Tapanuli Orangutan
- January 18, 2024
- 0 comment
The Tapanuli orangutan, scientifically known as Pongo tapanuliensis, is a critically endangered species of great ape native to the Batang Toru forest region in North Sumatra, Indonesia. These orangutans were only officially recognized as a distinct species in 2017, making them one of the most recently discovered great ape species. They are characterized by their unique facial morphology, which includes a moustache-like beard and distinct cheek flanges that differentiate them from their Sumatran and Bornean relatives.
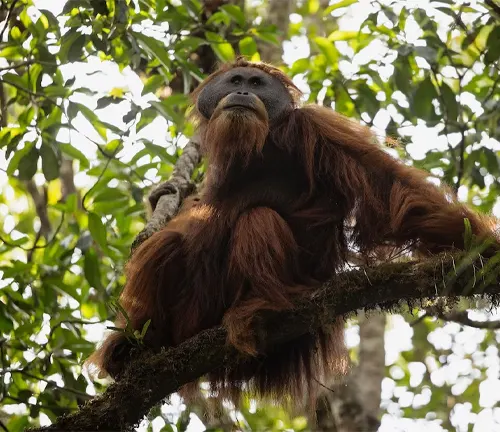

Unfortunately, the Tapanuli orangutans face numerous threats, including habitat destruction due to illegal logging and palm oil plantations, as well as poaching for the illegal pet trade. Conservation efforts are underway to protect their habitat, rehabilitate confiscated individuals, and raise awareness about their plight. With fewer than 800 estimated to remain in the wild, the Tapanuli orangutans are among the rarest great apes on Earth, making their conservation a matter of utmost importance.
| Specification | Details |
|---|---|
| Scientific Name | Pongo tapanuliensis |
| Common Name | Tapanuli orangutan |
| Habitat | Batang Toru forest, North Sumatra, Indonesia |
| Discovery Year | Officially recognized as a distinct species in 2017 |
| Unique Characteristics | Prominent moustache-like beard and distinct cheek flanges |
| Conservation Status | Critically Endangered |
| Estimated Population in the Wild | Fewer than 800 individuals |
| Primary Threats | Habitat destruction, poaching, illegal pet trade |
| Conservation Efforts | Establishment of protected areas, rehabilitation and release programs |
| Importance | One of the rarest great ape species on Earth |
Tapanuli Orangutan (Pongo tapanuliensis) The Rarest Great Ape on Earth
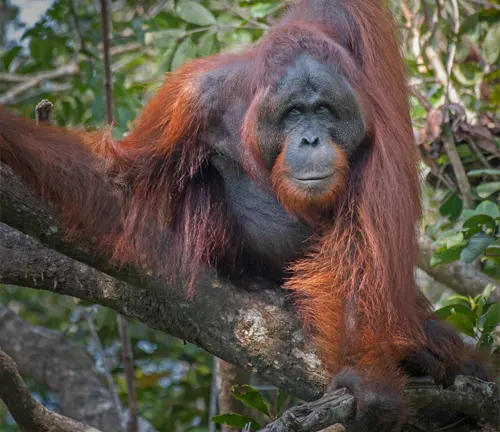

The Tapanuli orangutan (Pongo tapanuliensis) is a remarkable and critically endangered species of great ape that is often overshadowed by its more famous cousins, the Bornean and Sumatran orangutans. In this article, we will delve into the fascinating world of the Tapanuli orangutan, exploring its unique characteristics, habitat, threats, and conservation efforts. Join us on this journey to discover the incredible story of one of the rarest great apes on Earth.
The Origins of Tapanuli Orangutans
Tapanuli orangutans were only officially recognized as a distinct species in 2017, making them the most recently identified great ape species. Their discovery was a groundbreaking moment in the field of primatology and conservation. Let’s delve into their origins and what sets them apart from other orangutans.
Taxonomic Classification
Tapanuli orangutans belong to the Pongo genus, which includes all orangutans. However, they are classified as a separate species due to their distinct genetic and morphological characteristics.
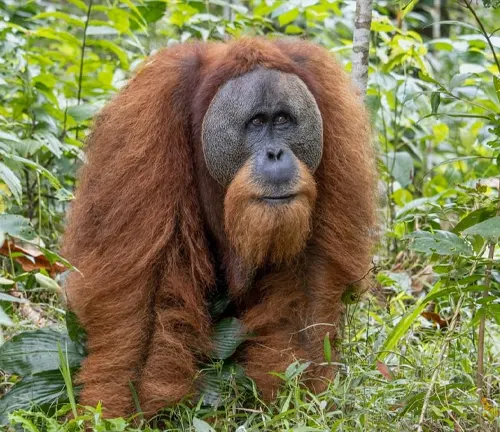

Physical Characteristics
One of the key features that distinguish Tapanuli orangutans is their unique facial morphology. They have a prominent moustache-like beard and distinct cheek flanges that differ from their Sumatran and Bornean relatives.
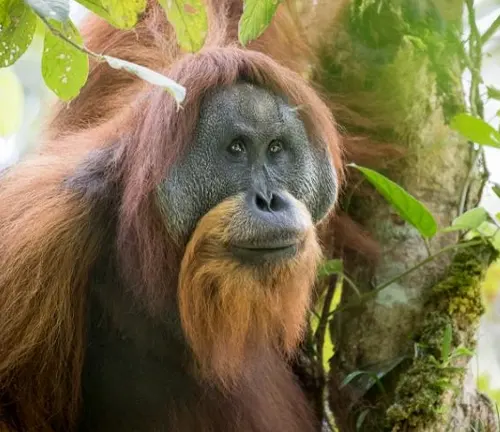

Habitat and Distribution
Tapanuli orangutans are exclusively found in the Batang Toru forest region of North Sumatra, Indonesia. This habitat is crucial for their survival, as it provides the necessary resources for their sustenance and reproduction.
Batang Toru Ecosystem
The Batang Toru ecosystem is a lush and diverse rainforest that houses an impressive array of flora and fauna. It serves as the last bastion of hope for Tapanuli orangutans.
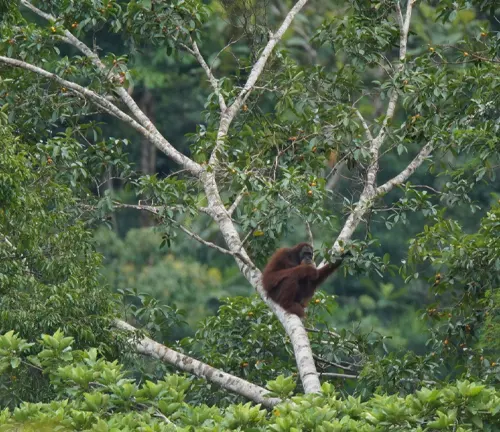

Threats to Tapanuli Orangutans
Despite their recent discovery and protected status, Tapanuli orangutans face a multitude of threats that put their existence in jeopardy.
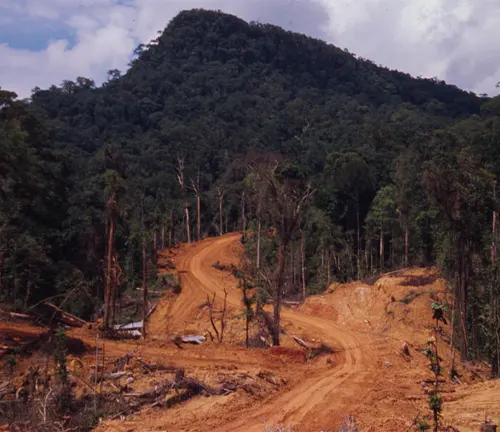

Habitat Destruction
One of the most significant threats is habitat destruction due to illegal logging, palm oil plantations, and infrastructure development. As their forest home dwindles, Tapanuli orangutans are pushed further towards the brink of extinction.
Poaching and Illegal Trade
Tapanuli orangutans are sought after in the illegal pet trade market, and their young are often captured and sold as exotic pets. Poaching poses a severe threat to their population.
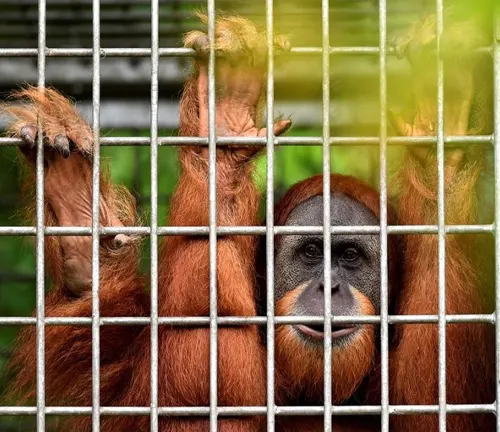

Conservation Efforts
Efforts to conserve Tapanuli orangutans have intensified since their recognition as a distinct species. Conservation organizations and local authorities are working tirelessly to protect their habitat and raise awareness about their plight.
Protected Areas
Establishment of protected areas within the Batang Toru ecosystem has been a crucial step in safeguarding the Tapanuli orangutans and their habitat.
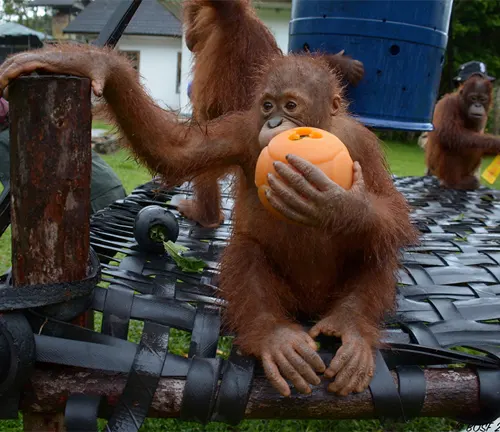

Rehabilitation and Release Programs
Organizations are also running rehabilitation and release programs to rescue and rehabilitate confiscated orangutans, with the ultimate goal of returning them to the wild.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
- What is a Tapanuli orangutan, and how is it different from other orangutan species?
A Tapanuli orangutan (Pongo tapanuliensis) is a distinct species of orangutan, identified in 2017. They differ from other orangutan species in their unique facial morphology, habitat, and genetic markers. - Where are Tapanuli orangutans found in the wild?
Tapanuli orangutans are exclusively found in the Batang Toru forest region of North Sumatra, Indonesia. - How many Tapanuli orangutans are estimated to remain in the wild?
There are fewer than 800 Tapanuli orangutans estimated to remain in the wild, making them critically endangered. - Why are Tapanuli orangutans considered critically endangered?
They are critically endangered due to habitat destruction, poaching, and the illegal pet trade, which have significantly reduced their population. - What are the unique physical characteristics of Tapanuli orangutans?
Tapanuli orangutans have a moustache-like beard and distinct cheek flanges, setting them apart from other orangutan species. - What is the primary threat to Tapanuli orangutans’ survival in the wild?
The primary threat is habitat destruction caused by illegal logging, palm oil plantations, and infrastructure development. - Are there any protected areas established for Tapanuli orangutans?
Yes, protected areas have been established within the Batang Toru ecosystem to safeguard Tapanuli orangutans and their habitat. - Can Tapanuli orangutans be rehabilitated and reintroduced into the wild successfully?
Yes, rehabilitation and release programs are being conducted to rescue and rehabilitate confiscated individuals and reintroduce them to the wild. - How can I contribute to the conservation of Tapanuli orangutans?
You can support conservation organizations, raise awareness, and make sustainable choices to reduce the demand for palm oil products. - Are there any ongoing research projects focused on Tapanuli orangutans?
Yes, ongoing research projects aim to study their behavior, genetics, and habitat to better inform conservation efforts. - What is the historical significance of the discovery of Tapanuli orangutans as a distinct species?
The discovery marked a significant milestone in primatology and conservation, highlighting the importance of preserving biodiversity. - Are Tapanuli orangutans related to other orangutan species?
They are closely related to Sumatran orangutans but are distinct enough to be classified as a separate species. - What is the role of local communities in the conservation of Tapanuli orangutans?
Local communities play a vital role in conservation by participating in awareness programs and sustainable practices. - Are there any international organizations involved in Tapanuli orangutan conservation?
Yes, international organizations collaborate with local efforts to protect Tapanuli orangutans and their habitat. - How do Tapanuli orangutans contribute to their ecosystem?
Tapanuli orangutans play a crucial role in seed dispersal, helping maintain the health and diversity of their forest ecosystem.














Leave your comment