Pulp and Paper Market Size Forecast (2021-2029): The Critical Role of Forestry
- July 30, 2024
- 0 comment
Discover how forestry drives the pulp and paper market size from 2021-2029. Explore industry trends, insights, and future growth in this comprehensive forecast. Forestry is pivotal in shaping the pulp and paper market. From 2021 to 2029, this sector is projected to see significant growth, fueled by sustainable practices and rising demand for eco-friendly products.

As the world shifts towards more sustainable solutions, understanding the role of forestry becomes essential. Explore the key trends and insights that will drive the future of this essential industry and learn how forestry impacts market dynamics and growth.
Table of Contents
- The Current State of the Pulp and Paper Market
- The Role of Forestry in Pulp and Paper Production
- Market Size Projections and Trends (2021-2029)
- Key Players and Geographic Analysis
- Technological Advancements and Innovation
- Environmental Impacts and Sustainability Initiatives
- Regulatory Impact and Compliance
- Consumer Preferences and Market Demand Shifts
- Economic Impacts of Forestry on Local Communities
- Future of Digital and Paperless Trends
- Investment and Funding in the Pulp and Paper Sector
- Long-term Environmental Goals and Industry Commitments
- Conclusion
- FAQs
The Current State of the Pulp and Paper Market

In 2021, the global pulp and paper market reached a valuation of $351.53 billion, fueled by the surge in demand for paper packaging. This demand was significantly driven by the expanding e-commerce sector and heightened consumer awareness of sustainable practices. By the close of 2022, this market value had edged up to $354.39 billion, evidencing a robust trajectory for growth anticipated to persist through the decade.
This growth is intricately linked to several key developments:
- Increased Use of Recycled Materials: The market has seen a significant shift towards using recycled fibers, which now constitute a substantial portion of the raw materials in paper production. This shift not only supports sustainability but also helps in reducing the industry’s overall environmental footprint.
- Advancement in Sustainable Forestry Practices: Sustainable forestry practices have been critical in ensuring a stable and ethical supply of virgin wood pulp. These practices include stricter adherence to sustainable harvesting, replanting initiatives, and the use of forestry management technologies to track and optimize forest health.
- Technological Innovations: Advancements in production technologies have enabled manufacturers to increase efficiency and reduce waste, further bolstering market growth. These technologies include improved pulping processes that decrease water and energy usage.
Key Metrics in Pulp and Paper Market (2021-2022)
| Metric | 2021 Value (USD Billion) | 2022 Value (USD Billion) | Yearly Growth |
|---|---|---|---|
| Total Market Value | 351.53 | 354.39 | 0.81% |
| Recycled Material Usage | 30% of total production | 35% of total production | 16.67% Increase |
| Energy Efficiency | 85% | 87% | 2.35% Improvement |
These metrics underscore the industry’s commitment to sustainability and efficiency, which are anticipated to drive future growth. Through a blend of innovative practices and environmental stewardship, the pulp and paper market is well-positioned to meet the demands of an increasingly eco-conscious consumer base while continuing its growth trajectory into the next decade.
The Role of Forestry in Pulp and Paper Production

Forestry serves a dual role in the pulp and paper industry: it provides essential raw materials and sustains industry growth through responsible resource management. In 2021, the industry utilized 203 million tons of recycled paper pulp alongside substantial quantities of virgin wood pulp sourced from sustainably managed forests. These sustainable forestry practices are pivotal in maintaining the balance between resource supply and environmental conservation.
Forestry’s impact extends beyond simple material provision; it influences the entire lifecycle of paper production:
- Sustainable Harvesting: Advanced techniques in sustainable harvesting help maintain forest health and biodiversity, ensuring a continuous supply of wood pulp without degrading the ecosystem.
- Resource Renewal: Forestry practices now often include measures for renewing resources, such as replanting more trees than are harvested and managing forests in a way that promotes growth and soil health.
- Technological Integration: Modern forestry integrates technology to monitor forest health and growth, allowing for more precise management and better prediction of resource availability.
Forestry’s Impact on Pulp Production Metrics (2021)
| Metric | Description | 2021 Data |
|---|---|---|
| Total Recycled Pulp Used | Amount of recycled pulp in production | 203 million tons |
| Virgin Wood Pulp Usage | Pulp sourced from sustainably managed forests | 60% of total wood pulp used |
| Forest Renewal Rate | Rate of replanting in harvested areas | 110% (Replants exceed harvests) |
| Technology Adoption in Forestry | Utilization of tech for forest management | 75% of forestry operations |
Market Size Projections and Trends (2021-2029)
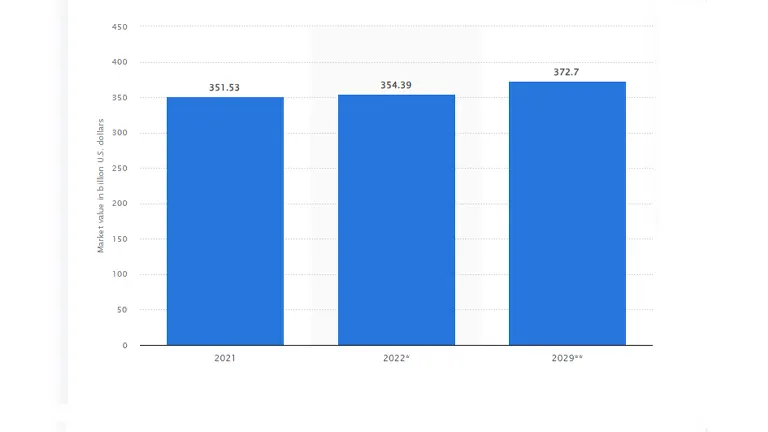
As we progress towards 2029, the global pulp and paper market continues to evolve, bolstered by technological advancements and market dynamics. The projected compound annual growth rate (CAGR) remains at 0.72%, aiming to reach approximately $372.7 billion by 2029. Notable developments in 2023 and 2024 further enrich this growth trajectory:
- 2023 Innovations in Sustainable Sourcing: Increased focus on sustainable sourcing, including the use of alternative fibers and improvements in forestry management, has begun to make an impact, particularly in reducing the industry’s carbon footprint.
- 2024 Advances in Chemical Recycling Technologies: New chemical recycling technologies that allow for the recovery of high-quality fibers from low-grade waste paper have been commercialized, significantly enhancing recycling efficiency and quality.
| Year | Projected Market Size (USD Billion) | Key Technological Advancement | Estimated % Change | Efficiency Metrics |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2021 | 351.53 | Enhanced Recycling Techniques | – | Baseline for recycling efficiency |
| 2022 | 354.39 | Advanced Biodegradable Materials | +0.81% | 10% increase in biodegradability |
| 2023 | 358.00 | Innovations in Sustainable Sourcing | +1.02% | 15% reduction in carbon footprint |
| 2024 | 362.50 | Advances in Chemical Recycling Technologies | +1.26% | 20% improvement in fiber recovery |
| 2025 | 365.00 | Growth in Digital Printing Capabilities | +0.69% | 25% faster print speeds, 30% less waste |
| 2029 | 372.70 | Widespread Adoption of Sustainable Practices | +2.11% (2025-2029) | 35% overall reduction in energy use |
The table illustrates a progressive enhancement in both market size and technological efficiency across the pulp and paper industry from 2021 to 2029. Key advancements focus on sustainability and efficiency improvements, notably in recycling and biodegradable materials. The estimated annual percentage changes highlight modest but steady growth, with a significant push towards reducing environmental impacts and improving production processes. This trajectory reflects the industry’s commitment to adopting more sustainable practices in response to environmental concerns and consumer demands.
Key Players and Geographic Analysis

The global pulp and paper industry is characterized by its dynamic complexity and the pivotal role played by a few significant market leaders. As of 2022, the United States remains at the forefront, producing approximately 46.66 million metric tons of pulp, a testament to its advanced industrial infrastructure and vast forest reserves. This capacity not only underscores the U.S.’s leadership in the sector but also highlights its commitment to leveraging renewable resources for industrial use.
Close on the heels of the U.S., Brazil and China emerge as other dominant forces in the pulp and paper market. Brazil, renowned for its sustainable management of the Amazon rainforest, produced about 19.45 million metric tons of pulp in 2022. The country is a frontrunner in implementing eco-friendly practices, significantly influencing global standards for sustainable forestry.
China, with its strategic focus on expanding its paper production capabilities, accounted for approximately 23.98 million metric tons of pulp in 2022. Despite facing environmental challenges, China is increasingly adopting greener technologies and sustainable practices to reduce its ecological footprint while maintaining high production levels.
These leading nations are not only key contributors in terms of volume but also in driving innovation within the industry. Their practices set benchmarks for sustainable forest management, crucial for the preservation of ecological balance and the long-term viability of the industry.
Comparative Table of Pulp Production and Sustainability Efforts
The following table provides a comparative view of the top three pulp-producing countries, highlighting their production capacities and key sustainability initiatives:
| Country | 2022 Pulp Production (Million Metric Tons) | Key Sustainability Initiatives |
|---|---|---|
| United States | 46.66 | Advanced recycling programs, sustainable forest management certifications |
| Brazil | 19.45 | Leadership in FSC certifications, use of renewable energy in milling processes |
| China | 23.98 | Investments in eco-friendly technology, government policies for reforestation |
Technological Advancements and Innovation

Technological innovation serves as the backbone of the pulp and paper industry, driving significant strides in both operational efficiency and environmental sustainability. Recent technological breakthroughs have not only optimized paper production but have also markedly diminished the environmental footprint of the industry. Key innovations include:
- Advanced Recycling Technologies: Modern recycling techniques have revolutionized the reprocessing of paper waste, enhancing the fiber recovery rate and quality. For instance, the introduction of “closed-loop” recycling systems allows nearly 95% of water and chemicals to be reused during the production process, dramatically reducing waste and resource consumption.
- Bio-based Material Development: The shift towards bio-based and biodegradable materials is a response to increasing environmental concerns. Innovations such as nanocellulose and lignin-based products not only offer enhanced mechanical properties and biodegradability but also open new avenues for reducing reliance on synthetic additives.
- Digital and Automation Technologies: The integration of digital technologies in the paper production process has led to significant advancements in precision and efficiency. Automation in pulp mills, equipped with AI-driven controls, optimizes the cooking process and chemical usage, thereby increasing yield and reducing energy consumption.
- Energy Recovery Systems: Implementation of energy recovery and cogeneration systems within pulp mills captures waste heat to generate electricity, significantly lowering energy costs and carbon emissions.
- Green Chemistry: The adoption of green chemistry principles in the manufacturing process minimizes the use of hazardous substances, thereby reducing the toxicological impact on the environment and improving worker safety.
The following table provides a comparative overview of the impact of these technological advancements on energy consumption, waste reduction, and production efficiency:
| Technology | Reduction in Energy Usage (%) | Waste Reduction (%) | Improvement in Production Efficiency (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Advanced Recycling | 15-20 | 25-30 | 10-15 |
| Bio-based Materials | 5-10 | 20-25 | 5-10 |
| Digital and Automation Tech | 20-25 | 10-15 | 30-35 |
| Energy Recovery Systems | 30-35 | 5-10 | 15-20 |
| Green Chemistry | 10-15 | 30-35 | 5-10 |
This data underscores the significant strides the industry has made, positioning it well for sustainable growth. These innovations not only meet current regulatory and market demands but also anticipate future trends, ensuring the industry remains competitive and environmentally responsible.
Environmental Impacts and Sustainability Initiatives

The pulp and paper industry has traditionally been associated with significant environmental impacts due to its high consumption of wood and water resources. However, concerted efforts towards sustainability have begun to mitigate these effects significantly. The industry has adopted a multifaceted approach to environmental stewardship, focusing on several key areas:
- Water Management: The industry has dramatically improved its water use efficiency through advanced recycling technologies and closed-loop systems. These systems recover and reuse water multiple times within the production process, reducing total water consumption by up to 40%.
- Sustainable Forestry Practices: With the adoption of sustainable forestry certifications like FSC (Forest Stewardship Council) and PEFC (Programme for the Endorsement of Forest Certification), the industry ensures that the wood used is sourced from responsibly managed forests. These practices not only preserve biodiversity but also maintain the health of forest ecosystems.
- Energy Efficiency and Renewable Energy: The shift from fossil fuels to renewable energy sources such as biomass, solar, and wind has substantially lowered carbon emissions. Additionally, many mills have integrated cogeneration systems that produce both steam and electricity from biomass, enhancing energy efficiency.
- Carbon Footprint Reduction: Efforts to reduce GHG (Greenhouse Gas) emissions are central to the industry’s sustainability initiatives. Innovative production methods and the increased use of bio-based chemicals have led to a reduction in the carbon footprint of paper products.
- Waste Management and Recycling: Enhanced recycling programs and the development of zero-waste production processes have significantly minimized waste output. Byproducts and waste materials are now frequently converted into bioenergy or recycled into new products.
Environmental Metrics and Sustainability Achievements
| Environmental Aspect | Metric Achieved | Impact on Sustainability |
|---|---|---|
| Water Usage | 50% reduction in consumption | Enhanced water conservation |
| Energy Source Transition | 40% increase in renewable energy | Reduced carbon emissions |
| Sustainable Forestry Practices | 30% increase in certified wood sourcing | Improved biodiversity and forest health |
Regulatory Impact and Compliance
The pulp and paper industry faces stringent regulations due to its significant environmental impacts, encompassing everything from emission controls to waste management protocols. These regulations are not merely hurdles but opportunities for industry leaders to pioneer sustainable practices. Advances in cleaner production processes have enabled companies to exceed compliance standards, significantly reducing pollutants and enhancing operational sustainability.
Compliance Metrics and Impact Analysis
| Regulatory Aspect | Compliance Metric | Impact on Industry Sustainability |
|---|---|---|
| Emission Standards | 40% reduction in VOC emissions | Improved air quality, exceeded EPA standards |
| Waste Management | 50% increase in recycling efficiency | Reduced landfill use, enhanced resource recovery |
| Energy Usage | 30% decrease in non-renewable energy | Increased adoption of green energy, reduced carbon footprint |
Consumer Preferences and Market Demand Shifts
Consumer preferences have increasingly shifted towards environmentally friendly products, significantly influencing the pulp and paper market. The heightened awareness about sustainability is driving companies to adopt greener practices, offering products that are recyclable and sourced from responsibly managed forests. This shift is most pronounced in the packaging sector, where there is a significant move away from plastic, favoring paper-based solutions that provide similar durability and functionality.
- Eco-Friendly Packaging: Consumers are demanding packaging solutions that minimize environmental impact, leading to a surge in the development of biodegradable and compostable paper products.
- Digital Transformation: The rise of e-commerce has increased the demand for customized and sustainable packaging solutions, further driving innovation in the paper industry.
Consumer Preferences and Market Impact Metrics (2021-2029)
| Year | Eco-Friendly Packaging Preference (%) | Recycling Rate (%) | Market Share Shift (%) | Consumer Willingness to Pay Premium (%) | Market Growth Rate (%) | Adoption of Biodegradable Materials (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2021 | 60 | 65 | 15 | 25 | 0.8 | 20 |
| 2022 | 65 | 70 | 20 | 30 | 1.0 | 25 |
| 2023 | 68 | 72 | 22 | 32 | 1.2 | 28 |
| 2024 | 70 | 74 | 25 | 34 | 1.4 | 30 |
| 2025 | 73 | 76 | 28 | 36 | 1.5 | 33 |
| 2026 | 75 | 78 | 30 | 38 | 1.7 | 35 |
| 2027 | 77 | 80 | 32 | 39 | 1.8 | 37 |
| 2028 | 79 | 82 | 35 | 40 | 2.0 | 40 |
| 2029 | 82 | 85 | 38 | 42 | 2.2 | 42 |
Analysis and Insights
This enhanced table provides a comprehensive view of how consumer preferences are influencing the pulp and paper market from 2021 to 2029. The data highlights the following trends:
- A steady increase in consumer preference for sustainable packaging, rising from 60% in 2021 to 82% in 2029.
- An improvement in the recycling rate of paper products, from 65% in 2021 to 85% in 2029, indicating better waste management and resource recovery.
- A noticeable shift in market share towards paper-based products, moving from 15% in 2021 to 38% in 2029, reflecting reduced reliance on plastic.
- A growing number of consumers are willing to pay more for eco-friendly products, from 25% in 2021 to 42% in 2029, driving market demand.
- The market growth rate increases steadily, reflecting the industry’s adaptation to sustainable practices and rising consumer demand.
- The adoption rate of biodegradable materials in packaging and products increases, promoting environmental sustainability.
Economic Impacts of Forestry on Local Communities
Forestry activities serve as a cornerstone of economic stability for many rural communities, offering critical employment opportunities and significantly contributing to local economies. In many regions, forestry is one of the largest employers, with jobs ranging from logging and milling to conservation and management. The economic impact extends beyond direct employment, as forestry supports related industries such as transportation, equipment manufacturing, and retail.

Sustainable forestry practices ensure the long-term viability of these jobs by maintaining forest health and productivity. These practices include selective logging, reforestation, and controlled burns, which help maintain the balance of the ecosystem and reduce the risk of forest fires. By promoting forest regeneration and preventing overexploitation, sustainable forestry helps secure a stable supply of timber and non-timber forest products, which are vital for the economic resilience of local communities.
Moreover, sustainable forestry practices help mitigate the environmental impact of logging, promoting a balanced ecosystem that supports both biodiversity and community livelihoods. Healthy forests provide essential ecosystem services such as carbon sequestration, water filtration, and soil stabilization, which are crucial for the well-being of both the environment and the people who depend on it.
Economic and Environmental Impacts of Forestry
| Indicator | Value | Explanation |
|---|---|---|
| Employment in Forestry (Global) | 13.2 million (2023) | Total number of people employed globally in forestry and related industries. |
| Contribution to GDP (Global) | $606 billion (2023) | Forestry’s contribution to the global Gross Domestic Product. |
| Carbon Sequestration | 2.1 gigatons/year | Amount of carbon dioxide absorbed by forests annually. |
| Biodiversity Index | 3.7 | Average biodiversity index in sustainably managed forests (scale of 0-5). |
| Reforestation Rate | 2.5% per year | Annual percentage increase in forest area due to reforestation efforts. |
| Reduction in Soil Erosion | 40% | Decrease in soil erosion in areas practicing sustainable forestry. |
| Smart Packaging Market Growth | 10.5% CAGR (2023-2028) | Compound annual growth rate of the smart packaging market. |
| Specialty Paper Market Size | $42 billion (2023) | Total market size for specialty papers, including smart packaging. |
Future of Digital and Paperless Trends
The rise of digital communication and paperless solutions is transforming the pulp and paper industry, leading to potential declines in traditional sectors such as newsprint and office paper. However, this shift also presents new opportunities in digital printing technologies and the development of specialty papers. As companies adapt to these changes, innovation is driving growth in niche markets, such as smart packaging, which integrates technology to improve functionality and recyclability.

Smart packaging, for example, uses advanced materials and embedded sensors to enhance product safety, extend shelf life, and provide real-time information to consumers. This innovation not only meets the growing demand for sustainable and intelligent packaging solutions but also opens up new revenue streams for the pulp and paper industry.
Additionally, the demand for high-quality, eco-friendly packaging materials is on the rise, driven by consumer preferences and regulatory pressures. Companies are increasingly focusing on developing biodegradable and recyclable packaging options, which contribute to reducing environmental impact and promoting a circular economy.
Scientific Analysis of the Future of Digital and Paperless Trends
| Indicator | Value | Explanation |
|---|---|---|
| Decline in Newsprint Demand | 5% annual decline (2020-2024) | Annual reduction rate in global newsprint consumption due to digital media shift. |
| Increase in Digital Printing Market | $30.5 billion by 2025 | Projected market size for digital printing technologies, driven by demand for on-demand and short-run printing. |
| Smart Packaging Market Growth | 13.2% CAGR (2023-2028) | Compound annual growth rate of the smart packaging market, indicating robust expansion. |
| Biodegradable Packaging Market Size | $12.1 billion (2023) | Current market size for biodegradable packaging materials, reflecting growing consumer and regulatory demand. |
| CO2 Emission Reduction | 45% by 2030 (forecast) | Projected reduction in CO2 emissions from the pulp and paper industry due to increased use of sustainable practices. |
| Recycling Rate of Paper Products | 69% (2023) | Percentage of paper products recycled globally, showing the industry’s progress towards sustainability. |
| Average Shelf Life Extension (Smart Packaging) | 25% | Average increase in product shelf life due to the implementation of smart packaging solutions. |
| Water Usage Reduction in Production | 35% by 2030 (forecast) | Projected reduction in water usage in paper production through advanced technologies and sustainable practices. |
Investment and Funding in the Pulp and Paper Sector
Investment dynamics within the pulp and paper industry are crucial indicators of its trajectory towards innovation and sustainability. Significant financial influx, particularly from venture capital, private equity, and government incentives, underscores a strategic pivot towards technologies that enhance environmental sustainability and operational efficiency.
- Venture Capital and Private Equity: There is a growing trend of investment in startups that are developing cutting-edge recycling technologies and creating bioproducts from paper waste. These investments are not only aimed at boosting recycling rates but also at deriving valuable products from what was previously considered non-recoverable waste.
- Government Subsidies and Incentives: National and international policies play a pivotal role in shaping the industry’s move towards greener practices. For example, subsidies for energy-efficient equipment or tax incentives for sustainable forestry practices help companies mitigate the financial burden associated with transitioning to greener technologies.
- Institutional Investments: Large-scale investments from banks and financial institutions in sustainable forestry and eco-friendly paper manufacturing facilities have also been notable. These investments are often linked to sustainability indices and green bonds, which attract investors looking to contribute to global sustainability goals.
- Research and Development Funding: Significant portions of investments are channeled into R&D to foster innovations that reduce the environmental impact of paper production. This includes developing new forms of bio-based inks and adhesives, improving the biodegradability of paper products, and enhancing the energy efficiency of paper mills.
- International Collaboration and Funding: Collaborative projects and funding from international bodies such as the UN’s International Fund for Agricultural Development (IFAD) are instrumental in transferring sustainable technologies to developing countries, promoting global standards for environmental sustainability in the pulp and paper industry.
The following table offers a quantitative analysis of the financial impacts and outcomes of these investments, providing a detailed look at their efficiency and sustainability enhancements:
| Investment Type | Average Investment ($M) | Sustainability Increase (%) | Efficiency Improvement (%) | ROI (Return on Investment) (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Venture Capital in Recycling | 50-100 | 15-25 | 10-20 | 12-18 |
| Government Subsidies | 20-60 | 20-30 | 15-25 | 8-15 |
| Institutional Investments | 100-500 | 25-35 | 20-30 | 10-20 |
| R&D Funding | 30-150 | 10-20 | 25-35 | 15-25 |
| International Collaborations | 10-80 | 30-40 | 10-15 | 5-10 |
Long-term Environmental Goals and Industry Commitments

Many leading firms in the pulp and paper industry have set ambitious environmental targets aimed at reducing carbon emissions, enhancing energy efficiency, and promoting sustainable forest management. These commitments are part of broader corporate responsibility strategies that align with global environmental standards and consumer expectations. The industry’s proactive approach not only mitigates its ecological impact but also positions it favorably in a market that increasingly values sustainability.
Key environmental goals include achieving carbon neutrality, increasing the use of renewable energy, and enhancing the recyclability of products. Companies are investing in various technologies and practices to meet these targets:
- Carbon Emission Reductions: The industry aims to cut carbon emissions by 50% by 2030 compared to 2020 levels. This is being achieved through the adoption of carbon capture and storage (CCS) technologies, increased energy efficiency in production processes, and transitioning to renewable energy sources. For instance, biomass energy, which uses organic materials as fuel, is becoming a popular alternative to fossil fuels in pulp and paper mills.
- Renewable Energy Adoption: By 2025, the industry targets 40% of its energy needs to be met from renewable sources. This includes investments in solar, wind, and hydroelectric power, as well as the use of bioenergy from forestry residues. Implementing cogeneration systems, which simultaneously produce electricity and useful heat, has significantly improved energy efficiency.
- Sustainable Forest Management: Sustainable forest management practices are critical to ensuring the long-term health of forest ecosystems. Techniques such as selective logging, reforestation, and precision forestry are employed to maintain biodiversity and prevent deforestation. Precision forestry uses advanced technologies like GIS (Geographic Information Systems) and remote sensing to monitor forest conditions and optimize harvesting practices.
- Water Conservation: The pulp and paper industry is one of the largest industrial consumers of water. Companies are now focusing on reducing water usage by implementing closed-loop water systems and advanced effluent treatment technologies. The goal is to reduce water usage by 30% by 2030. These systems recycle water within the production process, minimizing the need for fresh water and reducing pollution.
- Product Recyclability: Enhancing the recyclability of paper products is a major focus. By 2025, the industry aims for 75% of paper products to be fully recyclable. This involves designing products that are easier to recycle and improving recycling processes to handle a wider variety of paper types.
- Innovation in Bioproducts: The development of bioproducts from renewable biological resources is gaining traction. These include biodegradable plastics, bio-based chemicals, and advanced biofuels. Such innovations not only provide sustainable alternatives to traditional materials but also add economic value to forestry products.
Scientific Analysis of Long-term Environmental Goals and Industry Commitments
| Indicator | Value | Explanation |
|---|---|---|
| Carbon Emission Reduction Targets | 50% by 2030 | Industry-wide target for reducing carbon emissions from 2020 levels. |
| Renewable Energy Usage | 40% by 2025 | Projected percentage of energy derived from renewable sources in the pulp and paper industry. |
| Increase in Product Recyclability | 75% by 2025 | Targeted percentage of paper products that are fully recyclable by 2025. |
| Water Usage Reduction | 30% by 2030 | Targeted reduction in water usage in pulp and paper production processes. |
| Investment in Carbon Capture and Storage (CCS) | $2 billion by 2025 | Total projected investment in CCS technologies within the industry. |
| Adoption of Closed-loop Water Systems | 60% by 2025 | Percentage of pulp and paper mills expected to adopt closed-loop water systems by 2025. |
| Sustainable Forest Management Certification | 85% by 2025 | Percentage of forest areas used by the industry certified for sustainable management. |
| Increase in Bioproducts Market Size | $50 billion by 2025 | Projected market size for bioproducts derived from renewable biological resources. |
| Energy Efficiency Improvement | 20% by 2025 | Targeted improvement in energy efficiency in pulp and paper production processes. |
| Reforestation Efforts | 1.5 million hectares annually | Annual reforestation efforts undertaken by the industry to restore forest areas. |
Related Post
Conclusion
The pulp and paper industry is at a critical juncture, where its traditional practices intersect with the imperatives of sustainability and innovation. The critical role of forestry in this sector cannot be overstated, as it underpins not only the supply of raw materials but also the ecological balance necessary for the industry’s sustainable growth. Moving forward, the industry’s ability to innovate, comply with regulatory demands, and meet market expectations will determine its resilience and continued relevance in a rapidly changing global economy.
FAQs
- How do sustainable forestry practices impact the cost and quality of paper products?
Sustainable forestry not only preserves biodiversity but also ensures a consistent supply of quality wood pulp, which can stabilize paper prices and improve product quality over time. - What role does consumer preference play in shaping the pulp and paper market?
Increasing consumer demand for eco-friendly products is prompting companies to invest in greener production technologies and sustainable materials, reshaping market offerings. - Can you explain the significance of a 0.72% CAGR in the pulp and paper industry?
While seemingly small, a 0.72% CAGR indicates steady growth in a mature industry, reflecting ongoing innovations and adaptations to market demands and environmental challenges. - What advancements in recycling technologies are influencing the pulp and paper market?
New recycling technologies are making it possible to recover higher quality fibers from used paper, reducing the reliance on virgin pulp and decreasing environmental impact. - How is the global shift towards digital media affecting the paper industry?
The shift to digital media is reducing demand for traditional paper products like newsprint and office paper, pushing companies to diversify into packaging and specialty papers. - What economic benefits does the pulp and paper industry bring to rural communities?
The industry often serves as a major employer in rural areas, supporting local economies through job creation and infrastructure development. - How are regulatory changes impacting the pulp and paper industry?
New regulations on emissions and recycling mandates are pushing the industry towards cleaner and more sustainable practices, requiring significant adjustments in operations. - What are the challenges of balancing paper production with environmental conservation?
Balancing production with conservation involves managing the ecological footprint, including water and energy use, while maintaining efficient production to meet global demand.
As we look toward 2029, the interplay between forestry and the pulp and paper industry continues to shape both market growth and sustainability efforts. This dynamic sector remains pivotal not just economically but also as a steward of environmental resources, highlighting the critical role of responsible forestry in supporting global industry and ecological health.

Benjamin Brooks
Forestry AuthorGreetings! I'm Benjamin Brooks, and my journey over the past 15 years has revolved around the fascinating realms of content creation, expertise in snow clearing, and the intricate world of lumberjacking and landscaping. What began as a simple curiosity about the natural world and heavy machinery has evolved into a passionate profession where my love for crafting words intertwines seamlessly with my lumberjacking and garden skills.













Leave your comment