Amazon Tree Boa
- December 17, 2023
- 0 comment
The Amazon Tree Boa, scientifically known as Corallus hortulanus, is a striking and arboreal snake species native to the rain forests of South America, spanning regions such as the Amazon Basin and the Guiana Shield. Renowned for its vibrant coloration and unique patterning, these boas exhibit a captivating mix of earthy browns, vivid greens, and bold reds, which serves as both camouflage in the dense vegetation and a visual spectacle for observers.
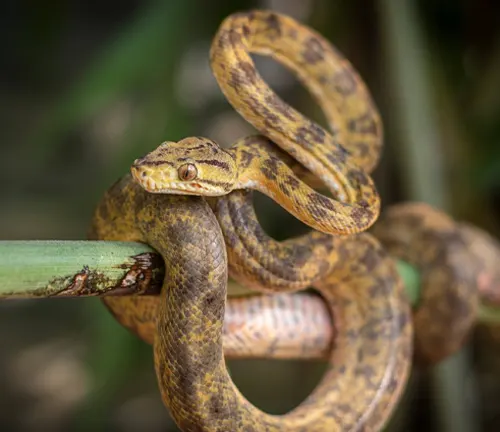
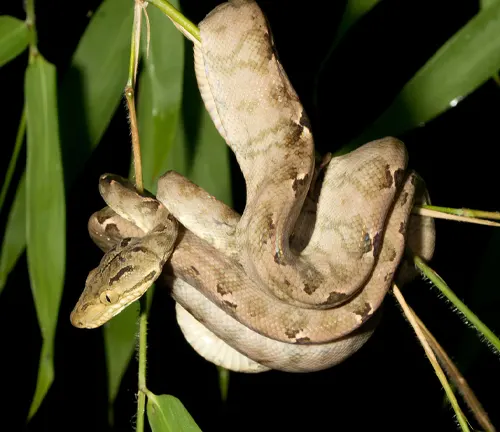


With an average length of 4 to 6 feet, though some individuals can surpass this range, the Amazon Tree Boa is equipped with a prehensile tail and a sleek body, enabling it to navigate the treetops with remarkable agility. A nocturnal hunter, it primarily feeds on small mammals and birds, ambushing them from above. This species plays a crucial role in maintaining ecological balance within its habitat.
Despite their visually striking appearance, these boas are often elusive, blending seamlessly into their surroundings. However, they are occasionally encountered by herpetologists and wildlife enthusiasts, who marvel at the intricate beauty and ecological significance of the Amazon Tree Boa in the heart of the lush South American rain forests.
| Characteristic | Details |
|---|---|
| Scientific Name | Corallus hortulanus |
| Habitat | Rainforests of South America, including the Amazon Basin and the Guiana Shield |
| Size | Average length of 4 to 6 feet, with some individuals exceeding this range |
| Coloration | Vibrant mix of earthy browns, vivid greens, and bold reds |
| Body Structure | Sleek and arboreal with a prehensile tail |
| Movement | Agile and adept at navigating treetops |
| Nocturnal Behavior | Primarily active during the night |
| Diet | Feeds on small mammals and birds, often ambushing prey from above |
| Ecological Role | Plays a crucial role in maintaining ecological balance by controlling small mammal and bird populations |
| Camouflage | Excellent at blending into its surroundings |
| Encounters | Elusive, but occasionally observed by herpetologists and wildlife enthusiasts |
| Geographic Range | Native to South America, particularly in rainforest regions |
| Conservation Status | Varies, but some populations may face threats due to habitat loss and collection for the pet trade |
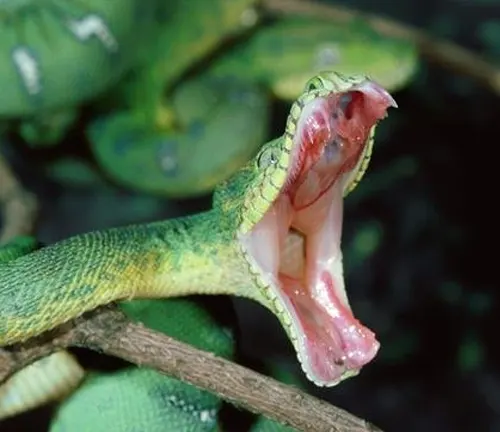
Venomous or Not Venomous?
One of the intriguing aspects of the Amazon Tree Boa is the ongoing debate surrounding its venomous nature. Despite being a constrictor and not possessing venom glands, its powerful bite and potential for infection have led to misconceptions. Exploring the nuances of this topic sheds light on the fascinating adaptations that make this species an apex predator without relying on venom for subduing its prey.

Ecological Importance
Delving into the ecological importance of the Amazon Tree Boa reveals its crucial role in maintaining balance within the rainforest ecosystems. As a nocturnal hunter, these boas help control populations of small mammals and birds, preventing unchecked proliferation that could disrupt the delicate ecological equilibrium of their habitat.
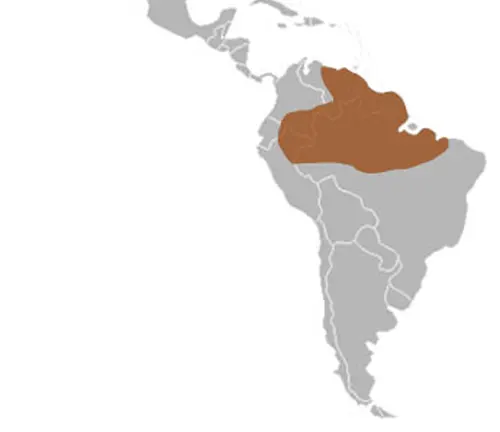
Habitat
The Amazon Tree Boa’s habitat spans the sprawling rain forests of South America, including the iconic Amazon Basin and the bio diverse Guiana Shield. Its preference for high, thick branches and dense vegetation showcases its remarkable adaptability to the challenging conditions of the treetops.
Behaviour
Equipped with a prehensile tail and a sleek body, the Amazon Tree Boa exhibits agile and adept behaviour, navigating the treetops with remarkable skill. Understanding its behaviour provides insights into its elusive nature, as well as its hunting strategies, which often involve ambushing prey from above under the cover of darkness.
Art and Culture
The Amazon Tree Boa has left an indelible mark on the art and culture of the indigenous communities inhabiting the rain forests. Its vibrant colours and unique patterns frequently find representation in traditional artwork and folklore, symbolising both the beauty and the mysteries of the dense jungles.
Survival
Survival in the challenging rain forest environment requires a set of unique adaptations. The Amazon Tree Boa’s ability to blend into its surroundings, coupled with its nocturnal habits, showcases the evolutionary traits that contribute to its long-term survival in a habitat teeming with life and competition.

Conservation
As with many species inhabiting rain forests, the Amazon Tree Boa faces threats to its existence, primarily due to habitat loss and collection for the pet trade. Exploring conservation efforts aimed at protecting these fascinating creatures and their fragile ecosystems becomes imperative for ensuring their continued survival.
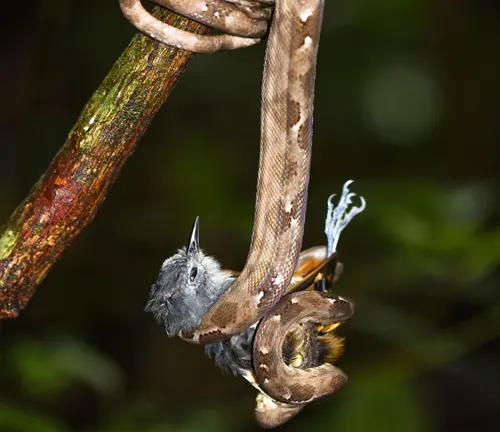

Common Food
A closer look at the Amazon Tree Boa’s diet reveals its preference for small mammals and birds. Understanding its feeding habits provides insights into the delicate balance of predator-prey relationships within the rain forest, highlighting the interconnections of its ecosystem.
Benefits
Beyond its role in maintaining ecological balance, the Amazon Tree Boa offers additional benefits to the rain forest. Its presence contributes to the regulation of insect populations, thereby indirectly benefiting the flora and fauna that form the intricate web of life within this biodiversity hot spot.
Different Species
Corallus hortulanus hortulanus
This is the nominate subspecies, representing the Amazon Tree Boa found in the Amazon Basin. It is known for its vibrant coloration and is often the one referred to when discussing the general characteristics of the species.


Corallus hortulanus annulatus
Found in the region of Venezuela, this subspecies is characterised by distinct Annunciations (ring-like patterns) on its body. The markings contribute to its unique appearance.
Corallus hortulanus cooki
This subspecies is found in the eastern part of the Amazon Basin, including parts of Brazil. It exhibits variations in coloration and patterning, often with a mix of earthy tones and vivid greens.
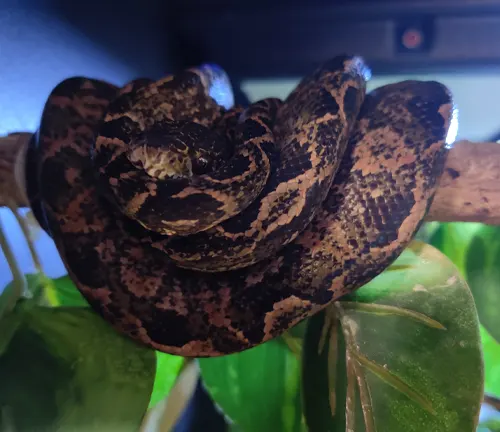
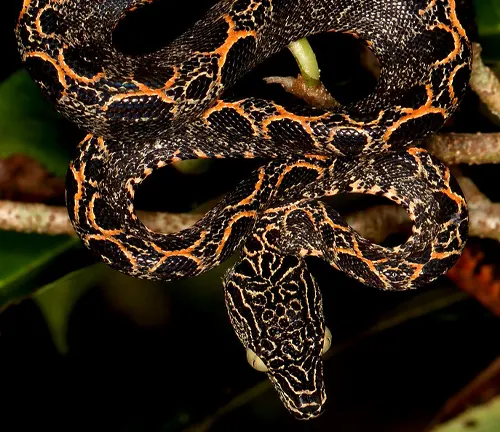


Corallus hortulanus osbornei
Native to the Guiana Shield region, including areas of Guyana and Suriname, this subspecies is adapted to the diverse rain forest habitats in that particular geographic area.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the Amazon Tree Boa captivates not only with its botanical beauty but also with its ecological significance. From its vibrant colours to its nocturnal habits, this species weaves itself into the intricate tapestry of the South American rain forests, showcasing the delicate balance that defines life in one of the planet’s most diverse ecosystems. As we explore and appreciate the many facets of the Amazon Tree Boa, we gain a deeper understanding of the importance of conservation efforts in preserving the wonders of our natural world.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
- Are Amazon Tree Boas venomous?
No, Amazon Tree Boas are not venomous. They are constrictors, relying on powerful constriction to subdue their prey rather than venom. - What is the average size of an Amazon Tree Boa?
Amazon Tree Boas typically have an average length of 4 to 6 feet, although some individuals can exceed this range. - Where are Amazon Tree Boas found in the wild?
They are native to the rain forests of South America, including the Amazon Basin and the Guiana Shield. - What do Amazon Tree Boas eat?
They primarily feed on small mammals and birds. Their hunting strategy often involves ambushing prey from above. - How do Amazon Tree Boas move in their habitat?
Amazon Tree Boas are arboreal and have a prehensile tail, allowing them to navigate the treetops with agility. - Are Amazon Tree Boas dangerous to humans?While not venomous, Amazon Tree Boas can bite if they feel threatened. The bites are generally not dangerous, but they can cause infection if not properly treated.
- What is the significance of their vibrant coloration?
The vibrant colors of Amazon Tree Boas serve as both camouflage in the dense vegetation and a visual spectacle. The patterns help them blend into their surroundings. - Do Amazon Tree Boas make good pets?
Keeping Amazon Tree Boas as pets requires specific care and expertise. They have specific habitat and dietary needs, and potential owners should research thoroughly before considering them as pets. - How do Amazon Tree Boas reproduce?
They are ovoviviparous, meaning the females give birth to live young. The gestation period is around six months, and the number of offspring can vary. - Are there different species of Amazon Tree Boas?
Yes, the Amazon Tree Boa (Corallus hortulanus) is a species complex with several recognised subspecies, each adapted to different regions within their native range. - What is their role in the ecosystem?
Amazon Tree Boas play a crucial role in maintaining ecological balance by controlling populations of small mammals and birds, thus preventing overpopulation and potential disruptions to the ecosystem. - Are there conservation concerns for Amazon Tree Boas?
Yes, like many species in the rain forest, Amazon Tree Boas face threats such as habitat loss and collection for the pet trade. Conservation efforts are important to ensure their survival and the preservation of their ecosystems.














Leave your comment