Eastern Hoolock Gibbon
- January 17, 2024
- 0 comment
The Eastern hoolock gibbon, scientifically known as Hoolock leuconotus, is a captivating primate species that finds its home in the lush landscapes of Southeast Asia. These remarkable gibbons are characterized by their unique physical features, including a specific size and weight range that sets them apart within the primate family. Known for their arboreal lifestyle, Eastern hoolock gibbons navigate the dense canopies with agility, showcasing behaviors that highlight their intricate social structures and communication methods.
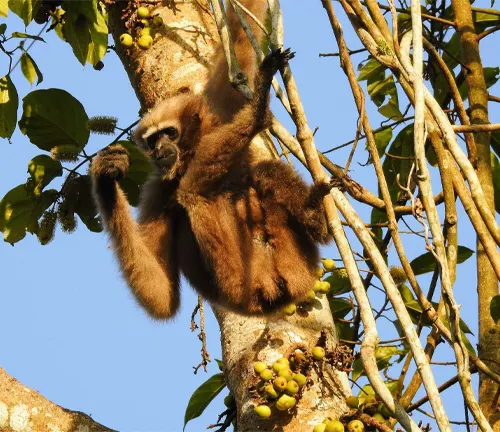

Reproduction and family life are integral aspects of their existence, with distinct mating rituals, gestation periods, and strong parental bonds contributing to the survival of their species. Unfortunately, the Eastern hoolock gibbon faces numerous threats, including deforestation, habitat loss, and illegal hunting. Conservation efforts have been initiated to address these challenges and preserve the delicate balance they maintain within their ecosystems.
| Feature | Description |
|---|---|
| Scientific Name | Hoolock leuconotus |
| Common Name | Eastern Hoolock Gibbon |
| Classification | Kingdom: Animalia, Phylum: Chordata, Class: Mammalia, Order: Primates, Family: Hylobatidae, Genus: Hoolock |
| Geographical Distribution | Southeast Asia |
| Habitat | Lush tropical and subtropical forests |
| Size | Medium-sized, varying between 60 to 90 cm |
| Weight | Typically 6 to 9 kg |
| Physical Features | White eyebrows, distinct black fur, and a throat sac |
| Lifestyle | Arboreal, spending most of their time in trees |
| Social Structure | Family-oriented, forming small groups |
| Communication | Vocalizations, including elaborate songs |
| Reproduction | Monogamous mating, with a gestation period of around 7 months |
| Conservation Status | Vulnerable (IUCN Red List) |
| Main Threats | Deforestation, habitat loss, and illegal hunting |
| Conservation Initiatives | Various organizations working towards habitat protection and awareness |
| Cultural Significance | Symbolic in local cultures, often featuring in folklore and traditions |
| Ecological Role | Seed dispersal and maintaining forest biodiversity |
Eastern Hoolock Gibbon (Hoolock leuconotus) Guardians of the Eastern Canopy
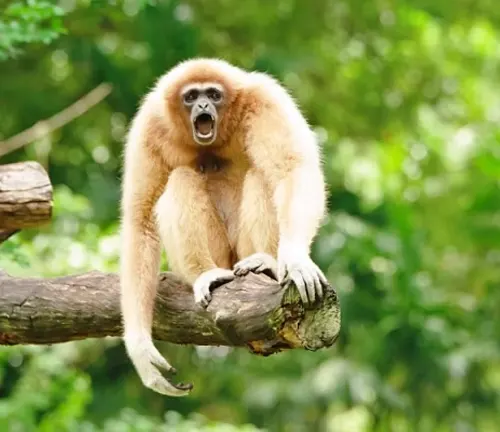

Taxonomy and Distribution
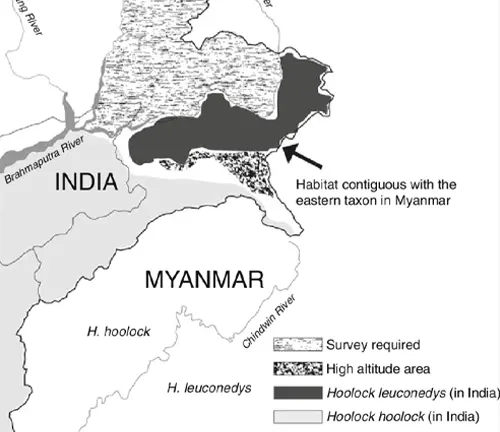
The Eastern hoolock gibbon, scientifically identified as Hoolock leuconotus, holds a unique place in the primate family. Classified under the genus Hoolock, these fascinating creatures are primarily found in the lush landscapes of Southeast Asia. From the dense canopies of Myanmar to the vibrant forests of China and India, their geographical distribution paints a vivid picture of a species deeply connected to the diverse ecosystems of the region.
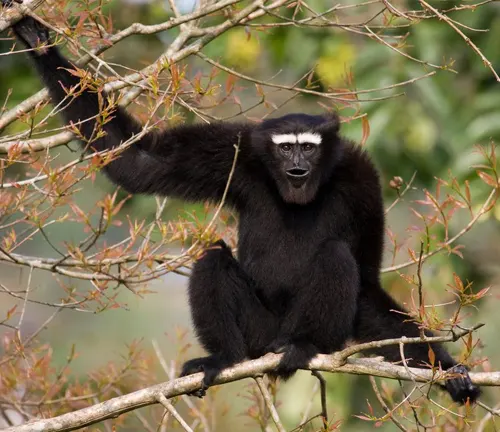

Physical Characteristics
Standing as nature’s acrobats, Eastern hoolock gibbons exhibit distinctive physical features that make them a captivating species. With a medium-sized frame ranging from 60 to 90 cm and weighing between 6 to 9 kg, their white eyebrows and distinct black fur set them apart in the primate world. Notably, their throat sac adds an element of uniqueness, contributing to the mesmerizing allure of these arboreal creatures.
Behavior and Social Structure
In the lofty heights of their forested homes, Eastern hoolock gibbons showcase a complex social structure. Family-oriented and forming small groups, these gibbons engage in intricate communication through vocalizations, including elaborate songs that echo through the treetops. Their daily activities, from foraging for food to acrobatic displays, offer a glimpse into the dynamic and social lives they lead.
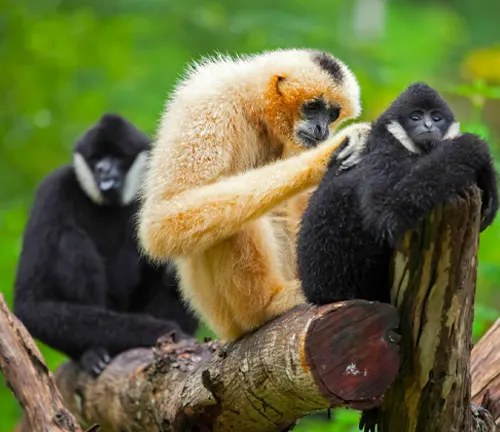
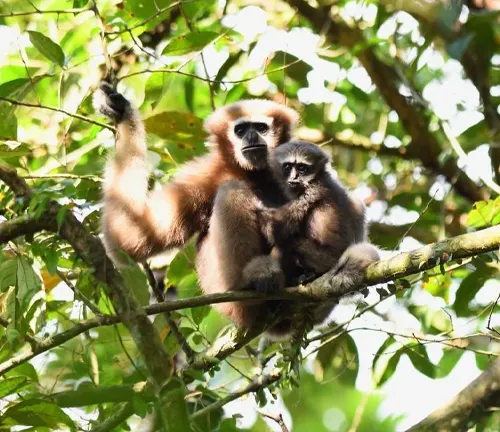


Reproduction and Family Life
The journey of the Eastern hoolock gibbon extends to matters of the heart. Monogamous in nature, they engage in unique mating rituals, forming strong pair bonds. A gestation period of around 7 months precedes the birth of offspring, marking the beginning of a dedicated period of parental care. This family-centric approach contributes significantly to the survival and thriving of their species.
Threats and Conservation Status
Despite their resilience, Eastern hoolock gibbons face numerous threats that challenge their existence. Deforestation, habitat loss, and illegal hunting pose significant risks to their populations. Recognized as “Vulnerable” on the IUCN Red List, concerted conservation efforts are crucial to mitigating these threats and ensuring the long-term survival of this remarkable species.
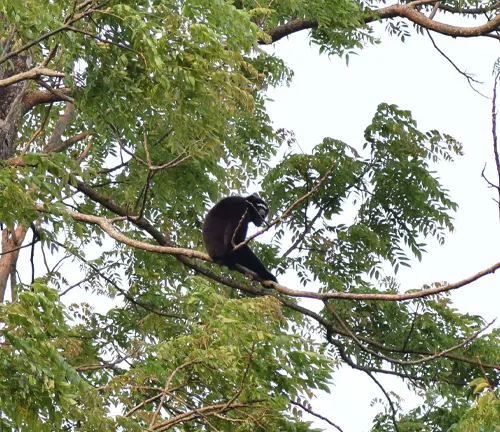


Role in Ecosystem
Delving into the ecological significance of Eastern hoolock gibbons unveils their role as guardians of the forest canopy. As adept tree-dwellers, they contribute to seed dispersal and play a vital role in maintaining the biodiversity of their habitats. Their interconnectedness with other species within the ecosystem highlights the delicate balance they uphold.
Ecotourism and Public Awareness
The potential for ecotourism emerges as a positive force for Eastern hoolock gibbon conservation. Drawing attention to the benefits of responsible tourism, these creatures become ambassadors for their ecosystems. Public awareness, fueled by the enchantment of observing these primates in their natural habitat, becomes a powerful tool in fostering a collective commitment to their protection.

Different Species
Western Hoolock Gibbon
(Hoolock hoolock)
Found in India, Bangladesh, and Myanmar, the Western hoolock gibbon is a close relative to its Eastern counterpart. Known for its black or dark brown fur and unique vocalizations, it inhabits a variety of forest types.
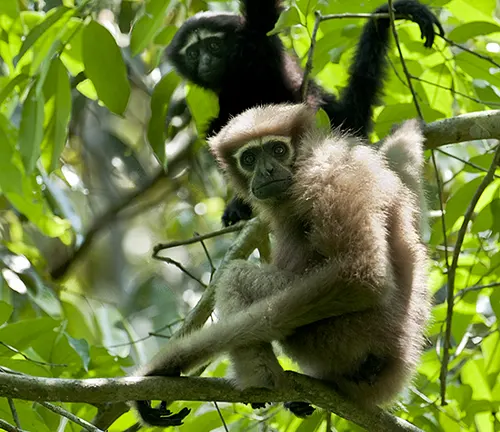
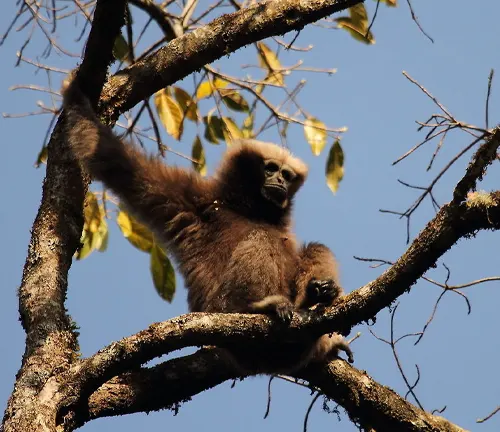


Eastern Hoolock Gibbon
(Hoolock leuconedys)
Endemic to specific regions in Myanmar, China, and possibly parts of India, the Eastern hoolock gibbon is distinguished by its lighter-colored fur and vocalizations that set it apart from the Western hoolock gibbon.
Frequently Asked Question (FAQs)
- What is the lifespan of Eastern hoolock gibbons in the wild?
Eastern hoolock gibbons typically have a lifespan of around 25 to 30 years in their natural habitat. - How do Eastern hoolock gibbons communicate with each other?
Gibbons communicate through a combination of vocalizations, including elaborate songs and calls, as well as physical gestures. - Do Eastern hoolock gibbons form monogamous pairs?
Yes, Eastern hoolock gibbons are known for forming monogamous pairs, with a male-female bond that lasts for a considerable period. - What is the role of Eastern hoolock gibbons in seed dispersal?
Eastern hoolock gibbons play a crucial role in seed dispersal as they consume fruits and later disperse seeds throughout their habitat. - Are Eastern hoolock gibbons strictly arboreal?
Yes, Eastern hoolock gibbons are arboreal creatures, spending the majority of their lives in trees and exhibiting incredible agility in the forest canopy. - How do Eastern hoolock gibbons contribute to forest canopy maintenance?
Gibbons help in maintaining the forest canopy by moving through trees, which aids in the pruning of branches and supports overall canopy health. - Are there any distinctive markings or features that help identify individual Eastern hoolock gibbons?
While individual identification can be challenging, researchers may use variations in fur color, facial markings, or unique behaviors to distinguish between gibbons. - What are the main differences between Western and Eastern hoolock gibbons?
Western hoolock gibbons have darker fur, and their distribution covers India, Bangladesh, and Myanmar, while Eastern hoolock gibbons have lighter fur and are found in parts of Myanmar and China. - How has habitat loss affected Eastern hoolock gibbons?
Habitat loss, mainly due to deforestation and human encroachment, poses a significant threat to Eastern hoolock gibbons by diminishing their living space and disrupting their natural behaviors. - Do Eastern hoolock gibbons play a role in controlling insect populations in their habitat?
Yes, gibbons may help control insect populations indirectly by influencing the structure of their habitat, which affects the abundance of insects. - What is the significance of the white eyebrows seen in Eastern hoolock gibbons?
The distinctive white eyebrows in Eastern hoolock gibbons are thought to serve as visual signals during communication, playing a role in social interactions. - How do Eastern hoolock gibbons adapt to changes in their environment?
Eastern hoolock gibbons display behavioral adaptations to environmental changes, such as adjusting their foraging patterns or vocalizations in response to alterations in their habitat.














Leave your comment