Sustainable Management of Renewable Forest Resources
- January 30, 2025
- 0 comment
Sustainable management of renewable forest resources is a comprehensive approach that balances the ecological, economic, and social functions of forests to ensure their longevity and productivity for future generations. This method integrates practices such as selective logging, reforestation, and conservation of biodiversity, aiming to maintain the health and diversity of forest ecosystems. By managing forests sustainably, we can continue to harvest timber and non-timber products without depleting these vital resources. It also involves protecting watersheds, preserving wildlife habitats, and maintaining soil stability, all of which contribute to the overall resilience of the environment.

Sustainable forest management supports local communities by providing ongoing employment opportunities and resources while fostering a deeper connection between people and nature. Through careful planning and the use of advanced technologies, this approach helps mitigate climate change by enhancing carbon sequestration and reducing greenhouse gas emissions. Ultimately, sustainable management of renewable forest resources ensures that forests continue to provide essential ecological services and economic benefits, safeguarding them for the enjoyment and use of future generations.
Title of Content
- Sustainable Management of Renewable Forest Resources
- Principles of Sustainable Forest Management
- Practices and Techniques
- Environmental Benefits
- Economic and Social Impacts
- Future Directions
Sustainable Management of Renewable Forest Resources
Sustainable management of renewable forest resources is an essential practice aimed at preserving forests’ ecological, economic, and social benefits while ensuring their availability for future generations. This article delves into the principles, practices, benefits, challenges, case studies, and future directions of sustainable forest management.
Principles of Sustainable Forest Management

Balance between Resource Extraction and Conservation
Sustainable forest management seeks a balance between the extraction of resources and the conservation of the forest ecosystem. This balance ensures that forests can continue to provide valuable resources without compromising their health and biodiversity.
Maintenance of Forest Health and Biodiversity
A core principle of sustainable forest management is maintaining the overall health and biodiversity of forests. This involves protecting various plant and animal species, ensuring ecosystem stability, and preventing the degradation of forest environments.
Long-term Planning and Monitoring
Long-term planning and continuous monitoring are crucial for sustainable forest management. These processes involve setting goals for forest conservation, regularly assessing forest health, and making necessary adjustments to management practices based on monitoring data./
Practices and Techniques

Selective Logging
Selective logging involves carefully choosing which trees to harvest to minimize environmental impact. This practice is based on specific criteria for tree selection and aims to maintain the forest structure and biodiversity.
Criteria for Tree Selection
Tree selection in selective logging is guided by criteria such as tree age, size, species, and overall health. This ensures that only mature trees are harvested, allowing younger trees to grow and sustain the forest.
Impact on Forest Structure
By selectively logging trees, the forest structure remains largely intact, supporting continued biodiversity and ecosystem services. This contrasts with clear-cutting methods, which can devastate forest landscapes.
Reforestation and Afforestation
Reforestation involves planting trees in areas where forests have been depleted, while afforestation is the creation of new forests in previously non-forested areas. Both practices are vital for ecosystem recovery and sustainability.
Techniques and Species Selection
Reforestation and afforestation require careful selection of techniques and tree species. Native species are often preferred as they are best suited to the local environment and contribute to biodiversity.
Importance for Ecosystem Recovery
These practices help restore ecosystems, improve soil health, and enhance water cycles, supporting overall environmental resilience and productivity.
Conservation of Biodiversity
Conserving biodiversity is a key aspect of sustainable forest management. This involves protecting endangered species and maintaining genetic diversity within forest ecosystems.
Protection of Endangered Species
Efforts to protect endangered species focus on preserving their habitats and ensuring that logging practices do not threaten their survival.
Maintenance of Genetic Diversity
Maintaining genetic diversity within tree populations ensures resilience against diseases, pests, and changing environmental conditions, contributing to long-term forest health.
Agroforestry and Mixed-use Management
Agroforestry integrates agriculture and forestry, providing benefits to local communities and ecosystems. This practice supports sustainable land use by combining tree cultivation with crops or livestock.
Integration of Agriculture and Forestry
Agroforestry practices can include planting trees alongside crops or using trees to provide shade and shelter for livestock, enhancing the productivity and sustainability of both agriculture and forestry.
Benefits for Local Communities and Ecosystems
Agroforestry provides economic benefits to local communities through diversified income sources and improved ecosystem services, such as enhanced soil fertility and biodiversity.
Environmental Benefits
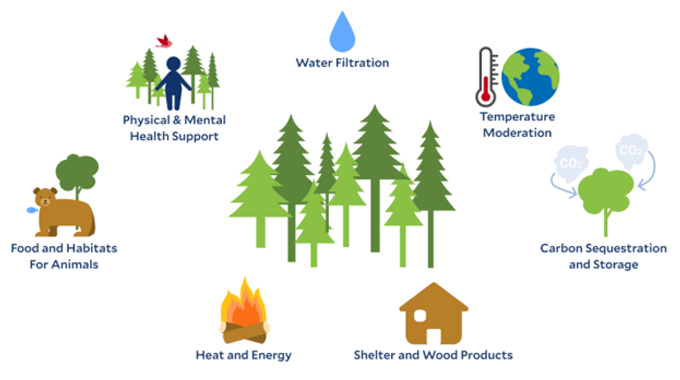
Enhanced Carbon Sequestration
Sustainable forest management enhances carbon sequestration, helping mitigate climate change by absorbing and storing carbon dioxide from the atmosphere.
Soil Stability and Prevention of Erosion
By maintaining vegetation cover and root structures, sustainable practices help stabilize soil and prevent erosion, protecting both the forest and surrounding areas.
Protection of Water Quality and Watershed Management
Forests play a crucial role in maintaining water quality and managing watersheds. Sustainable management ensures that forests continue to filter and regulate water, benefiting ecosystems and human populations.
Preservation of Wildlife Habitats
Preserving wildlife habitats is a significant environmental benefit of sustainable forest management. It ensures that diverse species can thrive and that ecosystems remain balanced and resilient.
Economic and Social Impacts

Sustainable Timber and Non-timber Product Harvesting
Sustainable management supports the harvesting of timber and non-timber products in a way that maintains forest health and productivity, providing long-term economic benefits.
Economic Benefits and Market Stability
Sustainable practices create market stability by ensuring a steady supply of forest products, promoting economic resilience, and supporting livelihoods dependent on forest resources.
Examples of Sustainable Products
Examples of sustainably harvested products include certified timber, non-timber forest products like nuts and berries, and eco-tourism services that leverage the forest’s natural beauty.
Employment Opportunities in Forest Management
Sustainable forest management generates employment opportunities in areas such as conservation, reforestation, and eco-tourism, contributing to local economies.
Training and Education for Sustainable Practices
Providing training and education for sustainable forest management practices is essential for building a skilled workforce capable of implementing and maintaining these practices.
Long-term Job Creation
Sustainable management practices lead to long-term job creation by ensuring that forest resources remain viable and productive over time.
Benefits to Local and Indigenous Communities
Local and indigenous communities benefit from sustainable forest management through resource rights, management involvement, and the preservation of cultural and social values.
Resource Rights and Management Involvement
Empowering local and indigenous communities with resource rights and involving them in management decisions fosters sustainable practices and respects their traditional knowledge.
Cultural and Social Values of Forests
Forests hold significant cultural and social values for many communities. Sustainable management ensures that these values are preserved and respected.
Challenges and Solutions
Initial Costs and Investment in Sustainable Practices
Implementing sustainable practices can involve initial costs and investments in training, equipment, and infrastructure. However, these costs are often offset by long-term benefits and savings.
Need for Continuous Education and Training
Ongoing education and training are necessary to keep up with advancements in sustainable practices and ensure effective implementation.
Balancing Economic Demands with Conservation Efforts
Balancing economic demands with conservation efforts is a critical challenge. Sustainable management seeks to find a middle ground that meets economic needs while preserving forest ecosystems.
Policy and Regulatory Support
Strong policy and regulatory support are essential for promoting sustainable forest management practices. Governments and international organizations play a crucial role in providing incentives and enforcing regulations.
Role of Government and International Organizations
Governments and international organizations can support sustainable management through funding, research, and policy development, promoting global collaboration.
Effective Enforcement and Incentives
Effective enforcement of regulations and providing incentives for sustainable practices encourage compliance and promote widespread adoption.
Future Directions
Advances in Technology and Sustainable Practices
Advances in technology and sustainable practices continue to improve the effectiveness and efficiency of forest management, offering new tools and methods for sustainability.
Potential for Global Adoption and Collaboration
There is significant potential for the global adoption of sustainable forest management practices through international collaboration and knowledge sharing.
Role of Public Awareness and Consumer Behavior
Increasing public awareness and influencing consumer behavior toward sustainable products play a crucial role in supporting sustainable forest management.
Vision for the Future of Forest Management
The future of forest management lies in the widespread adoption of sustainable practices, driven by innovation, collaboration, and a commitment to preserving our planet’s vital forest resources.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
- What is Sustainable Management of Renewable Forest Resources?
Sustainable management of renewable forest resources involves practices that balance the ecological, economic, and social functions of forests to ensure their long-term health and productivity. It aims to meet current needs for forest products without compromising the ability of future generations to meet their own needs. - Why is Sustainable Forest Management important?
Sustainable forest management is crucial for maintaining biodiversity, supporting ecosystem services like carbon sequestration and water regulation, providing economic benefits through timber and non-timber products, and preserving cultural and social values associated with forests. - What principles guide Sustainable Forest Management?
The principles of sustainable forest management include balancing resource extraction with conservation, maintaining forest health and biodiversity, and implementing long-term planning and monitoring to adapt to changing conditions and ensure sustainability. - What are some key practices and techniques used in Sustainable Forest Management?
Key practices include selective logging, reforestation and afforestation, conservation of biodiversity, and agroforestry. These practices are designed to minimize environmental impact, promote ecosystem recovery, and integrate multiple land uses to benefit both the environment and local communities. - How does Selective Logging contribute to sustainability?
Selective logging involves carefully choosing which trees to harvest based on specific criteria, such as age and species, to minimize disruption to the forest structure. This practice helps maintain biodiversity, supports forest regeneration, and reduces soil erosion and habitat destruction. - What are the environmental benefits of Sustainable Forest Management?
Environmental benefits include enhanced carbon sequestration, improved soil stability and prevention of erosion, protection of water quality, and preservation of wildlife habitats. These benefits contribute to the overall health and resilience of forest ecosystems. - How does Sustainable Forest Management impact local communities?
Sustainable forest management provides economic benefits through job creation, supports livelihoods through sustainable harvesting of timber and non-timber products, and involves local and indigenous communities in management decisions. It also preserves cultural and social values tied to forests. - What challenges are faced in implementing Sustainable Forest Management?
Challenges include initial costs and investments, the need for continuous education and training, balancing economic demands with conservation efforts, and ensuring effective policy and regulatory support. Addressing these challenges requires collaboration between governments, organizations, and communities. - Are there successful examples of Sustainable Forest Management?
Yes, there are numerous successful examples from various regions and forest types. These projects demonstrate the feasibility and benefits of sustainable practices and offer valuable lessons and models for replication in other areas. - What is the future potential of Sustainable Forest Management?
The future potential includes advancements in technology and sustainable practices, wider global adoption through international collaboration, increased public awareness, and consumer behavior shifts towards sustainable products. The vision is for sustainable management to become the standard practice worldwide.

Benjamin Brooks
Forestry AuthorGreetings! I'm Benjamin Brooks, and my journey over the past 15 years has revolved around the fascinating realms of content creation, expertise in snow clearing, and the intricate world of lumberjacking and landscaping. What began as a simple curiosity about the natural world and heavy machinery has evolved into a passionate profession where my love for crafting words intertwines seamlessly with my lumberjacking and garden skills.













Leave your comment