Capuchin Monkeys
- January 16, 2024
- 0 comment
The Capuchin monkey, scientifically known as Cebidae, is a captivating and intelligent primate native to Central and South America. Renowned for its distinctive appearance, these monkeys are characterized by their small to medium size, with fur that often showcases a mix of black, brown, and white shades. The name “Capuchin” is derived from their facial markings, which bear a resemblance to the hoods worn by certain religious orders. Living primarily in diverse habitats such as tropical rainforests and mountainous regions, Capuchin monkeys exhibit remarkable adaptability. Their social structure revolves around living in troops, consisting of related females and their offspring, with males joining periodically.
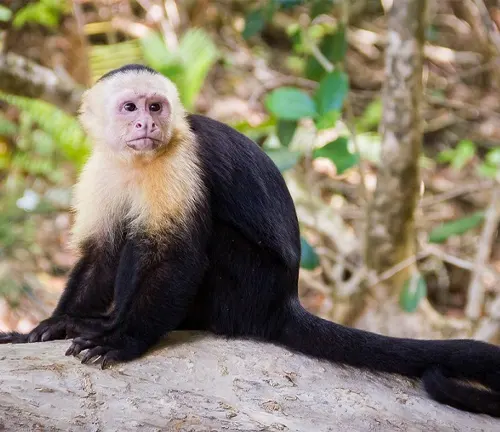

Communication within these groups involves a complex interplay of vocalizations, facial expressions, and body language. Capuchin monkeys are omnivores, displaying a versatile diet that includes fruits, insects, and small mammals. Noteworthy for their problem-solving skills, these monkeys are adept at using tools, showcasing their high cognitive abilities. While they have historical significance in various cultures, including depictions in art and folklore, Capuchin monkeys face challenges in the modern world, including habitat loss and the illegal pet trade. Understanding and appreciating the intricacies of their lives is essential for both conservation efforts and fostering responsible interactions with these fascinating primates.
| Specification | Details |
|---|---|
| Scientific Name | Cebidae |
| Size | Small to medium-sized |
| Fur Color | Varied, including black, brown, and white |
| Distinctive Markings | Resemblance to hooded appearance |
| Habitat | Diverse, including tropical rainforests |
| Social Structure | Troops consisting of related females and offspring |
| Communication | Vocalizations, facial expressions, body language |
| Diet | Omnivorous, consuming fruits, insects, small mammals |
| Problem-Solving Skills | High cognitive abilities, adept at tool usage |
| Adaptability | Thrives in various environments |
| Historical Significance | Cultural depictions in art and folklore |
| Challenges | Faces threats like habitat loss and illegal pet trade |
| Conservation Status | Varies by species; some are endangered |
| Role in Ecosystem | Seed dispersal, contributes to plant diversity |
| Interactions with Humans | Ethical considerations as pets and performers |
| Lifespan | Approximately 15 to 25 years in the wild |
Capuchin Monkeys: Fascinating Creatures in the Wild and Beyond
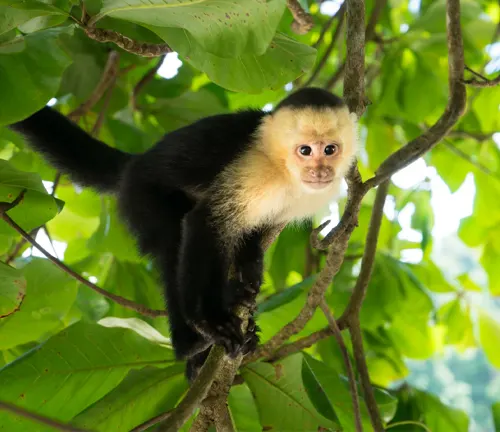

Capuchin monkeys, with their endearing faces and lively antics, have captivated the fascination of both researchers and animal enthusiasts alike. In this comprehensive exploration, we delve into their physical characteristics, natural habitat, social structure, cognitive abilities, and much more. Join us on this journey to uncover the captivating world of Capuchin monkeys.
Capuchin monkeys, scientifically known as Cebidae, are small to medium-sized primates found primarily in Central and South America. Known for their distinct appearance and remarkable intelligence, these monkeys have become subjects of intrigue for scientists and admirers alike.
Their engaging behaviors, from tool usage to complex social structures, make Capuchin monkeys a captivating subject of study. In this article, we aim to shed light on various aspects of their lives, both in the wild and their interactions with humans.
Physical Characteristics
Size and appearance
Capuchin monkeys typically range from 12 to 22 inches in length, with prehensile tails nearly as long as their bodies. Their fur varies in color, often displaying a mix of black, brown, and white, creating distinctive facial markings.
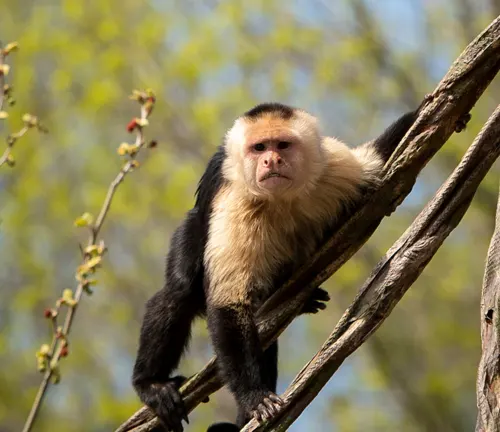

Unique features
Notably, their faces bear a resemblance to hooded monks, which inspired their name. Their prehensile tails aid in navigation through treetops, showcasing their adaptability to arboreal life.
Natural Habitat
Geographic distribution
Capuchin monkeys inhabit a diverse range of ecosystems, including tropical rainforests, dry forests, and even mountainous regions. Their adaptability allows them to thrive in various environments across Central and South America.
Preferred environments
While they are comfortable in different habitats, Capuchin monkeys often prefer areas rich in vegetation, providing ample opportunities for foraging and social interactions.
Social Structure
Group dynamics
Capuchin monkeys exhibit a complex social structure, living in groups called troops. These troops consist of related females and their offspring, with males joining and leaving periodically.
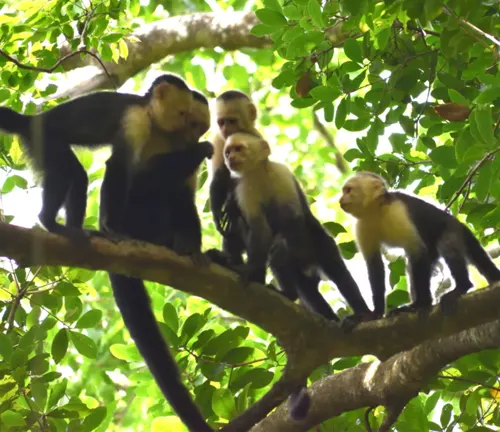

Communication within the group
Communication plays a vital role in their social dynamics, involving vocalizations, facial expressions, and body language. Understanding their communication methods provides insight into their cooperative behaviors.
Diet and Feeding Habits
Omnivorous nature
Capuchin monkeys are opportunistic omnivores, consuming a varied diet that includes fruits, insects, small mammals, and even bird eggs. Their adaptable diet contributes to their widespread distribution.
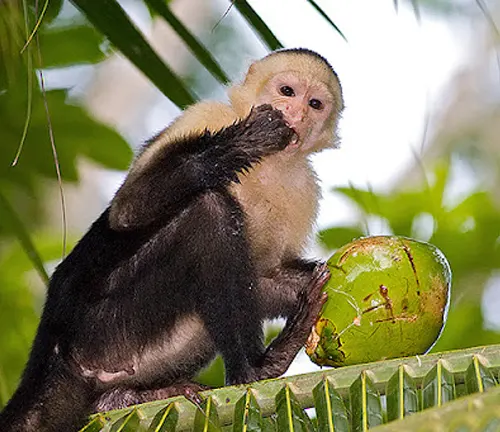

Hunting and foraging techniques
Their clever hunting and foraging techniques, such as using tools to extract insects or crack open nuts, showcase their problem-solving abilities and resourcefulness in the wild.
Cognitive Abilities
Problem-solving skills
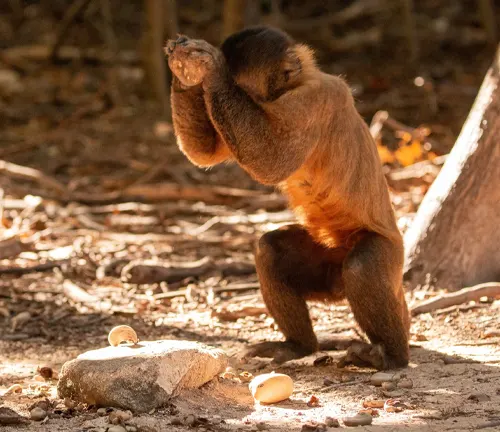
Studies have revealed the remarkable problem-solving skills of Capuchin monkeys, demonstrating their ability to use tools for various tasks. These cognitive abilities contribute to their survival and dominance in their ecosystems.
Tool usage
Capuchin monkeys display a sophisticated understanding of tools, using sticks to extract insects from tree bark or using stones to crack open hard-shelled fruits. This tool usage highlights their intelligence and adaptability.

Interaction with Humans
Historical significance
Throughout history, Capuchin monkeys have played roles in various cultures, often depicted in art and folklore. Their association with certain religious orders has contributed to their unique status.
Current roles as pets and in entertainment
In contemporary times, Capuchin monkeys have found roles as exotic pets and performers in the entertainment industry. However, concerns arise regarding the ethical treatment and well-being of these creatures in human environments.
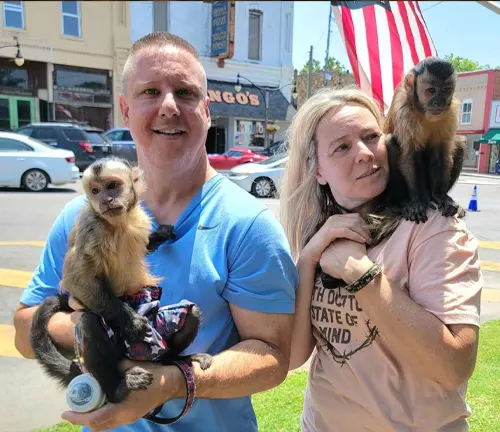

Conservation Status
Threats to Capuchin monkeys
Capuchin monkeys face threats such as habitat loss, illegal wildlife trade, and diseases transmitted by humans. Understanding these challenges is crucial for their conservation.

Conservation efforts
Conservation initiatives, including habitat protection and rehabilitation programs, aim to mitigate the threats faced by Capuchin monkeys. These efforts play a vital role in preserving their natural habitats and ensuring their survival.
Challenges in Capuchin Monkey Conservation
Human-related threats
Anthropogenic activities, including deforestation and habitat fragmentation, pose significant challenges to Capuchin monkey populations. Addressing these threats is crucial for their long-term survival.
The impact of habitat loss
As human activities continue to encroach upon natural habitats, the consequences for Capuchin monkeys are dire. Understanding the cascading effects of habitat loss is essential for effective conservation strategies.
Capuchin Monkeys in Popular Culture
Representation in movies and literature
Capuchin monkeys have left an indelible mark on popular culture, appearing in movies like “Night at the Museum” and literature such as children’s books. Their charming demeanor and clever antics make them memorable characters.
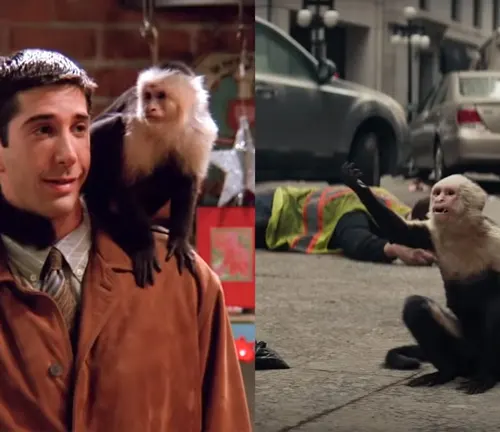

Cultural significance
Beyond entertainment, Capuchin monkeys hold cultural significance in various societies, symbolizing qualities like intelligence, adaptability, and a connection to nature.
Different Species
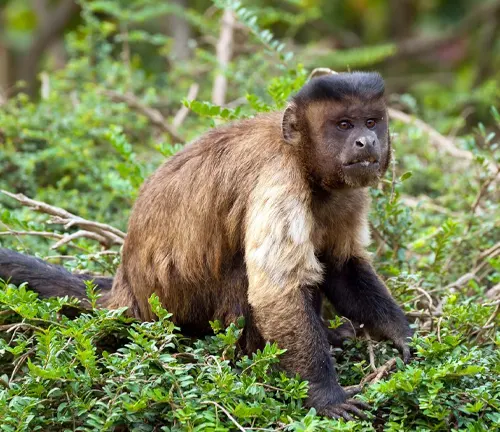
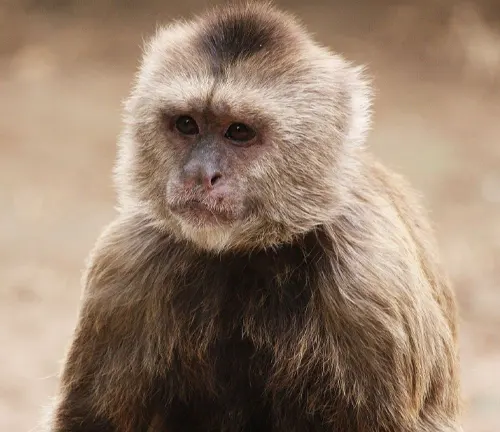
Tufted Capuchin
(Cebus apella)
Recognizable by a crown of fur on its head (tuft), these monkeys are found in South America. Display a diverse range of fur colors, including black, brown, and cream.


Weeper Capuchin
(Cebus olivaceus)
Identified by its olive-colored fur, Weeper Capuchins inhabit the rainforests of South America. Known for their expressive faces, often resembling a “weeping” appearance.
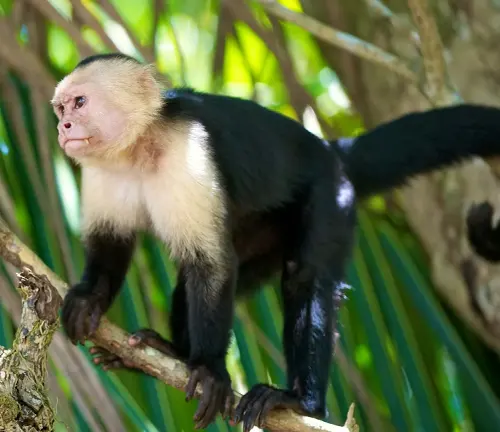
White-headed Capuchin
(Cebus capucinus)
Found in Central and South America, these capuchins have a distinctive white or light-colored crown on their heads. Highly intelligent and adaptable, often seen in various habitats.
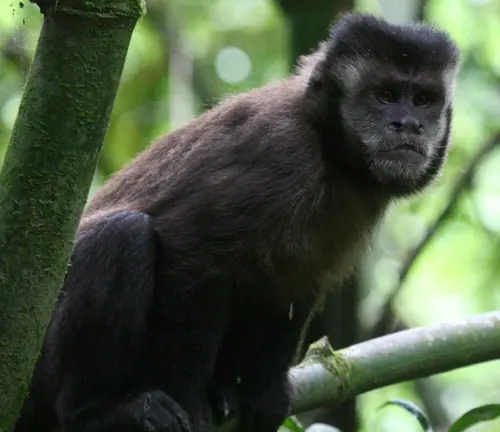


Black Capuchin
(Sapajus nigritus)
Native to Brazil and Paraguay, the Black Capuchin is characterized by its dark fur. Often observed in groups, displaying complex social behaviors.
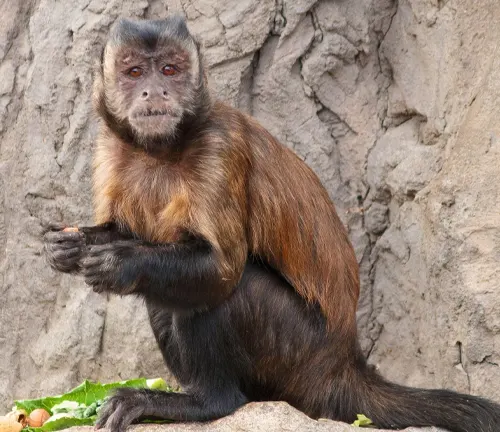
Hooded Capuchin
(Cebus cucullatus)
Inhabiting the forests of South America, these capuchins have a hood-like pattern on their heads. Known for their agility and skill in navigating through treetops.
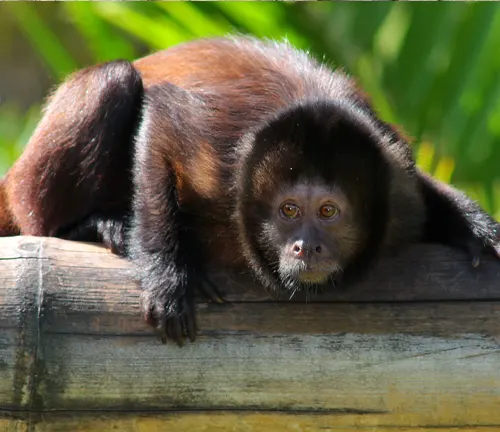


Robust Tufted Capuchin
(Sapajus robustus)
Endemic to Brazil, these capuchins are larger compared to other species. Recognized for their robust build and strong jaws.
Wedge-capped Capuchin
(Cebus olivaceus weddelli)
Residing in the Amazon rainforest, these capuchins have a distinct wedge-shaped cap on their heads. Play a crucial role in seed dispersal within their ecosystems.
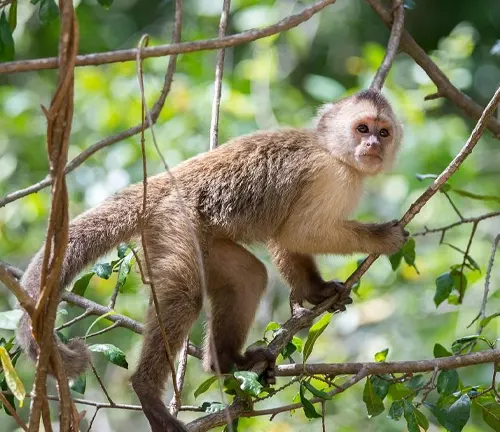
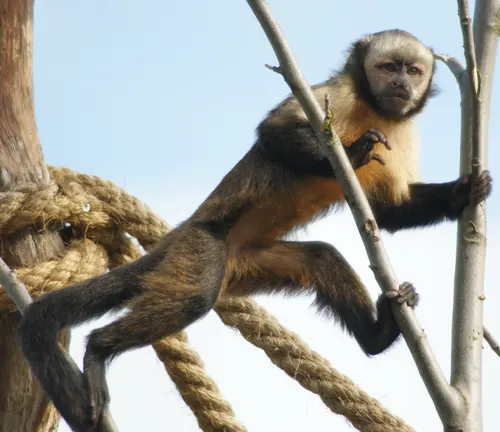


Golden-bellied Capuchin
(Sapajus xanthosternos)
Endangered species found in Brazil, distinguished by their golden-colored fur on the belly. Face threats due to habitat loss and illegal pet trade.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
- What is the lifespan of Capuchin monkeys in the wild?
Capuchin monkeys typically live around 15 to 25 years in the wild, depending on factors such as species and environmental conditions. - Are Capuchin monkeys endangered?
While some species of Capuchin monkeys are classified as least concern, others, like the Golden-bellied Capuchin, are endangered due to habitat loss and the illegal pet trade. - How do Capuchin monkeys communicate with each other?
Capuchin monkeys use a combination of vocalizations, facial expressions, and body language to communicate within their social groups. - Do Capuchin monkeys use tools in the wild?
Yes, Capuchin monkeys are known for their tool usage. They employ sticks to extract insects from tree bark and stones to crack open nuts. - Can Capuchin monkeys swim?
Capuchin monkeys are generally not strong swimmers. While some may wade in shallow water, they are not adapted for extensive swimming. - What is the role of Capuchin monkeys in seed dispersal?
Capuchin monkeys play a crucial role in seed dispersal by consuming fruits and then dispersing seeds in different locations through their feces. - How do Capuchin monkeys defend themselves from predators?
Capuchin monkeys rely on agility and group cooperation to evade predators. They may vocalize loudly and use their intelligence to avoid threats. - Can Capuchin monkeys be kept as pets in all countries?
The legality of keeping Capuchin monkeys as pets varies by country and region. Many places have strict regulations due to ethical and conservation concerns. - Do Capuchin monkeys form strong bonds with humans?
Capuchin monkeys are social animals and can form strong bonds with humans, but their needs for socialization and enrichment must be met for healthy relationships. - Are there any specific health concerns associated with keeping Capuchin monkeys as pets?
Yes, potential health concerns include zoonotic diseases, aggression, and the need for specialized veterinary care. Prospective owners must be well-informed and responsible.














Leave your comment