European Pond Turtle
- April 3, 2024
- 0 comment
The European Pond Turtle, scientifically known as Emys orbicularis, is an intriguing reptile species native to various regions across Europe. Renowned for its distinct appearance and ecological significance, this species has captured the interest of scientists and nature enthusiasts alike. With a moderate size and a shell adorned with intricate patterns, the European Pond Turtle possesses a unique charm. It favors aquatic habitats such as marshes, ponds, lakes, and slow-moving rivers, where it can often be found foraging for its omnivorous diet consisting of aquatic plants, insects, small fish, and amphibians. During the breeding season, females lay their eggs in sandy or gravelly substrates near water bodies, contributing to the continuation of their species
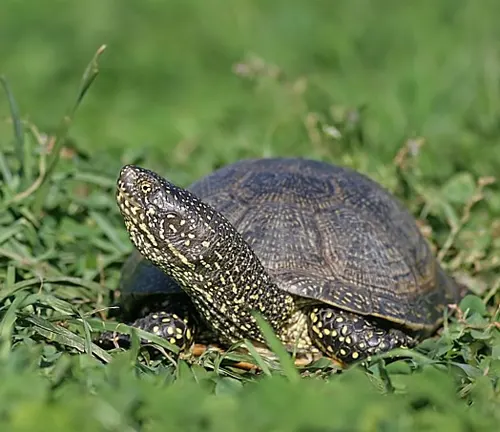

Despite its widespread distribution, the European Pond Turtle faces various threats, including habitat destruction, pollution, and illegal trade, leading to its vulnerable conservation status. Conservation efforts are underway to safeguard and restore its habitats, emphasizing the importance of preserving this remarkable species for future generations to appreciate and admire
| Specification | Description |
|---|---|
| Scientific Name | Emys orbicularis |
| Common Name | European Pond Turtle |
| Size | Moderate, typically 20 to 30 centimeters in length |
| Weight | Varies, typically lightweight |
| Shell Morphology | Rounded shell with intricate patterns of various colors |
| Habitat | Marshes, ponds, lakes, slow-moving rivers |
| Diet | Omnivorous, feeding on aquatic plants, insects, small fish, and amphibians |
| Reproduction | Oviparous, females lay eggs in sandy or gravelly substrates near water bodies during the breeding season |
| Conservation Status | Vulnerable due to habitat loss, pollution, and illegal trade |
| Threats | Habitat destruction, pollution, illegal trade |
| Lifespan | Several decades, typically 30 to 50 years or more |
European Pond Turtle: A Fascinating Species of Europe
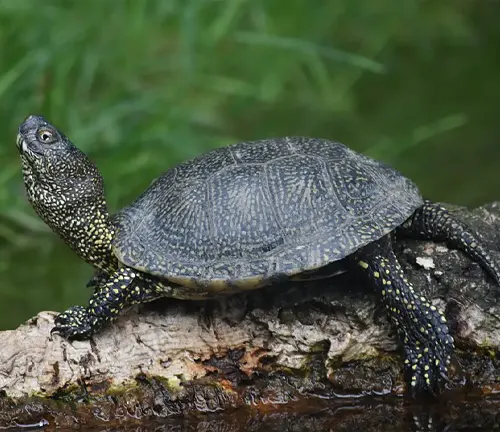

The European Pond Turtle, scientifically known as Emys orbicularis, is a captivating reptile species native to various regions of Europe. With its distinct features and ecological significance, this species has garnered attention from both scientists and nature enthusiasts. Let’s delve into the world of the European Pond Turtle to understand its characteristics, habitat, conservation status, and more.
History and Distribution
The history and distribution of the European Pond Turtle, span across various regions of Europe. These fascinating reptiles have a rich evolutionary history, with fossil records indicating their presence dating back millions of years. Over time, they have adapted to diverse habitats, ranging from marshes and ponds to slow-moving rivers and lakes. European Pond Turtles can be found across much of Europe, including countries such as France, Spain, Italy, Germany, and the United Kingdom. Their distribution may vary slightly depending on local environmental conditions and habitat availability. Despite facing challenges such as habitat loss and fragmentation, European Pond Turtles persist in many regions, serving as an integral part of European ecosystems.
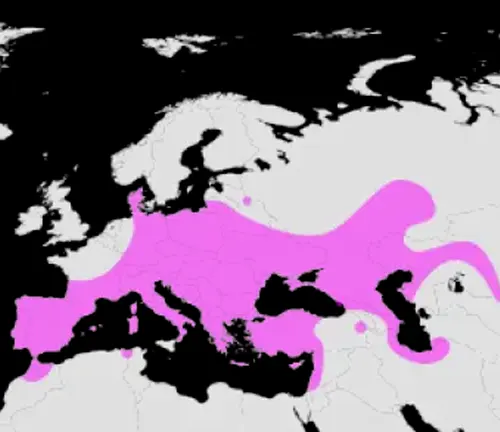
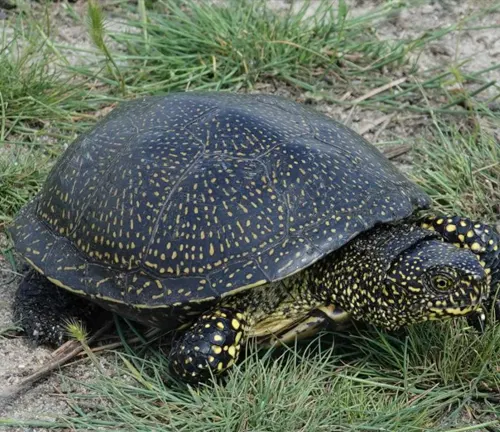
Physical Characteristics
The European Pond Turtle boasts a distinctive set of physical features that set it apart from other turtle species. One of its most notable characteristics is its moderate size, typically ranging from 20 to 30 centimeters in length. These turtles have a rounded shell, known as a carapace, which varies in coloration and may feature intricate patterns of yellow, brown, and green hues. Additionally, their shells are relatively flat compared to other turtle species, allowing them to navigate through aquatic environments with ease. European Pond Turtles also possess webbed feet, which aid in swimming and maneuvering underwater.

Their heads are equipped with strong jaws and sharp beaks, adapted for capturing prey and consuming a varied diet of aquatic plants, insects, small fish, and amphibians. Overall, the physical characteristics of the European Pond Turtle contribute to its success as a semi-aquatic species inhabiting wetland habitats across Europe.
Habitat and Behavior
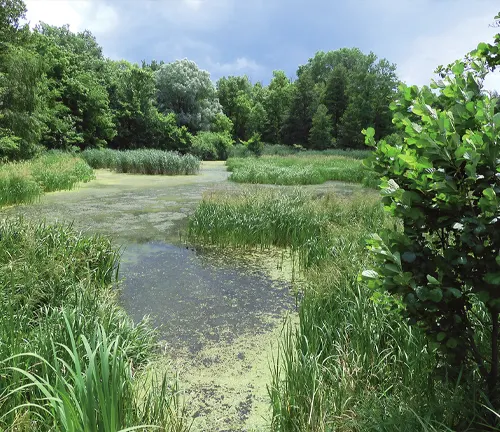
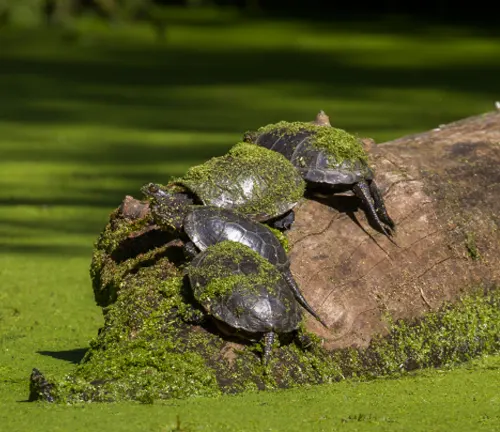


The European Pond Turtle is predominantly found in freshwater habitats throughout Europe. These turtles exhibit a preference for environments such as ponds, marshes, lakes, and slow-moving rivers, where they can find ample vegetation and access to both land and water. European Pond Turtles are well-adapted to their semi-aquatic lifestyle, spending much of their time basking on rocks or logs near the water’s edge and foraging for food underwater.
In terms of behavior, European Pond Turtles are relatively solitary creatures, although they may congregate in areas with abundant resources or during the breeding season. They are primarily diurnal, meaning they are most active during the daytime hours. During warmer months, they can often be seen sunbathing on rocks or logs to regulate their body temperature.
Conservation Status
The conservation status of the European Pond Turtle varies across its range, but it is generally considered vulnerable or threatened in many areas. Habitat loss, degradation, and fragmentation are significant threats to this species, as wetlands and freshwater habitats continue to be impacted by urbanization, agriculture, and infrastructure development. Pollution, including water pollution and habitat degradation, also poses a significant risk to European Pond Turtles, as it can affect water quality and the availability of prey species. Additionally, illegal collection for the pet trade and accidental capture in fishing gear contribute to the decline of wild populations.
Interaction with Humans
European Pond Turtles often interact with humans in various ways, both positive and negative. In some regions, they are valued for their role in controlling insect populations and maintaining the health of aquatic ecosystems. However, human activities such as habitat destruction, pollution, and illegal collection pose significant threats to their survival. Conservation efforts aim to raise awareness about the importance of protecting European Pond Turtles and their habitats, as well as promoting responsible behavior to minimize negative impacts on wild populations.
Legal Protection and Regulations
Several laws and regulations are in place to protect European Pond Turtles and regulate human interactions with this species. In many countries, it is illegal to capture, possess, or trade European Pond Turtles without proper permits or licenses. Additionally, there may be restrictions on activities such as habitat alteration, pollution, and fishing practices that could harm turtle populations. Conservation organizations work closely with government agencies and local communities to enforce these regulations and ensure compliance with laws aimed at protecting European Pond Turtles and their habitats.
Challenges and Threats
The European Pond Turtle faces numerous challenges and threats to its survival in the wild. One of the primary threats is habitat loss and degradation, as wetlands and freshwater habitats continue to be impacted by urbanization, agricultural expansion, and infrastructure development. This loss of habitat fragments populations and reduces the availability of suitable nesting sites and foraging areas for European Pond Turtles.
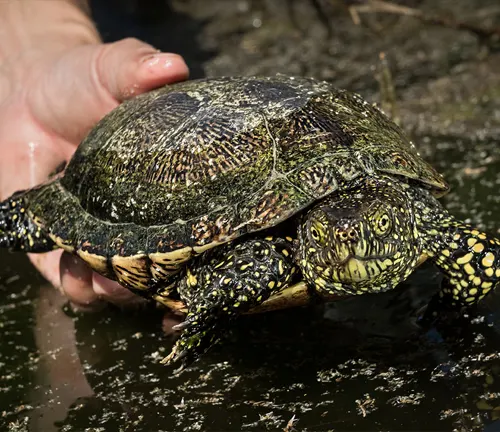

Pollution is another significant threat to European Pond Turtles, as water pollution from agricultural runoff, industrial discharge, and urban runoff can degrade water quality and harm aquatic ecosystems. Pollution can affect the availability of prey species and lead to the accumulation of toxins in turtle tissues, impacting their health and reproductive success.
Illegal collection for the pet trade is also a major threat to European Pond Turtles, as they are often sought after for use in the exotic pet market. Illegal harvesting of turtles from the wild can deplete populations and disrupt natural breeding patterns, further contributing to their decline.
Conservation Efforts
Conservation efforts for the European Pond Turtle encompass habitat restoration, captive breeding programs, and community engagement. By involving local communities and stakeholders, these initiatives aim to address the root causes of population decline and promote long-term sustainability.
Research and Studies
Scientific research plays a crucial role in understanding the ecology and behavior of the European Pond Turtle. Ongoing studies focus on population dynamics, genetic diversity, and the impact of human activities on their habitats.
Importance in Ecosystem
European Pond Turtles contribute to ecosystem functioning by regulating prey populations and facilitating nutrient cycling. Their presence indicates the overall health of wetland ecosystems and serves as an indicator of environmental quality.
Human Interaction and Coexistence
Efforts to mitigate human impacts on European Pond Turtles involve education, habitat restoration, and sustainable development practices. By fostering coexistence and promoting responsible behavior, we can ensure the long-term survival of these fascinating creatures.
Future Prospects
Despite the challenges ahead, there is hope for the conservation of the European Pond Turtle. Through collaborative efforts and innovative conservation strategies, we can secure a brighter future for this species and the ecosystems they inhabit.
Different Spieces
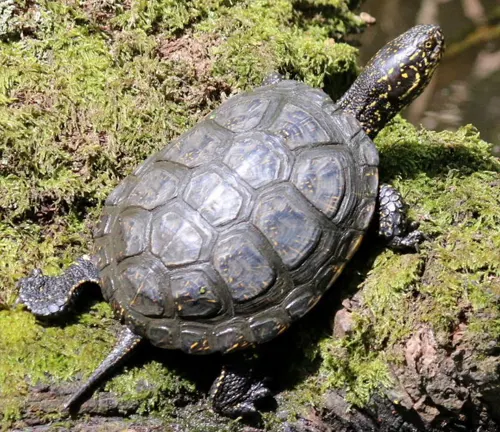
European Pond Turtle
(Emys orbicularis)
This is a species of semi-aquatic turtle found in various habitats across Europe, including ponds, marshes, and slow-moving rivers.
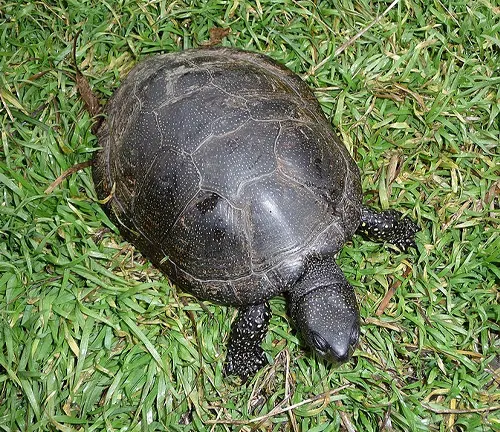


European Pond Terrapin
(Mauremys leprosa)
Also known as the Spanish Pond Terrapin, this species is found in southern Europe, particularly in Spain, Portugal, and parts of North Africa.
European Softshell Turtle
(Rafetus euphraticus)
Although primarily found in Asia, this softshell turtle species is known to inhabit parts of southeastern Europe, including Turkey and the Balkans.
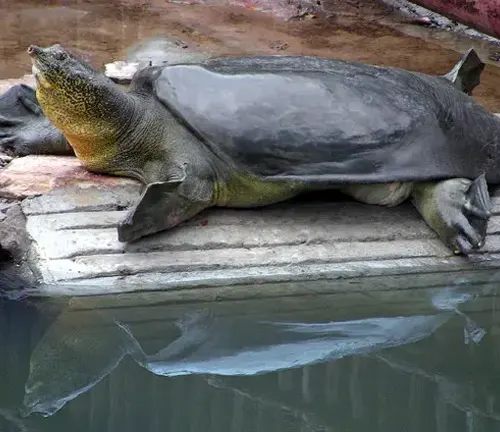
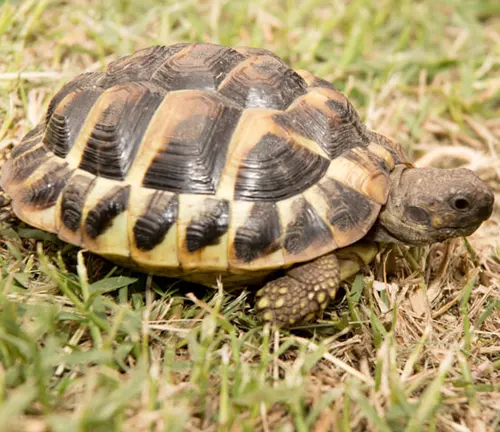


Hermann’s Tortoise
(Testudo hermanni)
While not a true turtle, Hermann’s Tortoise is a terrestrial species of tortoise native to southern Europe, particularly in Mediterranean regions.
Greek Tortoise
(Testudo graeca)
Another terrestrial tortoise species, the Greek Tortoise, is found in various habitats across Europe, including scrublands, grasslands, and rocky areas.
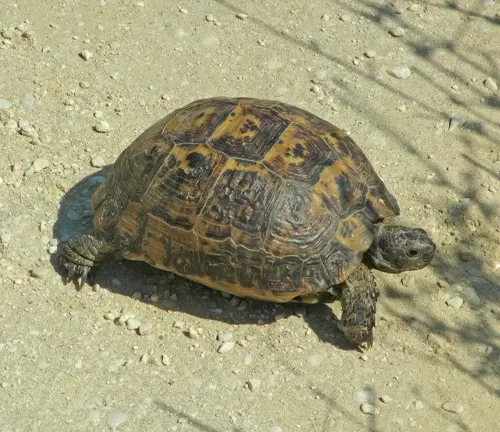

Frequently Asked Question (FAQs)
- How big do European Pond Turtles get?
This question seeks information about the size of the species. European Pond Turtles typically reach lengths of 20 to 30 centimeters when fully grown, although individual size may vary. - Are European Pond Turtles legal to keep as pets?
Many people wonder about the legality of owning European Pond Turtles as pets. Regulations regarding pet ownership of European Pond Turtles vary by region and may require permits or licenses. - What are the main threats to European Pond Turtles?
This question addresses concerns about the conservation of the species. European Pond Turtles face threats such as habitat loss, pollution, habitat degradation, illegal collection for the pet trade, and predation. - How do European Pond Turtles reproduce?
People often inquire about the reproductive behavior of the species. European Pond Turtles reproduce by laying eggs, with females typically laying their eggs in sandy or gravelly substrates near water bodies during the breeding season. - What are the differences between European Pond Turtles and other turtle species?
This question explores the distinctions between European Pond Turtles and other turtle species. Differences may include shell morphology, habitat preferences, diet, and behavior. - Can European Pond Turtles be kept in captivity?
Individuals interested in keeping European Pond Turtles as pets often ask about their suitability for captivity. While they can be kept in captivity under proper conditions, it’s essential to provide them with adequate space, habitat, and care. - Do European Pond Turtles require special care in captivity?
This question delves into the specific care requirements of European Pond Turtles when kept as pets. Proper care includes providing a suitable habitat with access to water, UV lighting, and a balanced diet. - How can I help conserve European Pond Turtles?
People interested in conservation often seek ways to contribute to the protection of European Pond Turtles. Conservation efforts may include supporting habitat restoration projects, reporting illegal activities, and raising awareness about the species’ plight. - What role do European Pond Turtles play in their ecosystems?
This question explores the ecological significance of European Pond Turtles. As omnivores, they play a vital role in maintaining ecosystem balance by controlling prey populations and facilitating nutrient cycling. - Are European Pond Turtles protected by law?
Individuals inquire about the legal protections afforded to European Pond Turtles. Depending on the region, these turtles may be protected under various conservation laws and regulations aimed at preserving their populations and habitats.














Leave your comment