Asian Badger
- January 15, 2024
- 0 comment
The Asian badger, a captivating creature found across diverse landscapes in Asia, captures the imagination with its unique traits and behaviors. These medium-sized mammals, belonging to the Mustelidae family, exhibit a range of species, each adapted to specific habitats. Known for their stout bodies, short legs, and iconic facial markings, Asian badgers boast a distinct appearance that sets them apart in the animal kingdom. Their fur, ranging from shades of gray to brown, not only serves as camouflage but also provides insulation in various climates.
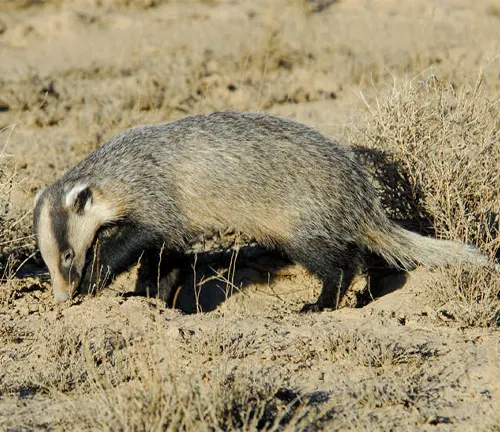

Nocturnal by nature, these creatures navigate the darkness with finesse, revealing intricate social structures and communication methods within their communities. From the Eurasian badger to the hog badger and Chinese ferret-badger, each species showcases unique adaptations and plays a vital role in its ecosystem. Beyond their ecological significance, Asian badgers hold cultural symbolism in various traditions, featuring folklore and myths that add depth to their mystique. However, like many wildlife species, Asian badgers face threats such as habitat loss and poaching, necessitating conservation efforts to ensure their survival. Studying these enigmatic creatures unveils not only the delicate balance of nature but also the importance of coexistence between humans and the fascinating world of Asian badgers.
| Feature | Description |
|---|---|
| Scientific Family | Mustelidae |
| Size | Medium-sized, varying by species |
| Appearance | Stout body, short legs, distinctive facial markings |
| Fur Color | Ranges from shades of gray to brown, providing camouflage and insulation |
| Nocturnal Behavior | Primarily active during the night |
| Social Structure | Exhibits intricate social structures and communication methods within communities |
| Species Diversity | Includes various species such as Eurasian badger, Japanese badger, hog badger, Chinese ferret-badger, and more |
| Habitats | Inhabits diverse ecosystems, including forests, grasslands, and agricultural landscapes |
| Diet | Omnivores, feeding on insects, small mammals, fruits, and occasionally carrion |
| Cultural Significance | Holds symbolic value in folklore and myths across different cultures |
| Conservation Status | Varied among species; faces threats like habitat loss, poaching, and road accidents |
| Adaptability to Urbanization | Some species show adaptability to urban landscapes, adjusting behaviors to coexist with human activities |
| Ecological Role | Plays a crucial role in the ecosystem by regulating pest populations, influencing plant growth through seed dispersal, and potentially acting as a keystone species in maintaining biodiversity |
| Lifespan | Varies by species; on average, 6-10 years in the wild |
Asian Badger: Unveiling Nature’s Stealth Expert
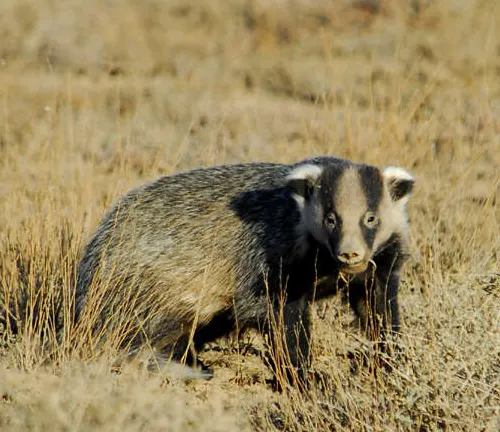

In the vast tapestry of Asian ecosystems, one creature stands out for its unique traits and fascinating behaviors—the Asian badger. These elusive mammals play a crucial role in maintaining ecological balance, yet their lives remain shrouded in mystery. In this article, we’ll delve into the intricate world of Asian badgers, exploring their characteristics, diverse species, conservation status, cultural significance, and much more.
Characteristics of Asian Badgers
Physical Features
Asian badgers boast a distinctive appearance with their stout bodies, short legs, and iconic facial markings. Their fur, ranging from shades of gray to brown, serves as both camouflage and insulation. Sharp claws and keen senses make them formidable hunters.
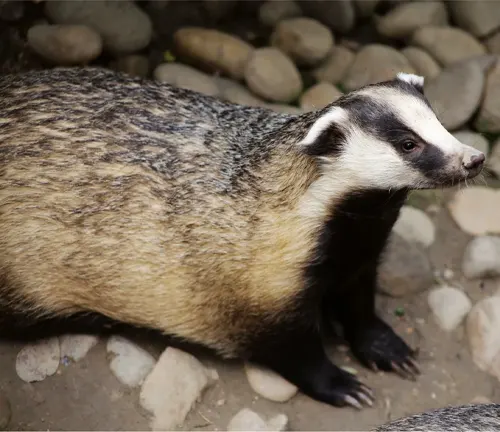
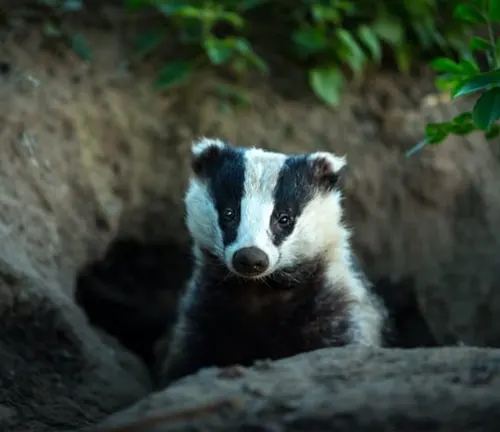


Behavioral Traits
Known for their nocturnal habits, Asian badgers are adept at navigating the darkness. Their social structures reveal intricate communication patterns, providing insights into their cooperative nature. Understanding these behaviors is key to appreciating their significance in the ecosystem.
Asian Badger Species
Different Species and Their Habitats
From the Japanese badger in Hokkaido to the hog badger in Southeast Asia, various Asian badger species inhabit diverse ecosystems. Each has unique adaptations suited to its environment, showcasing nature’s incredible ability to tailor species to specific niches.
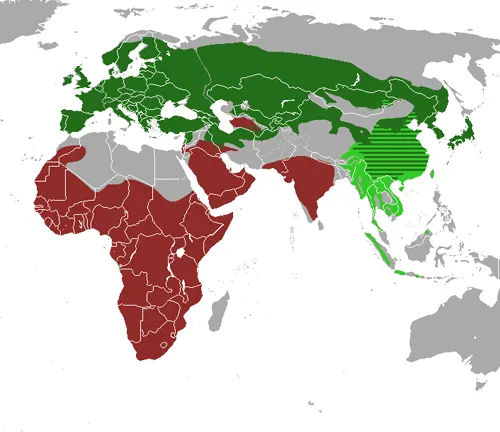
Unique Adaptations of Each Species
Exploring the adaptations of each species sheds light on their evolutionary journey. Whether it’s the robust build of the Eurasian badger or the specialized diet of the Chinese ferret-badger, these creatures have finely tuned characteristics.
Asian Badgers’ Role in the Ecosystem
Impact on Pest Control
Asian badgers are unsung heroes in pest control. Their diet, rich in insects and small mammals, helps regulate populations of pests, contributing to the overall health of their ecosystems. Understanding this role is crucial for appreciating their importance.
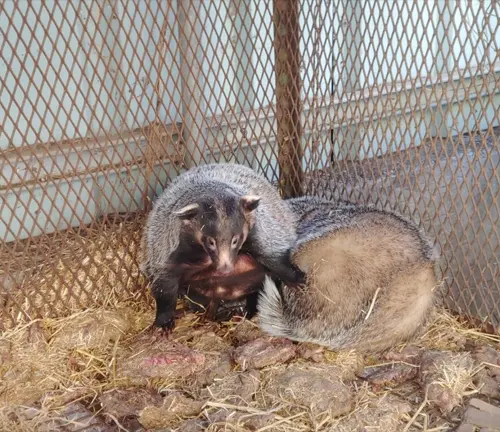

Interactions with Other Wildlife
As integral members of their ecosystems, Asian badgers interact with various species. Examining these interactions provides a holistic view of the intricate web of relationships in nature.
Conservation Status
Threats to Asian Badger Populations
Despite their importance, Asian badgers face threats. Habitat loss, poaching, and pollution pose significant challenges to their survival. Acknowledging these threats is the first step towards effective conservation.

Conservation Efforts in Place
Conservation initiatives are underway to safeguard Asian badgers. From habitat preservation to community education, various strategies aim to ensure the survival of these enigmatic creatures.
Asian Badgers in Folklore and Culture
Symbolism in Various Cultures
Asian badgers hold symbolic significance in different cultures. Exploring these cultural connections adds depth to our understanding of these creatures beyond their biological importance.
Stories and Myths Related to Asian Badgers
Ancient tales and myths often feature Asian badgers as characters. Unraveling these stories offers a glimpse into the cultural perceptions and beliefs surrounding these mysterious animals.
Asian Badgers and Human Interaction
Historical Perspectives
Human interaction with Asian badgers has a long history. Examining historical perspectives sheds light on the evolving relationship between these creatures and humans.
Current Conflicts and Coexistence Strategies
As urbanization encroaches on natural habitats, conflicts between humans and Asian badgers arise. Exploring coexistence strategies becomes crucial for mitigating these conflicts and ensuring the survival of both species.
Tracking and Studying Asian Badgers
Research Methods and Technologies
Advancements in research methods and technologies have allowed scientists to delve deeper into the lives of Asian badgers. Tracking their movements and studying their behaviors provide valuable insights.
Discoveries and Advancements in Badger Studies
Ongoing research continues to unravel new aspects of Asian badgers’ lives. From their communication methods to previously unknown behaviors, each discovery contributes to our knowledge of these remarkable creatures.
Challenges Faced by Asian Badgers
Environmental Changes
Asian badgers face challenges due to rapid environmental changes. Examining these challenges helps us understand the broader implications of human activities on wildlife.
Human-Related Threats
Poaching and habitat destruction pose immediate threats to Asian badgers. Acknowledging these issues is crucial for developing effective conservation strategies.
Different Species
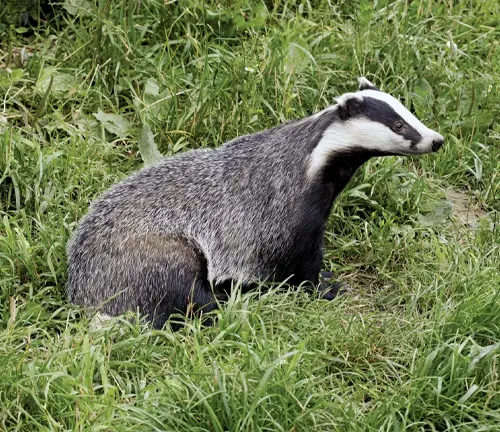
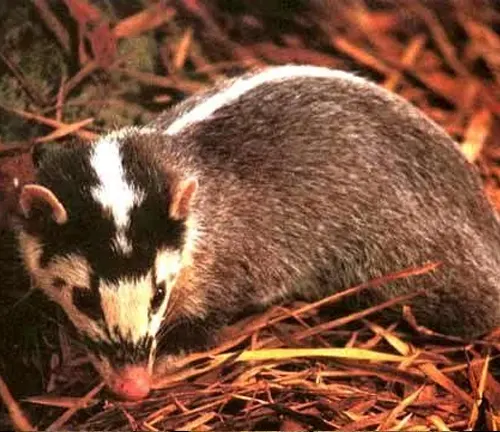
Eurasian Badger
(Meles meles)
Found across a large part of Eurasia, including Europe and parts of Asia, the Eurasian badger is perhaps the most well-known species. It has distinctive black and white facial markings.
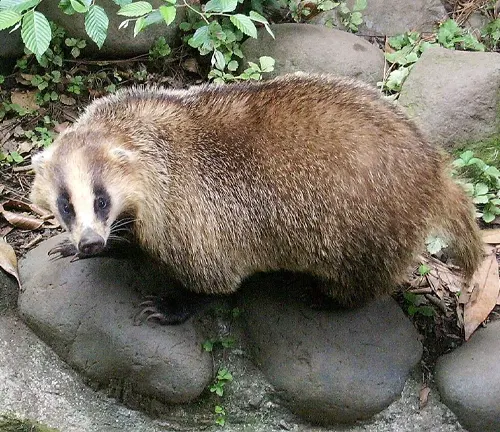


Japanese Badger
(Meles anakuma)
Endemic to Japan, the Japanese badger has a more robust build compared to its Eurasian counterpart. It inhabits a variety of habitats, from forests to agricultural landscapes.
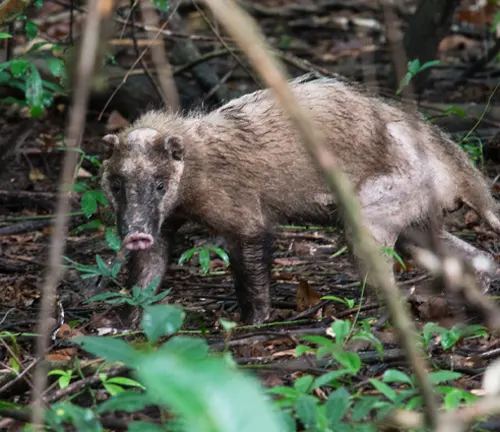
Hog Badger
(Arctonyx albogularis)
Native to Southeast Asia, the hog badger is recognized by its unique snout and distinct white throat markings. It is often found in hilly and forested regions.
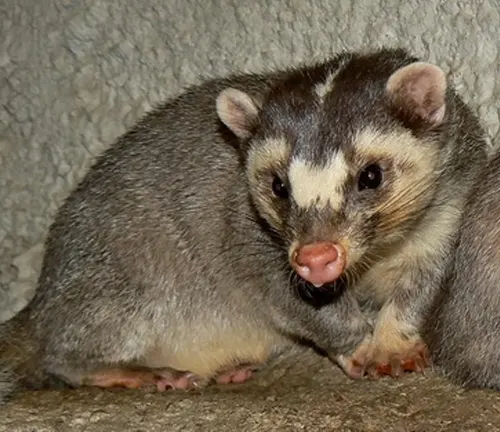


Chinese Ferret-Badger
(Melogale moschata)
This species is found in various parts of China and Southeast Asia. It has a slender body and is known for its musky odor, which is more prominent in males during the breeding season.
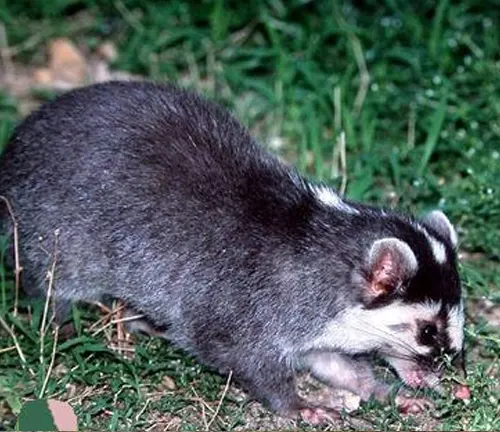
Burmese Ferret-Badger
(Melogale personata)
Endemic to Myanmar, this ferret-badger species has a distinctive facial mask and is typically found in subtropical or tropical moist forests.
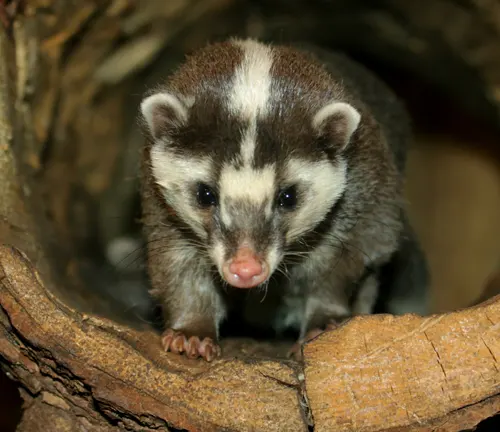


Javan Ferret-Badger
(Melogale orientalis)
Inhabiting the island of Java in Indonesia, this species has a dark mask on its face and is adapted to the island’s diverse ecosystems.
Everett’s Ferret-Badger
(Melogale everetti)
Found in Southeast Asia, including Borneo and Sumatra, this ferret-badger species has a unique appearance with a light-colored face and dark body.
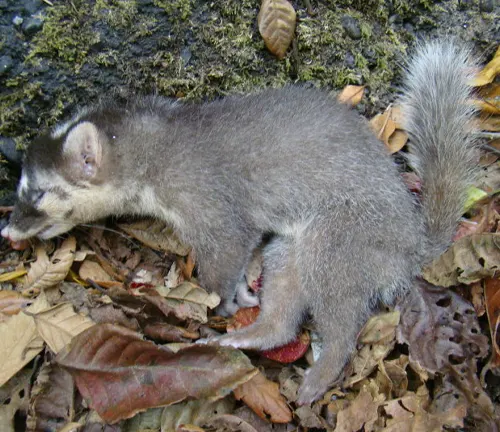


Bornean Ferret-Badger
(Melogale hosei)
Endemic to Borneo, this species is characterized by a dark face and a light stripe running down its back. It prefers a range of habitats, from forests to agricultural areas.
Frequently Asked Question (FAQs)
- What is an Asian badger?
Asian badgers are medium-sized mammals belonging to the Mustelidae family, known for their distinctive markings and behaviors. They are found in various regions of Asia. - How many species of Asian badgers are there?
There are several species of Asian badgers, including the Eurasian badger, Japanese badger, hog badger, Chinese ferret-badger, and more. - Where do Asian badgers live?
Asian badgers inhabit diverse ecosystems, ranging from forests and grasslands to agricultural landscapes. Their specific habitats depend on the species. - What do Asian badgers eat?
Asian badgers are omnivores, feeding on a diet that includes insects, small mammals, fruits, and sometimes carrion. Their diet can vary based on the availability of food in their habitat. - Are Asian badgers endangered?
The conservation status of Asian badgers varies among species. While some face threats such as habitat loss and poaching, others are relatively stable. Conservation efforts are in place to protect these species. - Do Asian badgers hibernate?
Unlike some other mustelids, Asian badgers do not hibernate. They remain active throughout the year, although their activity levels may decrease during harsh weather conditions. - Can Asian badgers be kept as pets?
Keeping Asian badgers as pets is not advisable. They are wild animals with specific needs and behaviors that are challenging to meet in a domestic setting. - Do Asian badgers have predators?
Adult Asian badgers typically have few natural predators. However, young badgers may be vulnerable to larger carnivores like wolves, big cats, and birds of prey. - How long do Asian badgers live in the wild?
The lifespan of Asian badgers in the wild varies by species. On average, they may live up to 6-10 years, depending on factors such as environmental conditions and predation. - What are the main threats to Asian badgers?
Habitat loss due to urbanization and agriculture, poaching for fur and body parts, and road accidents are among the main threats facing Asian badger populations. - Do Asian badgers have a significant role in folklore or mythology?
Yes, Asian badgers often appear in folklore and mythology across different cultures in Asia, symbolizing various traits and characteristics. - How do Asian badgers communicate with each other?
Asian badgers communicate through vocalizations, body language, and scent marking. Studying their communication methods provides insights into their social structures. - Are Asian badgers territorial animals?
Yes, Asian badgers can be territorial, marking their territory with scent markings. However, the extent of territorial behavior varies among species. - Can Asian badgers adapt to urban environments?
Some species of Asian badgers have shown adaptability to urban landscapes, adjusting their behaviors to coexist with human activities. - What role do Asian badgers play in the ecosystem?
Asian badgers play a crucial role in the ecosystem by regulating pest populations, influencing plant growth through seed dispersal, and potentially acting as keystone species in maintaining biodiversity.














Leave your comment