Javan Rhinoceros
- February 22, 2024
- 0 comment
The Javan rhinoceros, also known scientifically as Rhinoceros sondaicus, is a critically endangered species of rhinoceros native to Java, Indonesia. This majestic creature is characterized by its solitary horn and relatively small size compared to other rhinoceros species. Sadly, the Javan rhinoceros is one of the rarest large mammals on Earth, with only a handful of individuals believed to remain in the wild. Its existence is under severe threat due to habitat loss, primarily caused by deforestation and agricultural expansion, as well as poaching for its prized horn, which holds significant value in traditional Asian medicine.

Conservation efforts to safeguard the Javan rhinoceros include habitat preservation initiatives, stringent anti-poaching measures, and carefully managed captive breeding programs. Despite these efforts, the species continues to teeter on the brink of extinction, emphasizing the urgent need for intensified conservation actions to ensure its survival and protect the biodiversity of our planet.
| Specification | Description |
|---|---|
| Scientific Name | Rhinoceros sondaicus |
| Common Name | Javan Rhinoceros |
| Habitat | Dense tropical rainforests and grasslands of Java, Indonesia |
| Physical Characteristics | Solitary horn, smaller size compared to other rhinoceros species |
| Conservation Status | Critically Endangered |
| Population Estimate | Only a few individuals believed to remain in the wild |
| Threats | Habitat loss due to deforestation and agricultural expansion, poaching for its horn |
| Conservation Efforts | Habitat preservation, anti-poaching measures, captive breeding programs |
| Average Lifespan | Around 30-40 years in the wild |
| Diet | Herbivorous, primarily feeding on vegetation |
Physical Description
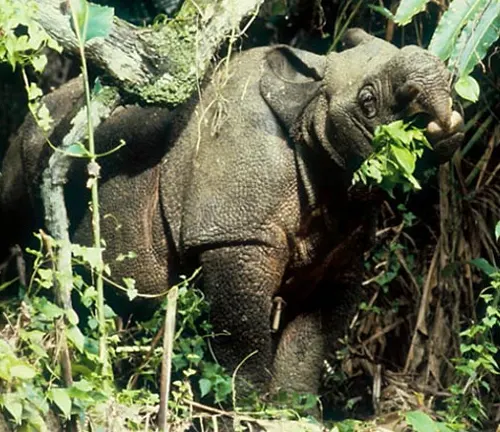
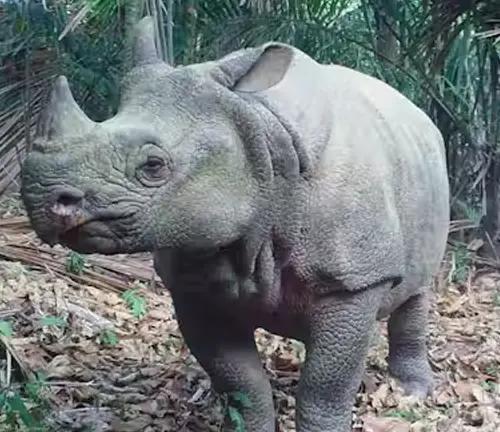
The Javan Rhinoceros, scientifically known as Rhinoceros sondaicus, is a magnificent creature that captivates with its unique physical features. Standing out with a solitary horn and a relatively smaller size compared to its counterparts, this species exudes an aura of mystery and rarity. Their sturdy build and thick, folded skin add to their distinctive appearance, making them easily recognizable amidst the lush landscapes of Java, Indonesia.
Size and Weight
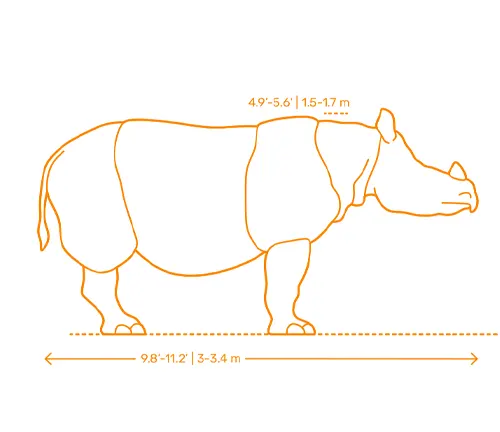
The Javan Rhinoceros (Rhinoceros sondaicus) is known for its relatively smaller size compared to other rhinoceros species. Adult Javan Rhinoceroses typically stand about 1.4 to 1.7 meters (4.6 to 5.6 feet) tall at the shoulder and measure around 3.1 to 3.2 meters (10 to 10.5 feet) in length. They exhibit sexual dimorphism, with males being slightly larger and heavier than females. Adult males typically weigh between 900 and 2,300 kilograms (2,000 to 5,000 pounds), while females weigh slightly less.
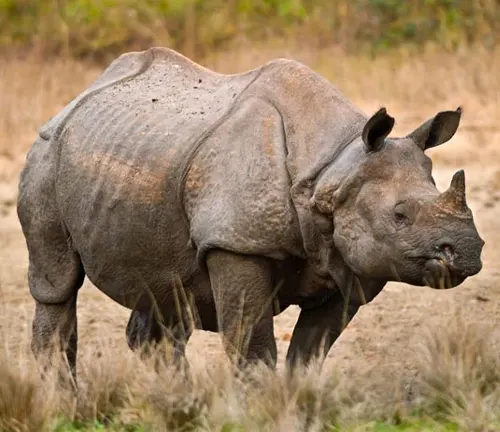

Skin and Horns
Javan Rhinoceroses possess a distinctive appearance characterized by their thick, folded skin, which is usually a dark grey or black color. Unlike some other rhinoceros species, they typically have a single horn, although occasional individuals may have two. Their horns are relatively small compared to other species, and they are made of keratin, the same protein found in human hair and nails. The horn grows continuously throughout their life and may reach lengths of up to 25 centimeters (10 inches).
Habitat and Distribution
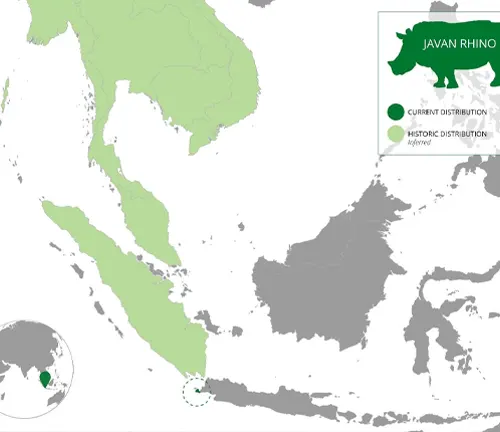
Found primarily in the dense tropical rainforests and grasslands of Java, Indonesia, the Javan Rhinoceros once roamed across a wider range. However, due to extensive deforestation and habitat loss, their distribution has become severely restricted. Today, only a few scattered individuals are believed to inhabit these dwindling habitats, highlighting the urgent need for conservation efforts to protect their remaining sanctuaries.
Geographic Range
The Javan Rhinoceros (Rhinoceros sondaicus) is native to the island of Java, Indonesia. Historically, its range extended across Southeast Asia, including parts of Myanmar, Thailand, Laos, Cambodia, and Vietnam. However, due to extensive habitat loss and hunting, the species is now restricted to a few scattered areas within Java. These remaining habitats include dense tropical rainforests, grasslands, and swampy areas.
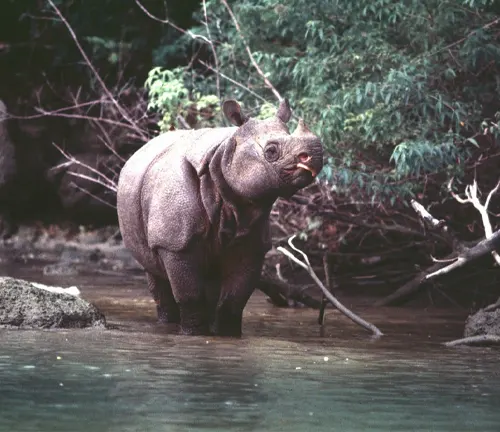

Preferred Environment
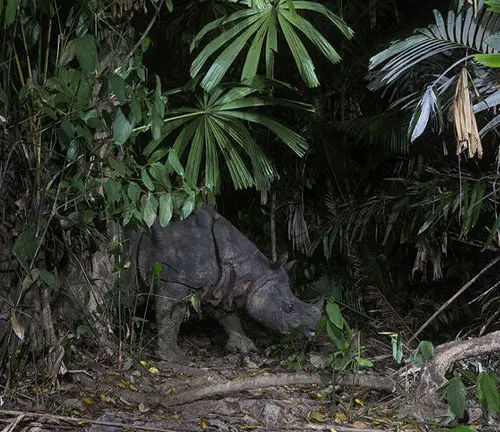
Javan Rhinoceroses inhabit dense tropical rainforests and adjacent grasslands, often near water sources such as rivers, streams, or marshes. They prefer areas with dense vegetation that provides both food and cover, as well as access to mud wallows for bathing and cooling off. These habitats typically offer a mix of forested areas for browsing on leaves and grassy clearings for grazing. Despite their adaptability, Javan Rhinoceroses are highly susceptible to habitat disturbance and prefer secluded areas away from human activity.
Behavior and Social Structure
As solitary creatures, Javan Rhinoceroses lead relatively solitary lives, preferring to roam and forage alone rather than in groups. They are known for their elusive nature, often shying away from human presence and remaining hidden within the dense vegetation of their habitats. Despite their solitary behavior, occasional interactions between individuals have been observed, particularly during mating season or when sharing common resources such as watering holes.

Diet and Feeding Habits
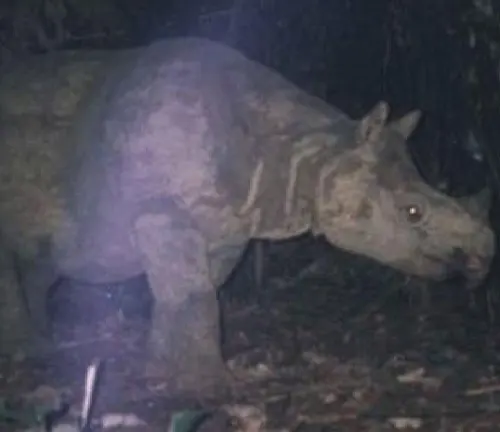
Javan Rhinoceroses are strict herbivores, primarily feeding on a diet consisting of various vegetation found within their habitats. Their diet typically includes grasses, leaves, shoots, and fruits, which they consume by browsing and grazing in the forest understory. Despite their massive size, they possess a selective feeding behavior, carefully choosing the most nutritious plant species to sustain their energy requirements.
Herbivorous Lifestyle
The Javan Rhinoceros (Rhinoceros sondaicus) is strictly herbivorous, meaning it consumes a diet consisting entirely of plant matter. This herbivorous lifestyle is typical of all rhinoceros species and is adapted to their specialized digestive system, which is designed to process fibrous plant material.

Feeding Patterns
Javan Rhinoceroses feed primarily on a variety of vegetation found within their habitat. Their diet includes grasses, leaves, shoots, fruits, and occasionally aquatic plants. They are known to browse on low-hanging vegetation in forested areas and graze on grasses in open clearings or grasslands.

Reproduction and Lifecycle
Reproduction in Javan Rhinoceroses is a rare and meticulously orchestrated event. Females reach sexual maturity at around six to seven years of age, while males typically mature slightly later. Breeding pairs come together briefly for mating, after which the female undergoes a gestation period of approximately 15 to 16 months. The birth of a single calf marks a significant milestone in the species’ lifecycle, with mothers providing attentive care and protection to their offspring in their early stages of life.
Mating Behavior
The Javan Rhinoceros (Rhinoceros sondaicus) typically engages in mating behavior during specific times of the year, although precise mating seasons can vary depending on environmental factors and individual reproductive cycles. Males may engage in courtship behaviors such as vocalizations, displays, and physical interactions to attract females and establish dominance. Once a mating pair forms, copulation occurs, typically lasting for a brief period.

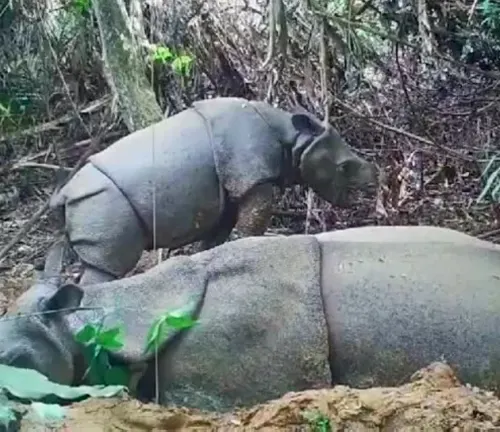
Gestation Period
After successful mating, female Javan Rhinoceroses undergo a gestation period of approximately 15 to 16 months before giving birth. This gestation period is one of the longest among terrestrial mammals. During this time, the female requires ample resources to support the developing fetus, emphasizing the importance of suitable habitat and access to nutritious food.

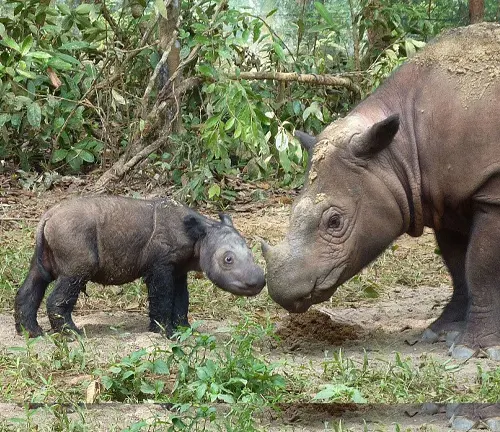
Offspring Care
Female Javan Rhinoceroses give birth to a single calf, which is born relatively large and well-developed compared to other ungulates. The newborn calf relies on its mother for nourishment and protection in the early stages of life. Mothers provide attentive care to their offspring, nursing them and ensuring their safety within the habitat. Young Javan Rhinoceroses may stay with their mothers for an extended period, learning essential survival skills before eventually becoming independent. The bond between mother and calf is strong, with the mother providing guidance and protection until the calf reaches maturity.
Conservation Status
Despite being one of the most iconic and cherished species of Indonesia, the Javan Rhinoceros faces an uphill battle for survival. Classified as critically endangered, their population has dwindled to just a handful of individuals, primarily due to habitat loss, poaching, and human encroachment. Conservation efforts, including habitat preservation, anti-poaching measures, and captive breeding programs, are underway to safeguard the species from extinction. However, the road ahead is fraught with challenges, necessitating continued dedication and collaboration to secure a future for the Javan Rhinoceros and preserve the rich biodiversity of our planet.
Different Species
The Javan Rhinoceros (Rhinoceros sondaicus) is a single species of rhinoceros native to Java, Indonesia. There are no recognized subspecies or different species of Javan Rhinoceros.

Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
- What is the Javan Rhinoceros?
The Javan Rhinoceros (Rhinoceros sondaicus) is a critically endangered species of rhinoceros native to Java, Indonesia. It is one of the rarest large mammals on Earth. - Where is the Javan Rhinoceros found?
The Javan Rhinoceros is found primarily in the dense tropical rainforests and grasslands of Java, Indonesia. - How many Javan Rhinoceroses are left in the wild?
Only a few individuals are believed to remain in the wild, with estimates ranging from less than 70 to possibly fewer than 100 individuals. - Why is the Javan Rhinoceros endangered?
The Javan Rhinoceros is endangered primarily due to habitat loss, poaching for its horn, and human encroachment into its natural habitat. - What are the main threats to the Javan Rhinoceros?
The main threats to the Javan Rhinoceros include habitat loss due to deforestation and agricultural expansion, poaching for its horn, and human disturbance. - What conservation efforts are in place to protect the Javan Rhinoceros?
Conservation efforts include habitat preservation initiatives, anti-poaching measures, community education, and captive breeding programs. - How big is a Javan Rhinoceros?
Javan Rhinoceroses are relatively smaller compared to other rhinoceros species, with adults typically weighing between 900 and 2,300 kilograms (2,000 to 5,000 pounds). - How long do Javan Rhinoceroses live?
In the wild, Javan Rhinoceroses have an average lifespan of around 30 to 40 years. - What do Javan Rhinoceroses eat?
Javan Rhinoceroses are herbivores, primarily feeding on various vegetation such as grasses, leaves, shoots, and fruits. - How do Javan Rhinoceroses behave in the wild?
Javan Rhinoceroses are solitary creatures, preferring to roam and forage alone rather than in groups. They are known for their elusive nature, often shying away from human presence. - Are there any Javan Rhinoceroses in captivity?
Yes, there are a few Javan Rhinoceroses kept in captivity as part of breeding programs aimed at preserving the species. - What is being done to combat poaching of Javan Rhinoceros horns?
Efforts to combat poaching include increased patrols, law enforcement measures, and public awareness campaigns to reduce demand for rhinoceros horn products. - How does habitat loss affect the Javan Rhinoceros population?
Habitat loss leads to fragmentation and degradation of the rhinoceros’s habitat, reducing available food and shelter and increasing human-wildlife conflict. - What is the difference between the Javan Rhinoceros and other rhinoceros species?
The Javan Rhinoceros is smaller in size compared to other rhinoceros species and has a single horn. Additionally, it has distinct folds of skin at its neck. - How can I help conserve the Javan Rhinoceros?
You can help conserve the Javan Rhinoceros by supporting conservation organizations, spreading awareness about the species’ plight, and advocating for stronger protection measures for their habitats. Additionally, avoiding products made from rhinoceros horn can help reduce demand and combat poaching.














Leave your comment