Sumatran Rhinoceros
- February 13, 2024
- 0 comment
The Sumatran Rhinoceros, scientifically known as Dicerorhinus sumatrensis, is a critically endangered species native to Southeast Asia. Renowned for its unique appearance and solitary nature, this majestic creature once roamed across vast stretches of forests in countries like Sumatra and Borneo. However, due to relentless poaching for its prized horns and extensive habitat loss caused by human activities such as deforestation and agricultural expansion, the Sumatran Rhinoceros population has dwindled to alarming levels.
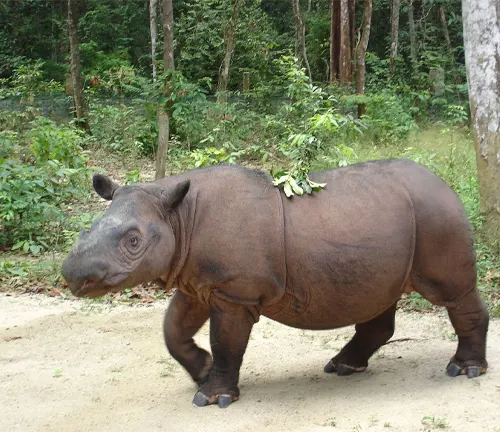

Distinctive features include its shaggy coat of reddish-brown to dark brown hair and two small horns, with the front horn being longer than the rear one. Despite conservation efforts aimed at protecting this iconic species, including captive breeding programs and habitat preservation initiatives, the future of the Sumatran Rhinoceros remains precarious. As one of the rarest large mammals on Earth, urgent action is needed to safeguard its existence and ensure its continued presence in the wild for generations to come.
| Attribute | Specification |
|---|---|
| Scientific Name | Dicerorhinus sumatrensis |
| Common Name | Sumatran Rhinoceros |
| Conservation Status | Critically Endangered |
| Habitat | Dense tropical rainforests, mountainous regions |
| Range | Sumatra and Borneo |
| Size | 1 to 1.5 meters (3 to 5 feet) tall at the shoulder |
| Weight | 500 to 1,000 kilograms (1,100 to 2,200 pounds) |
| Coat Color | Reddish-brown to dark brown |
| Horns | Two small horns, front horn longer than rear |
| Social Structure | Solitary |
| Lifespan | Approximately 30-45 years in the wild |
| Diet | Herbivorous, feeding on plants, fruits, and leaves |
| Reproduction | Gestation period of 15 to 16 months |
| Population Estimate | Fewer than 80 individuals in the wild |
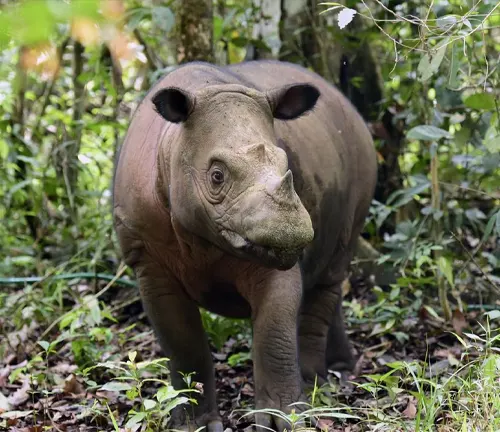

The Sumatran Rhinoceros, scientifically known as Dicerorhinus sumatrensis, is one of the world’s most critically endangered rhinoceros species. This majestic creature once roamed across Southeast Asia, but its population has drastically declined over the years due to various threats.
Physical Characteristics
Size and Weight
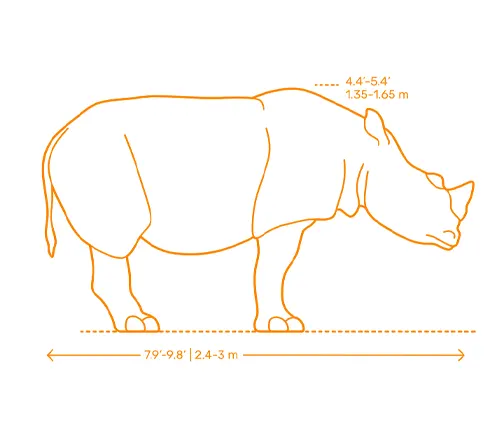
Sumatran Rhinoceroses are the smallest of the living rhinoceros species. They typically weigh between 500 to 1,000 kilograms (1,100 to 2,200 pounds) and stand about 1 to 1.5 meters (3 to 5 feet) tall at the shoulder. Despite their relatively small size, they are powerful animals with a robust build.
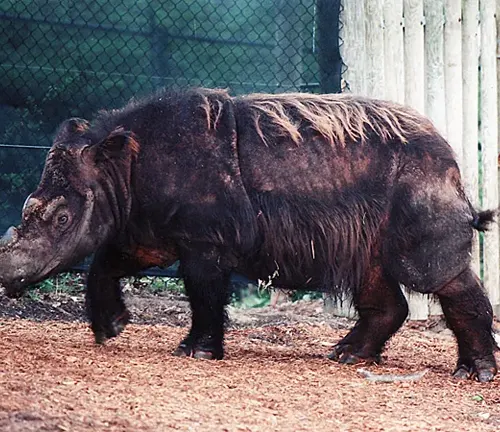

Unique Features
One distinguishing feature of the Sumatran Rhinoceros is its hairy body, which sets it apart from other rhino species. They have reddish-brown to dark brown skin covered in coarse hair, giving them a shaggy appearance. Another unique characteristic is their two small horns, with the front horn being longer than the rear one.
Habitat and Distribution
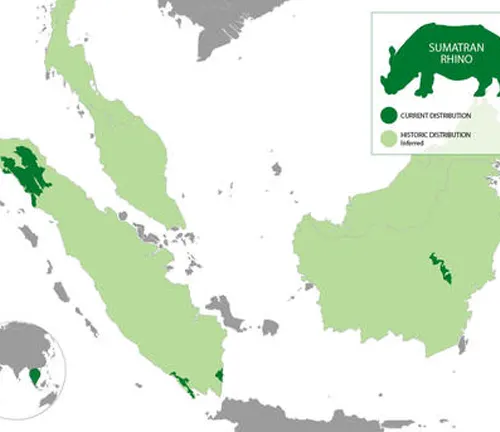
Sumatran Rhinoceroses inhabit dense tropical rainforests and mountainous regions in Sumatra and Borneo. They were once found in various parts of Southeast Asia, including Thailand, Malaysia, Indonesia, and Myanmar. However, due to habitat loss and fragmentation, their range has significantly shrunk, and they are now primarily confined to isolated pockets of forest.
Diet and Feeding Habits
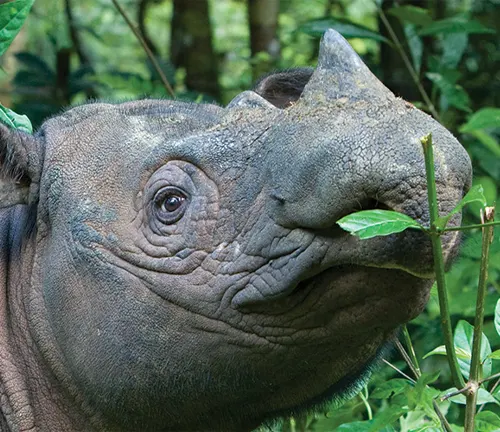

These rhinos are primarily herbivores, feeding on a variety of plants, fruits, and leaves. They are known to have a selective diet, preferring young saplings, shoots, and twigs. Despite their large size, they have a relatively low metabolic rate and do not require large amounts of food to sustain themselves.
Behavior and Social Structure
Solitary Nature
Sumatran Rhinoceroses are solitary animals, preferring to roam and forage alone in their forest habitats. They have large home ranges, which they mark with scent markings to communicate with other rhinos.
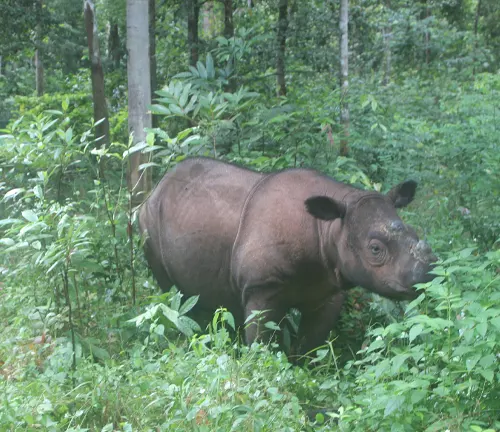
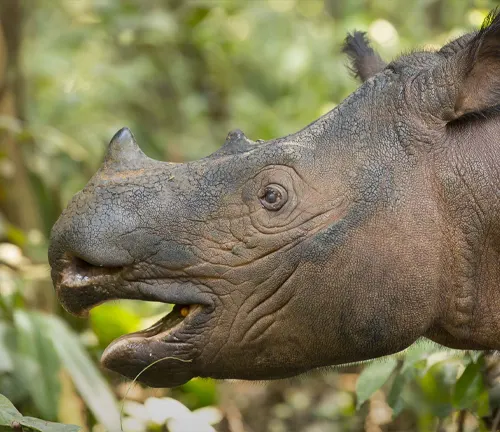


Communication Methods
Although solitary, Sumatran Rhinoceroses use various methods to communicate with each other, including vocalizations, body language, and scent marking. They produce a variety of vocal sounds, including snorts, grunts, and squeals, to convey different messages.
Reproduction and Lifecycle
Sumatran Rhinoceroses have a relatively long gestation period of around 15 to 16 months. Females give birth to a single calf, which they nurture and protect for several years. The calves stay with their mothers until they reach maturity, usually around 6 to 7 years old.
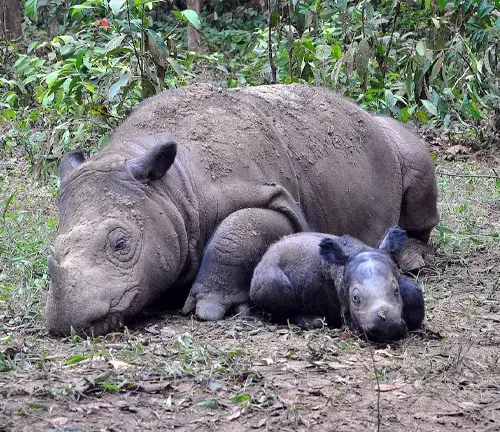
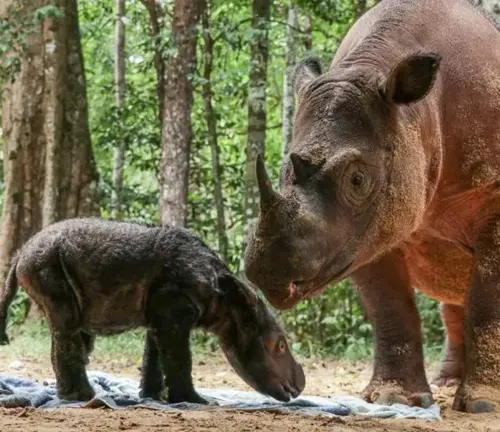


Cultural Significance
In local cultures and traditions, the Sumatran Rhinoceros holds significant symbolic value. It is often revered as a symbol of strength, resilience, and harmony with nature. In some indigenous communities, rhinos are considered sacred animals and play a vital role in folklore and rituals.
Importance of Sumatran Rhinoceros in Ecosystem
Sumatran Rhinoceroses play a crucial role in maintaining the health and balance of their forest ecosystems. As herbivores, they help regulate plant populations and shape the structure of the forest understory through their feeding habits. Additionally, their browsing behavior creates pathways for other smaller animals and contributes to seed dispersal.
Challenges Facing Conservation
Poaching
One of the most significant threats to the survival of the Sumatran Rhinoceros is poaching for their horns, which are highly prized in traditional Asian medicine markets. Despite international bans on the trade of rhino horns, illegal poaching continues to persist, driven by high demand and lucrative black markets.
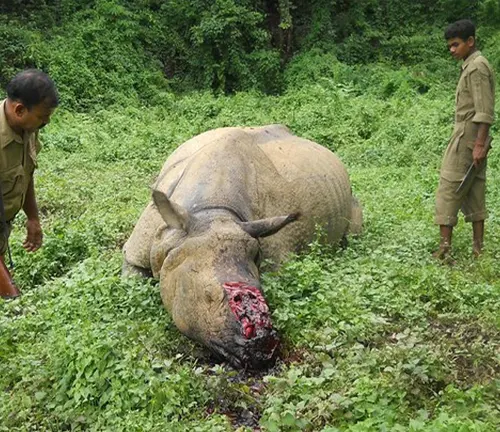
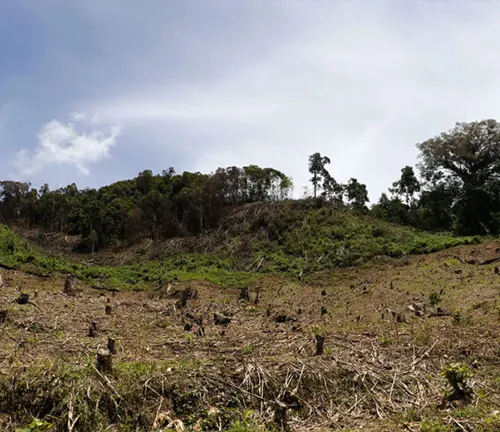


Habitat Loss
The rapid deforestation and degradation of their natural habitat pose a significant threat to Sumatran Rhinoceros populations. Forest clearance for agriculture, logging, and human settlement has resulted in the fragmentation and isolation of rhino habitats, making it difficult for populations to interbreed and maintain genetic diversity.
Government and NGO Initiatives
Governments, conservation organizations, and local communities are working together to address the challenges facing Sumatran Rhinoceros conservation. Initiatives such as habitat protection, law enforcement, community engagement, and public awareness campaigns are essential components of conservation efforts.
Success Stories in Conservation
Despite the daunting challenges, there have been some success stories in Sumatran Rhinoceros conservation. Captive breeding programs have successfully bred rhinos in captivity, contributing to the preservation of the species’ genetic diversity. Additionally, concerted efforts to protect and restore critical habitat areas have shown promising results in stabilizing rhino populations.
Public Awareness and Education
Raising public awareness about the plight of the Sumatran Rhinoceros is crucial for garnering support for conservation efforts. Education programs, outreach initiatives, and media campaigns play a vital role in informing the public about the importance of preserving these iconic animals and their habitats.
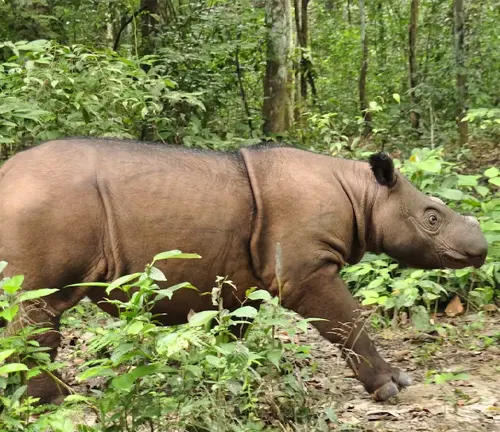
Different Species
The Sumatran Rhinoceros (Dicerorhinus sumatrensis) is a distinct species within the rhinoceros family, Rhinocerotidae.

Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
- What is the Sumatran Rhinoceros?
The Sumatran Rhinoceros (Dicerorhinus sumatrensis) is a species of rhinoceros native to Southeast Asia. It is one of the smallest rhinoceros species and is known for its distinctive hairy appearance. - Where does the Sumatran Rhinoceros live?
Sumatran Rhinoceroses primarily inhabit dense tropical rainforests and mountainous regions in Sumatra and Borneo. - How many Sumatran Rhinoceroses are left in the wild?
It is estimated that there are fewer than 80 Sumatran Rhinoceroses left in the wild, making them one of the rarest large mammals on Earth. - Why is the Sumatran Rhinoceros endangered?
The Sumatran Rhinoceros is endangered due to habitat loss, poaching for its horns, and human encroachment on its natural habitat. - What are the main threats to the Sumatran Rhinoceros?
The main threats to the Sumatran Rhinoceros include habitat loss and fragmentation, poaching for its horns, and human-wildlife conflict. - How big is a Sumatran Rhinoceros?
Sumatran Rhinoceroses typically weigh between 500 to 1,000 kilograms (1,100 to 2,200 pounds) and stand about 1 to 1.5 meters (3 to 5 feet) tall at the shoulder. - What does a Sumatran Rhinoceros eat?
Sumatran Rhinoceroses are herbivores and feed on a variety of plants, fruits, and leaves. They are known to have a selective diet, preferring young saplings, shoots, and twigs. - How long does a Sumatran Rhinoceros live?
Sumatran Rhinoceroses have a lifespan of approximately 30 to 45 years in the wild. - What are the unique features of the Sumatran Rhinoceros?
Unique features of the Sumatran Rhinoceros include its shaggy coat of reddish-brown to dark brown hair and two small horns, with the front horn being longer than the rear one. - What conservation efforts are being made to save the Sumatran Rhinoceros?
Conservation efforts include habitat conservation, anti-poaching measures, captive breeding programs, and public awareness campaigns. - Are Sumatran Rhinoceroses aggressive towards humans?
Sumatran Rhinoceroses are generally shy and reclusive animals and are not known to be aggressive towards humans unless provoked or threatened. - What is the difference between the Sumatran Rhinoceros and other rhinoceros species?
The Sumatran Rhinoceros is smaller in size compared to other rhinoceros species and has a distinctively hairy appearance. - How do Sumatran Rhinoceroses communicate with each other?
Sumatran Rhinoceroses communicate with each other through vocalizations, body language, and scent marking. - Are there any successful captive breeding programs for Sumatran Rhinoceroses?
Yes, there have been successful captive breeding programs aimed at increasing the population of Sumatran Rhinoceroses and preserving their genetic diversity. - What role does the Sumatran Rhinoceros play in its ecosystem?
Sumatran Rhinoceroses play a crucial role in maintaining the health and balance of their forest ecosystems through their feeding habits and browsing behavior. - Can Sumatran Rhinoceroses be reintroduced into the wild successfully?
Reintroducing Sumatran Rhinoceroses into the wild successfully requires careful planning, habitat restoration, and addressing the threats that led to their decline in the first place. - How can individuals help in the conservation of Sumatran Rhinoceroses?
Individuals can support conservation efforts by raising awareness, supporting reputable conservation organizations, and advocating for stronger laws to protect endangered species. - What is the historical significance of the Sumatran Rhinoceros in local cultures?
The Sumatran Rhinoceros holds significant symbolic value in local cultures and traditions, often revered as a symbol of strength, resilience, and harmony with nature.














Leave your comment