Honey Badger
- January 15, 2024
- 0 comment
The honey badger, scientifically known as Mellivora capensis, stands as a testament to nature’s resilience and adaptability. These medium-sized mammals, with their distinctive coat ranging from gray to brown, navigate a wide range of environments across Africa and parts of Asia. Renowned for their fearless nature, honey badgers possess a robust build, powerful jaws, and sharp claws that make them formidable in the wild. Despite their size, they showcase remarkable intelligence, exhibiting problem-solving skills and resourcefulness. Their diet is diverse, encompassing small mammals, birds, reptiles, insects, and even honey, showcasing their opportunistic feeding habits.
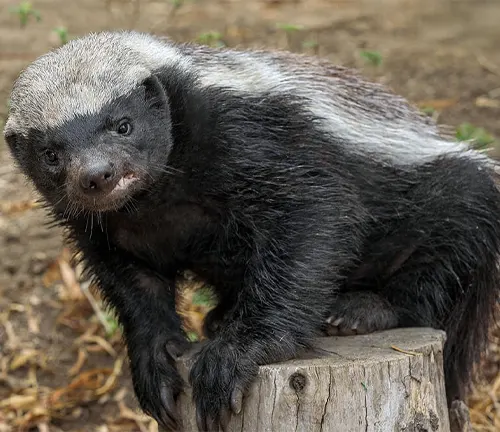

One of their most notable features is the ability to resist snake venom, enabling them to survive bites that would be fatal to other creatures. With a solitary lifestyle, honey badgers raise one to two cubs independently, passing on essential survival skills. Their interactions with other species, myth-busting their reputation, and their role in ecosystems add layers to their fascinating narrative. While facing threats such as habitat loss and human-wildlife conflict, the honey badger remains an iconic symbol of tenacity and adaptability in the natural world.
| Specification | Details |
|---|---|
| Scientific Name | Mellivora capensis |
| Size | Medium-sized |
| Coat Color | Gray to brown |
| Physical Build | Robust |
| Special Features | Loose and tough skin, powerful jaws, sharp claws |
| Geographic Range | Africa and parts of Asia |
| Habitat | Diverse, including grasslands, savannas, forests, and deserts |
| Diet | Omnivorous, includes small mammals, birds, reptiles, insects, and honey |
| Venom Resistance | Capable of surviving snake bites |
| Intelligence | Remarkably intelligent, exhibits problem-solving skills |
| Social Structure | Solitary |
| Reproduction | Females give birth to one to two cubs, raised independently |
| Behavior | Fearless and tenacious, stands ground against larger predators |
| Conservation Status | Faces threats like habitat loss, poaching, and human-wildlife conflict |
| Ecological Role | Predators and scavengers, contribute to maintaining ecological balance |
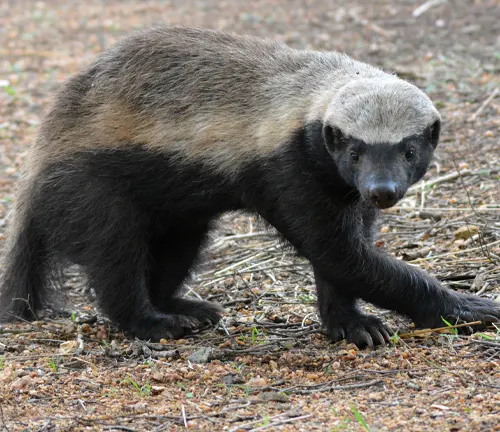

The honey badger, scientifically known as Mellivora capensis, is a fascinating creature that has captured the imagination of many due to its tenacious and fearless nature. Despite its relatively small size, this mammal is renowned for its remarkable abilities and distinct behaviors.
Honey Badger Physical Characteristics
Honey badgers are medium-sized mammals with a robust build. They typically have a distinctive coat that ranges from gray to brown, with a coarse texture. Their sturdy build, powerful jaws, and sharp claws make them well-equipped for their unique lifestyle.
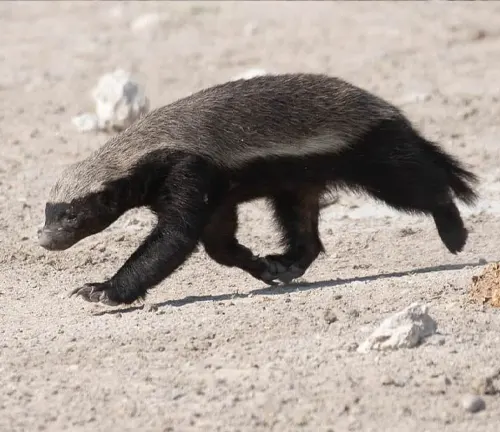

Habitat and Distribution
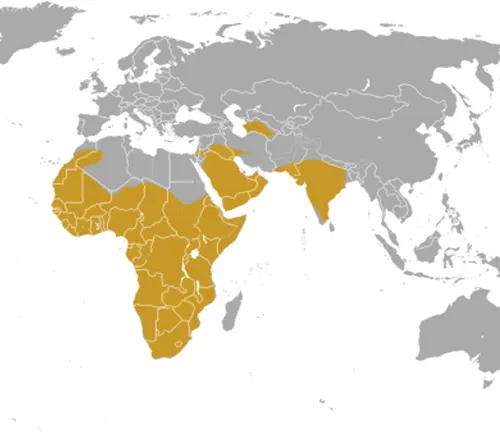
These resilient creatures are adaptable to various environments, ranging from grasslands and savannas to forests and deserts. Honey badgers are primarily found in Africa and parts of Asia, showcasing their ability to thrive in diverse landscapes.
Diet and Eating Habits
One of the notable aspects of honey badgers is their diverse diet. They are omnivores, feeding on a variety of prey and plant matter. Their diet includes small mammals, birds, reptiles, insects, and even honey, showcasing their opportunistic feeding habits.
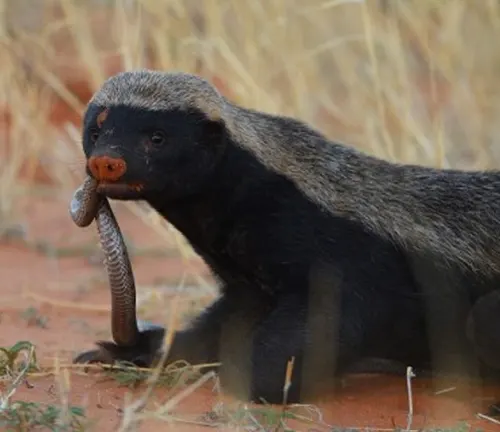

Adaptations for Survival
Honey badgers are equipped with several adaptations that aid in their survival. Their loose and tough skin allows them to twist and turn freely, making it challenging for predators to grasp them. Additionally, their strong jaws and sharp claws help them break into beehives, a behavior that earned them the name “honey badger.”
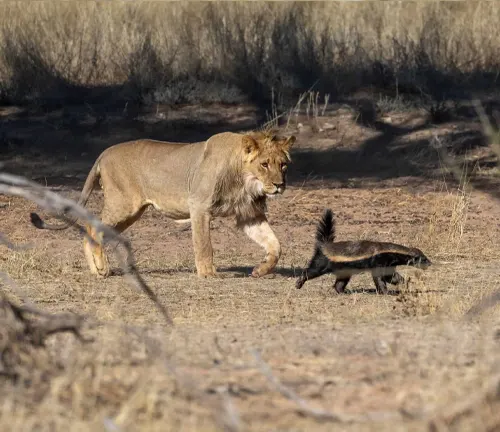

Remarkable Intelligence
Despite their size, honey badgers are known for their intelligence. They exhibit problem-solving skills and demonstrate the ability to overcome challenges, reflecting their resourcefulness in the wild.
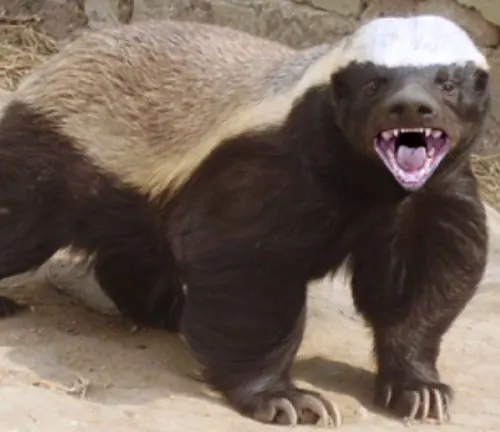
Honey Badger Behavior
The behavior of honey badgers is characterized by fearlessness and tenacity. They are known to stand their ground against larger predators, displaying a remarkable level of aggression when threatened. Their boldness and determination make them a force to be reckoned with in the animal kingdom.

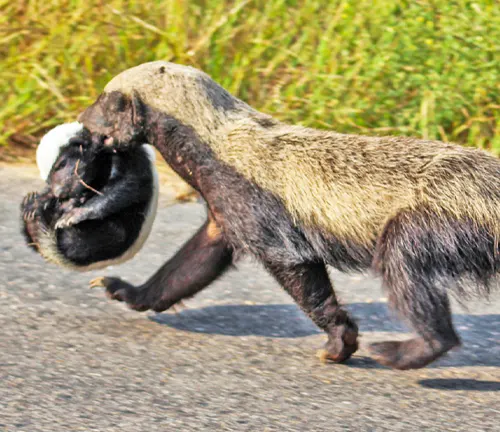
Reproduction and Family Structure
Honey badgers have a solitary lifestyle, and their mating habits are relatively unknown. Female honey badgers give birth to one to two cubs, which they raise independently. The cubs learn essential survival skills from their mothers before venturing out on their own.

Interaction with Other Species
Honey badgers interact with various species in their ecosystem. They may compete with other predators for food and territory, leading to interesting dynamics within the animal kingdom.
Mythbusting: Honey Badger vs. Popular Beliefs
Contrary to popular belief, honey badgers are not relentless attackers. While they are formidable when threatened, they prefer to avoid confrontation. Dispelling myths about their aggression helps us appreciate the true nature of these intriguing creatures.
Fascinating Facts about Honey Badgers
- Honey badgers are resistant to snake venom, making them capable of surviving snake bites that would be fatal to other animals.
- They are excellent climbers and swimmers, showcasing their versatility in different terrains.
- Honey badgers have a keen sense of smell, aiding them in locating food sources over long distances.
Honey Badger’s Role in Ecosystem
As predators and scavengers, honey badgers play a crucial role in maintaining ecological balance. Their interactions with other species contribute to the overall health and dynamics of their ecosystems.
Different Species
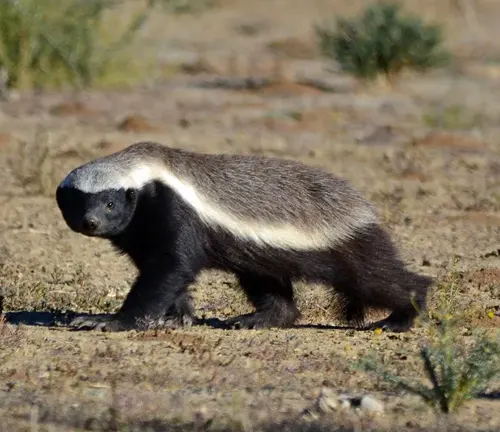
Mellivora capensis capensis
(Cape Honey Badger)
Found in Southern Africa, including South Africa, Namibia, and Botswana. This subspecies is known for its distinctive appearance and behaviors.

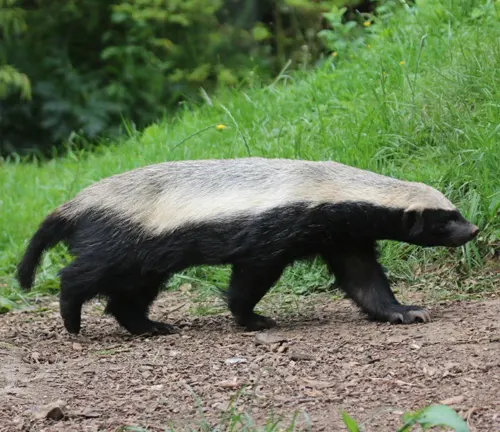
Mellivora capensis indica
(Indian Honey Badger)
Inhabits parts of the Indian subcontinent, including India and Nepal. The Indian honey badger may exhibit variations in its coat color and markings.

Frequently Asked Question (FAQs)
- What is a honey badger, and where are they found in the wild?
This question provides a basic introduction to honey badgers and their natural habitat. - Are honey badgers really immune to snake venom?
Addresses the commonly known fact about honey badgers and their resistance to snake bites. - How big do honey badgers typically get, and what do they look like?
Provides information about the physical characteristics and size of honey badgers. - What do honey badgers eat, and do they really eat honey?
Explains the diverse diet of honey badgers, including their occasional consumption of honey. - How do honey badgers defend themselves against predators?
Describes the defensive behaviors and adaptations that honey badgers employ when faced with threats. - Are honey badgers aggressive, and do they attack larger animals?
Clarifies misconceptions about honey badgers’ aggression and behavior toward larger predators. - What is the conservation status of honey badgers, and are they endangered?
Provides insights into the current conservation status of honey badgers and any associated threats. - Can honey badgers be kept as pets, and are they legal to own?
Addresses the feasibility and legality of keeping honey badgers as pets. - Do honey badgers live in groups or are they solitary animals?
Explores the social behavior of honey badgers, highlighting their predominantly solitary nature. - How do honey badgers contribute to the ecosystems they inhabit?
Discusses the ecological role and impact of honey badgers in their respective environments. - What are some interesting facts about honey badgers that people may not know?
Shares lesser-known or surprising facts about honey badgers, adding to their mystique. - Do honey badgers have any natural predators, and how do they cope with them?
Explores the interactions between honey badgers and potential predators in the wild. - How can I support honey badger conservation efforts?
Provides information on initiatives and actions individuals can take to contribute to honey badger conservation. - Are honey badgers related to other species, and what is their evolutionary history?
Offers insights into the evolutionary lineage and relationships of honey badgers with other species. - Can honey badgers be found in captivity, and are there any conservation programs for them?
Explores the presence of honey badgers in captivity and highlights any conservation programs focused on their well-being.














Leave your comment