Why My Chainsaw Won’t Start
- January 30, 2024
- 1 comment
Having a chainsaw that won’t start can be a frustrating experience, especially when you’re ready to tackle some work. Understanding the common reasons why a chainsaw might fail to start is the first step in solving the problem. This article explores the Top Five reasons your chainsaw might not be starting and provides practical advice for troubleshooting and fixing these issues.
List of Reasons Why Your Chainsaw Won’t Start:
- Spark Plug Issues
- Carburetor Clogs
- Fuel Filter Issues
- Recoil Spring Malfunctions
- Recoil Starter Assembly Problems
1. Spark Plug Issues
The spark plug is a pivotal component in starting your chainsaw. It delivers the electric spark that ignites the fuel mixture in the combustion chamber, a crucial step in the engine’s operation. Over time, the spark plug can become coated with a black, sooty residue, or the electrode at its tip can wear down. These issues can prevent the spark from occurring, meaning your chainsaw won’t start.
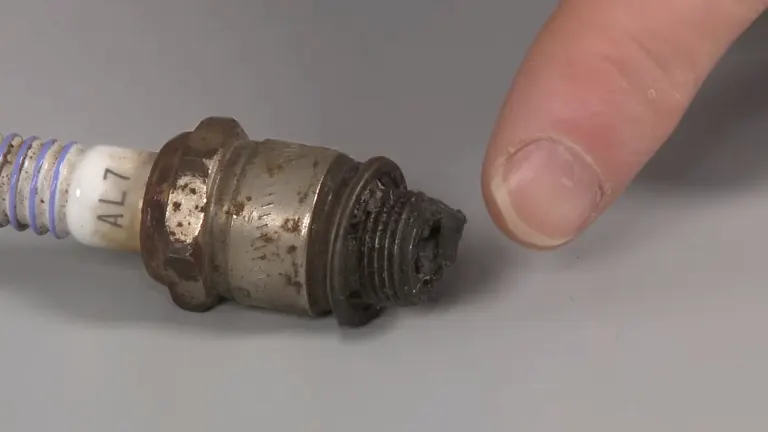

What to do:
- Carefully remove the spark plug and examine it for signs of wear, carbon buildup, or damage.
- Use a wire brush or spark plug cleaner to clean off any residue gently.
- Check the electrode gap with a feeler gauge and adjust it according to your chainsaw’s specifications.
- Utilize an ignition tester to confirm the spark plug’s functionality. If it’s not sparking, it’s time to replace it.
- As part of regular maintenance, replace the spark plug annually to avoid these issues.
2. Carburetor Clogs
The carburetor is responsible for mixing the right amount of air and fuel for the engine to run efficiently. Unfortunately, leaving old fuel in your chainsaw can lead to the formation of a sticky, varnish-like residue that clogs the carburetor’s small ports and jets. This blockage prevents the proper mixture of fuel and air from being delivered to the engine, stopping it from starting.
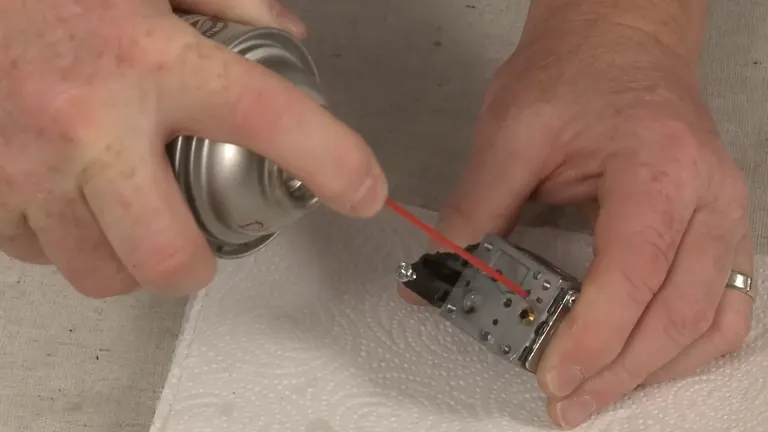

What to do:
- Always drain old fuel from the chainsaw if you’re not planning to use it for an extended period.
- Use fresh fuel with a high-quality fuel stabilizer to prevent the formation of residue.
- If you suspect the carburetor is clogged, remove it and clean it thoroughly with carburetor cleaner and a set of small brushes or a carburetor cleaning tool.
- In cases where cleaning doesn’t solve the problem, a carburetor repair kit may be necessary to replace worn or damaged components. For severe issues, installing a new carburetor might be the most reliable solution.
3. Fuel Filter Issues
The fuel filter keeps debris and impurities in the fuel tank from entering the carburetor and engine. Over time, especially with the use of old or contaminated fuel, the filter can become clogged, obstructing the flow of fuel to the engine and preventing your chainsaw from starting.
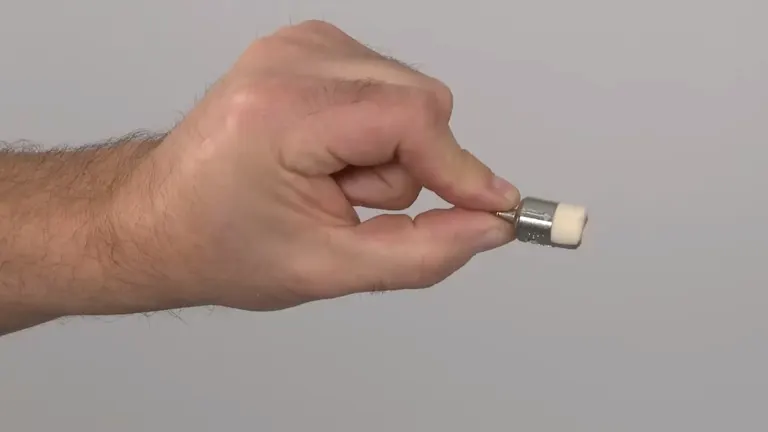

What to do:
- Locate and remove the fuel filter, usually found inside the fuel tank attached to the end of the fuel line.
- Inspect the filter. If it’s dirty or clogged, it’s best to replace it with a new one as cleaning may not be sufficiently effective.
- Regularly replacing the fuel filter, as part of your routine maintenance schedule, will ensure a clean fuel flow to the engine.
4. Recoil Spring Malfunctions
The recoil spring is an essential part of the chainsaw’s starting mechanism. When you pull the starter rope, the recoil spring is supposed to retract the rope onto the pulley. If the spring is broken or damaged, the rope won’t retract, and you won’t be able to start your chainsaw.
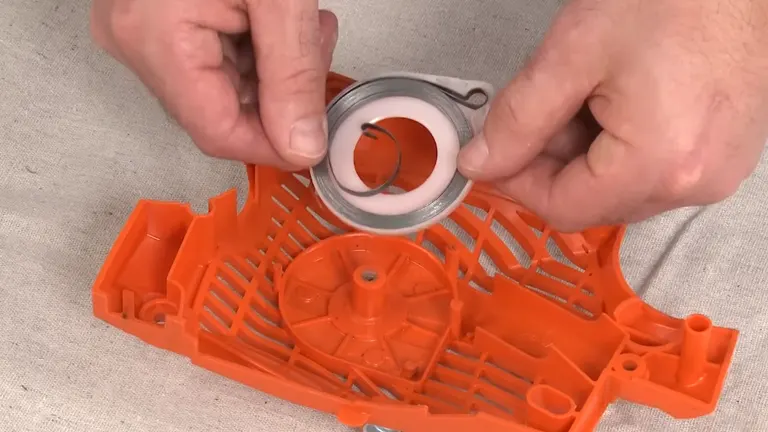
What to do:
- Disassemble the recoil starter assembly to inspect the recoil spring.
- Look for signs of wear, stretching, or damage. If the spring is broken, it will need to be replaced.
- While some recoil springs can be replaced individually, it may be more practical to replace the entire recoil starter assembly, especially if there are signs of wear on other components.
5. Recoil Starter Assembly Problems
Aside from the recoil spring, other parts of the recoil starter assembly can malfunction, such as the pulley, the recoil spring housing, or the starter rope. These issues can prevent the recoil starter from engaging with the engine’s crankshaft, making it impossible to start the chainsaw.
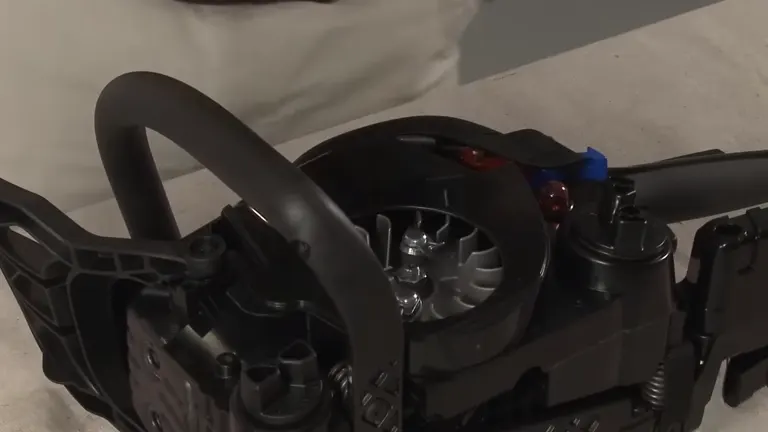

What to do:
- Dismantle the recoil starter assembly and inspect all components for wear or damage.
- Pay particular attention to the pulley and the housing for the recoil spring, as these areas are prone to wear.
- If any parts are damaged, consider replacing the entire recoil starter assembly. This ensures all components are in good working order and can prevent future starting problems.
Troubleshooting Flowchart or Checklist
- Check the Fuel: The type and condition of fuel are often the first culprits when a chainsaw refuses to start. It’s essential to verify that you’re using the correct mixture of fuel and oil, as specified by your chainsaw’s manufacturer. Over time, fuel can deteriorate, leading to poor engine performance or starting issues. If you suspect that the fuel in your chainsaw is old or contaminated, it’s best to drain it completely and refill the tank with a fresh, properly mixed batch. This simple step can often resolve starting issues and improve the performance of your chainsaw.
- Inspect the Spark Plug: The spark plug is a critical component that ignites the fuel in your chainsaw’s engine. A dirty or damaged spark plug can lead to starting difficulties or poor engine performance. Carefully remove the spark plug and examine it for signs of wear, damage, or carbon buildup. If the spark plug is dirty, use a specialized cleaner or a wire brush to gently clean it. However, if the spark plug is cracked, worn, or severely damaged, it’s best to replace it with a new one to ensure reliable ignition and optimal engine performance.
- Examine the Air Filter: A clean air filter is vital for your chainsaw’s engine to operate efficiently. The air filter prevents dust and debris from entering the engine, but over time, it can become clogged, restricting airflow. This restriction can lead to starting difficulties or a decrease in engine power. Remove the air filter and inspect it for dirt and debris. If it’s dirty, clean it according to the manufacturer’s instructions. However, if the air filter is damaged or excessively dirty, replacing it with a new one will ensure your chainsaw’s engine receives the clean air it needs for optimal performance.
- Look at the Fuel Filter: The fuel filter plays a crucial role in maintaining the cleanliness of the fuel entering your chainsaw’s engine. A clogged fuel filter can obstruct the flow of fuel, leading to starting problems or a sputtering engine. Locate and inspect the fuel filter, which is typically found inside the fuel tank, attached to the fuel line. If the filter appears dirty or clogged, replace it with a new one. Regularly replacing the fuel filter is a simple and effective way to ensure a consistent and clean fuel supply, contributing to the reliable operation of your chainsaw.
- Assess the Carburetor: The carburetor is responsible for mixing air and fuel at the correct ratio for combustion. However, it can become clogged with debris or residue, especially if old or improperly stored fuel has been used. If you suspect the carburetor is the source of starting difficulties, carefully clean it using a carburetor-specific cleaner and tools designed for this delicate task. If cleaning doesn’t resolve the issue, or if the carburetor is visibly damaged, you may need to use a carburetor repair kit or consider replacing the carburetor entirely. A well-maintained carburetor is crucial for efficient engine performance and starting reliability.
- Check the Recoil Starter: The recoil starter assembly is instrumental in starting your chainsaw’s engine. However, components of this assembly, such as the recoil spring or the starter rope, can wear out or break, preventing the chainsaw from starting. Carefully inspect the recoil starter assembly for signs of damage or wear. If you find broken parts, such as a snapped recoil spring or a frayed starter rope, these components should be replaced. In some cases, especially if multiple parts are damaged or worn, it may be more practical and efficient to replace the entire recoil starter assembly to ensure reliable starting and operation.
Words of Wisdom from the Pros
Renowned chainsaw expert John Cutter advises, “Respect your chainsaw’s capabilities and limitations. Regular maintenance isn’t just about prolonging the life of your tool; it’s about ensuring your safety with every cut. Don’t ignore the small signs of wear or malfunction. Addressing them early on can save you from bigger troubles down the line.“
Mechanic and chainsaw technician Sarah Chainwright adds, “The key to a smoothly running chainsaw is understanding its needs. A well-maintained chainsaw is a loyal partner in your woodworking endeavors. Regular checks and cleanings are your first line of defense against potential issues.“
By understanding these common issues and knowing how to address them, you can significantly reduce the downtime of your chainsaw and ensure it’s always ready for action. Regular maintenance, such as replacing the spark plug annually, using fresh fuel with a stabilizer, and routinely checking and replacing the fuel filter and other wear-prone parts, can prevent many of these problems from occurring in the first place. With this knowledge in hand, your chainsaw will be a reliable tool for many years to come.
FAQs
- How should I dispose of old chainsaw fuel properly?
Proper disposal of old chainsaw fuel is crucial to prevent environmental harm. Never pour old fuel down the drain or onto the ground. Instead, check with your local waste management facilities for guidelines on disposing of hazardous materials like gasoline. - Can I use any type of oil for the chainsaw’s chain and bar?
It’s important to use the correct type of oil for lubrication to ensure proper function and longevity of your chainsaw. Typically, a specific bar and chain oil is recommended because it’s designed to cling to the chain even at high speeds. Using other types of oil may not provide adequate lubrication and could damage your chainsaw. - What are the signs that the chainsaw’s clutch needs attention?
Signs of a worn or damaged clutch include difficulty in chain movement, excessive heat generation near the clutch, and visible wear or damage. If you notice these signs, it’s important to inspect and possibly replace the clutch to avoid further damage and maintain safety. - How can I determine the correct chain tension, and why is it important?
Proper chain tension is vital for safe and efficient operation. A correctly tensioned chain should sit snugly against the bar but still allow for easy movement by hand. Too loose, and it might come off the bar; too tight, and it can cause excessive wear or damage to the chainsaw. - What steps should I take if my chainsaw is producing smoke while cutting?
Smoke during cutting can indicate that the chain is dull and needs sharpening, or the chain’s tension is incorrect. It can also suggest inadequate lubrication. Stop the chainsaw, let it cool down, and check the chain tension, lubrication, and for signs of dullness. - How often should I perform maintenance checks on my chainsaw?
Regular maintenance checks are essential for the longevity and safety of your chainsaw. Before each use, check the chain tension, lubrication, and general condition. A more thorough inspection and maintenance routine should be performed every few months or according to the manufacturer’s recommendations. - What safety gear should I wear when operating a chainsaw?
Proper safety gear is crucial and should include sturdy work boots, cut-resistant pants or chaps, a long-sleeved shirt, gloves, eye protection, ear protection, and a hard hat. This gear can provide significant protection against common chainsaw injuries. - How can I tell if my chainsaw’s muffler is malfunctioning, and why is it important?
A malfunctioning muffler may show signs of excessive noise or smoke and can affect the chainsaw’s performance. It’s important because it helps to direct exhaust gases away from the user and reduces noise levels, contributing to safety and comfort. - Is it necessary to use a fuel stabilizer in my chainsaw?
Yes, if you’re not going to use all the fuel within a month. Fuel stabilizers prevent the fuel from degrading and forming deposits in the carburetor, especially during storage. This can help ensure that your chainsaw starts easily and runs smoothly when you need it. - What should I do if my chainsaw is leaking oil?
A chainsaw leaking oil can be a sign of a problem with the oiler system or a crack in the oil tank. Check the oil tank and lines for any signs of damage and ensure that the oil cap is secure and not damaged. If the leakage persists, it might be best to have your chainsaw inspected by a professional to prevent further issues.
Join our conversation below and become an integral part of our wood-cutting community. Whether you’ve mastered the art of the perfect cut or you’re just beginning your chainsaw journey, your insights and experiences are invaluable. Share your tips, tricks, and personal reviews to help others navigate the world of chainsaws with greater ease and confidence. Every contribution enriches our collective knowledge, fostering a supportive network for enthusiasts and professionals alike. Let’s grow together, shaping a well-informed and resourceful community for all chainsaw users!

David Murray
Forestry AuthorI'm David Murry, a forestry equipment specialist with a focus on chainsaw operation. With over 13 years of experience, I've honed my skills in operating and maintaining a wide range of machinery, from chainsaws to log splitters. My passion for the outdoors and commitment to sustainable forestry drive my work, which emphasizes safety, efficiency, and staying updated with industry advancements. Additionally, I'm dedicated to sharing my expertise and promoting environmental awareness within the forestry community.













One thing I'd like to add, do a compression check. I've dealt with a number of Stihl saws with scored cylinders that even feel pretty good on the 'thumb test' not have adequate compression. Pull the muffler and rotate the engine and look for scoring on the piston. This happens a lot with saw used by maintenance crews on farms where the operators run half throttle a lot. Gotta run 'em full throttle or idle... FWIW I've seen this mostly on MS261 saws and I know the guys are running Stihl HP Ultra at 50:1 so I know it's not mix...
Charlie Hubert
January 31, 2024 2:29 am