environmental laws are essential for protecting habitats from degradation.
- International Cooperation: Many wildlife species migrate across borders, requiring international cooperation for effective habitat management. Treaties and agreements between countries can help protect migratory routes and ensure the conservation of shared ecosystems.
Addressing Climate Change
Climate change is one of the most significant threats to wildlife habitats. Effective habitat management must consider the impacts of climate change and incorporate strategies to mitigate its effects.
- Climate-Resilient Habitats: Identifying and protecting habitats that are likely to remain stable in the face of climate change is a key strategy. These areas can serve as refuges for species affected by changing environmental conditions.
- Species Relocation: In some cases, it may be necessary to relocate species to areas where the climate is more suitable. This strategy, known as assisted migration, can help prevent species extinctions but requires careful planning and monitoring.
- Carbon Sequestration: Managing habitats to enhance their ability to sequester carbon can help mitigate climate change. For example, restoring wetlands and forests can increase carbon storage while also providing essential wildlife habitats.
Education and Public Awareness
Public support is crucial for the success of wildlife habitat management efforts. Educating the public about the importance of wildlife conservation and how they can contribute is an effective strategy.
- Educational Programs: Schools, nature centers, and conservation organizations can offer programs that teach people about local wildlife and the importance of habitat conservation. These programs can inspire a new generation of conservationists.
- Public Campaigns: Media campaigns, social media, and community events can raise awareness about the need for wildlife habitat management. Engaging the public through these platforms can lead to greater support for conservation initiatives.
- Citizen Science: Encouraging the public to participate in citizen science projects, such as wildlife monitoring and habitat restoration, can increase community involvement and provide valuable data for habitat management.
Conclusion
Improving wildlife habitat management is a complex and ongoing process that requires a multifaceted approach. By implementing strategies such as habitat restoration, corridor development, sustainable land use, and adaptive management, we can significantly enhance the quality of habitats for wildlife. Moreover, addressing climate change, leveraging technology, and promoting public awareness are essential components of a successful habitat management strategy. With the right combination of efforts, we can ensure that wildlife populations thrive and that ecosystems remain healthy and resilient for generations to come.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
- What is wildlife habitat management?
Wildlife habitat management involves the practices and strategies used to maintain, restore, or enhance the natural environments that support various wildlife species. The goal is to ensure that these habitats provide the necessary resources for wildlife to thrive, including food, water, shelter, and space. - Why is habitat restoration important for wildlife conservation?
Habitat restoration is crucial because it helps to recover ecosystems that have been degraded or destroyed by human activities. Restoring habitats can increase biodiversity, support endangered species, and improve the overall health of the environment, making it more resilient to future disturbances. - How does habitat fragmentation affect wildlife?
Habitat fragmentation occurs when large, continuous habitats are divided into smaller, isolated patches due to human activities such as urbanization, agriculture, and infrastructure development. This fragmentation can limit the movement of wildlife, reduce genetic diversity, and increase the risk of inbreeding and population decline. - What are wildlife corridors, and why are they important?
Wildlife corridors are natural or man-made strips of habitat that connect fragmented ecosystems, allowing animals to move safely between them. These corridors are vital for maintaining genetic diversity, enabling migration, and providing access to different resources throughout the year. - How can sustainable land use practices benefit wildlife habitats?
Sustainable land use practices, such as agroforestry, conservation tillage, and selective logging, help minimize the impact of human activities on wildlife habitats. These practices promote a balance between land productivity and conservation, ensuring that habitats remain viable for wildlife while also supporting human needs. - What role does climate change play in wildlife habitat management?
Climate change alters temperature, precipitation patterns, and ecosystems, impacting the habitats that wildlife depend on. Effective habitat management must incorporate strategies to mitigate and adapt to these changes, such as protecting climate-resilient areas and facilitating species migration to more suitable habitats. - How is technology used in wildlife habitat management?
Technology plays a significant role in wildlife habitat management by providing tools for monitoring, mapping, and tracking wildlife and their habitats. Geographic Information Systems (GIS), remote sensing, and GPS tracking are examples of technologies that help conservationists make informed decisions and manage habitats more effectively. - What are the challenges in implementing wildlife habitat management strategies?
Challenges include habitat fragmentation, limited funding, conflicting land-use interests, invasive species, and the impacts of climate change. Additionally, coordinating efforts across different stakeholders, such as governments, private landowners, and conservation organizations, can be complex. - How can individuals contribute to wildlife habitat management?
Individuals can contribute by supporting conservation initiatives, participating in habitat restoration projects, reducing their environmental footprint, and promoting awareness about the importance of wildlife conservation. Citizen science projects also offer opportunities for people to get involved in monitoring and protecting local wildlife habitats. - Why is monitoring and adaptive management important in wildlife habitat management?
Monitoring allows managers to assess the effectiveness of habitat management strategies and make necessary adjustments. Adaptive management is a flexible approach that uses ongoing monitoring data to refine and improve management practices over time, ensuring that conservation efforts remain effective in the face of changing conditions.

Benjamin Brooks
Forestry AuthorGreetings! I'm Benjamin Brooks, and my journey over the past 15 years has revolved around the fascinating realms of content creation, expertise in snow clearing, and the intricate world of lumberjacking and landscaping. What began as a simple curiosity about the natural world and heavy machinery has evolved into a passionate profession where my love for crafting words intertwines seamlessly with my lumberjacking and garden skills.













Leave your comment