Timber Rattlesnake
- December 17, 2023
- 0 comment
The Timber Rattlesnake, scientifically known as Crotalus horridus, is a venomous pit viper native to the eastern United States, particularly the deciduous forests and mixed woodlands of the Appalachian Mountains. Recognized for its distinctive appearance, the Timber Rattlesnake typically boasts a robust body covered in a pattern of dark, well-defined crossbands against a lighter background, providing effective camouflage in its natural habitat.
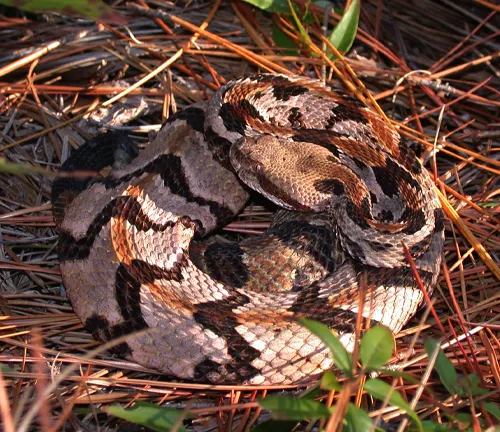
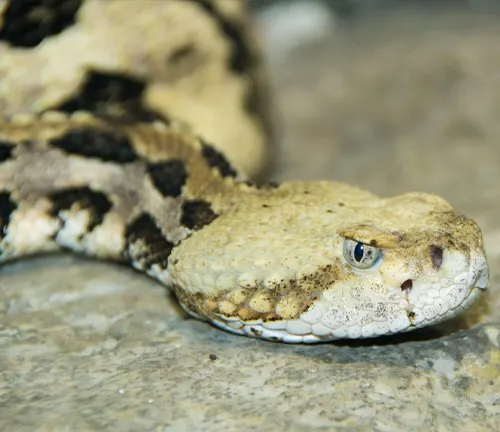


Its name is derived from the distinctive rattle located at the tip of its tail, which it uses as a warning signal when feeling threatened. This species plays a crucial role in maintaining ecological balance by controlling rodent populations, and it primarily preys on small mammals such as rodents and birds. While the Timber Rattlesnake’s venom is potent, it is generally not considered life-threatening to humans if prompt medical attention is sought.
Unfortunately, habitat loss, road mortality, and illegal collection pose significant threats to the survival of this species, leading to conservation concerns and efforts to protect its diminishing populations.
| Characteristic | Description |
|---|---|
| Scientific Name | Crotalus horridus |
| Family | Viperidae |
| Length | 3 to 5 feet (0.9 to 1.5 meters) |
| Weight | 1 to 2.5 pounds (0.45 to 1.13 kilograms) |
| Coloration | Dark crossbands on a lighter background |
| Body Shape | Stout and robust |
| Tail | Equipped with a rattle for warning |
| Venom | Hemotoxic, primarily affecting the circulatory system |
| Habitat | Deciduous forests, mixed woodlands, and mountains |
| Range | Eastern United States, particularly the Appalachians |
| Diet | Small mammals (rodents and birds) |
| Reproduction | Viviparous (giving birth to live young) |
| Conservation Status | Threatened due to habitat loss and human activities |
Venomous or Not Venomous?
A common question that surrounds the Timber Rattlesnake pertains to its venomous nature. While indeed possessing potent venom, this snake seldom poses a fatal threat to humans if proper medical attention is sought promptly. Understanding the nuances of its venomous capabilities is essential to dispel myths and foster a more accurate appreciation of this enigmatic creature.
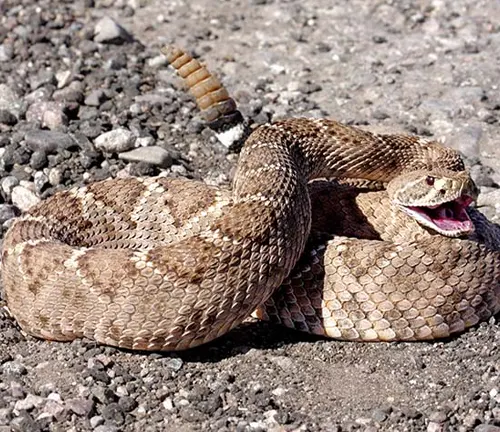

Ecological Importance
Beyond its fearsome reputation, the Timber Rattlesnake plays a pivotal role in maintaining ecological balance. Acting as nature’s pest controller, it helps manage rodent populations, thereby contributing to the health and equilibrium of its ecosystem. Recognizing the ecological importance of this species highlights the interconnectedness of all living organisms in a given habitat.
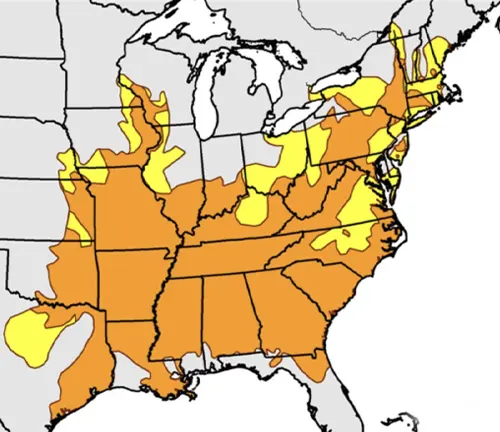
Habitat
The Timber Rattlesnake finds its niche in the eastern United States, predominantly dwelling in the Appalachian Mountains. Its habitat preference for deciduous forests and mixed woodlands underscores its adaptability to diverse environmental conditions. Exploring the specifics of its habitat provides insight into the geographical range crucial for its survival.
Behavior
Understanding the behavior of the Timber Rattlesnake is key to coexisting with this species. From the distinctive warning rattle at the tip of its tail to its hunting techniques, delving into the behavioral patterns of this serpent sheds light on its survival strategies and interactions with its environment.
Art And Culture
The Timber Rattlesnake has made its mark not only in nature but also in human art and culture. From indigenous folklore to contemporary symbolism, this snake has found a place in the cultural tapestry of various communities. Exploring the artistic and cultural significance of the Timber Rattlesnake reveals the enduring fascination humans have had with this intriguing creature.
Survival
Survival in the wild poses numerous challenges for the Timber Rattlesnake. Navigating threats such as habitat loss, road mortality, and illegal collection, this species constantly adapts to ensure its survival. Examining the strategies it employs to thrive in the face of adversity provides valuable insights into its resilience.
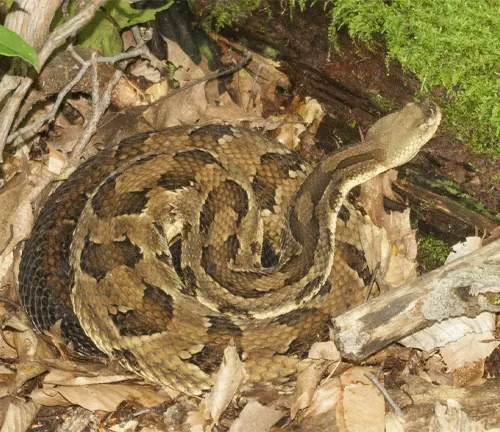

Conservation
With diminishing populations due to various anthropogenic factors, the conservation of the Timber Rattlesnake has become a pressing concern. Efforts to protect its habitats, raise awareness, and implement conservation measures are crucial for the continued existence of this species. Understanding the conservation challenges and initiatives sheds light on the broader picture of wildlife preservation.
Common Food
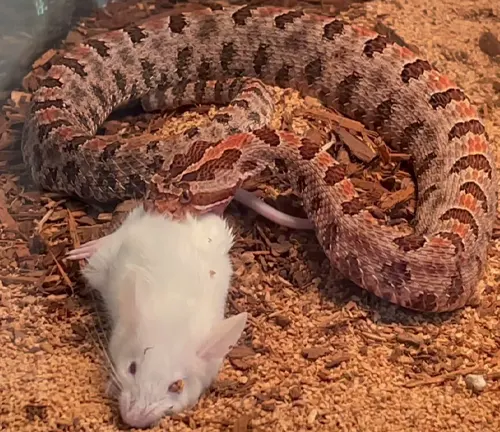

The diet of the Timber Rattlesnake primarily consists of small mammals such as rodents and birds. Exploring its feeding habits offers a glimpse into the predator-prey dynamics that shape its role in the ecosystem. Unraveling the intricacies of its diet provides valuable information for conservationists and researchers.
Benefits
Contrary to misconceptions, the Timber Rattlesnake brings tangible benefits to its environment. By controlling rodent populations, it aids in preventing the overabundance of pests that could negatively impact both flora and fauna. Acknowledging the benefits of this species contributes to a more holistic understanding of its ecological significance.
Different Species
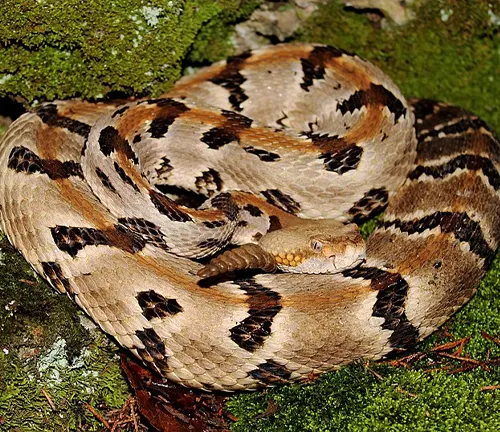

Crotalus horridus horridus
(Northern Timber Rattlesnake)
Found in the northern part of the Timber Rattlesnake’s range, including areas in the northeastern United States.
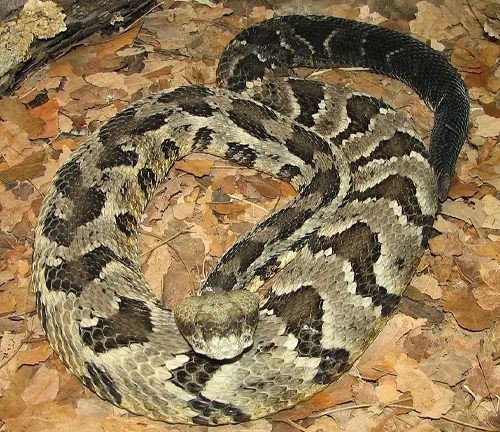
Crotalus horridus atricaudatus
(Southern Timber Rattlesnake)
Inhabits the southern part of the species’ range, including parts of the southeastern United States.
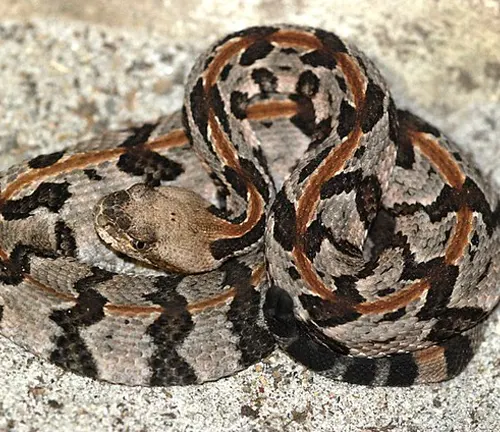


Crotalus horridus lutosus
(Canebrake Rattlesnake)
Found in the southeastern United States, this subspecies is often distinguished by a lighter coloration and is sometimes considered a distinct species, Crotalus lutosus.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the Timber Rattlesnake is a captivating creature that weaves its presence through the intricate threads of botanical beauty, ecological balance, and cultural symbolism. By dispelling myths, appreciating its role in nature, and actively participating in conservation efforts, we can ensure that this remarkable species continues to thrive in the rich tapestry of biodiversity that characterises the eastern United States.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1. Are Timber Rattlesnakes dangerous to humans?
While Timber Rattlesnakes are venomous, they are generally not considered lethal to humans if treated promptly. Most bites result from the snake feeling threatened and attempting to defend itself.
2. How can I identify a Timber Rattlesnake?
Timber Rattlesnakes are characterised by a robust body with dark cross bands against a lighter background. The tail is equipped with a rattle, and they are typically found in deciduous forests and mixed woodlands.
3. What is the purpose of the rattling sound?
The rattling sound produced by the Timber Rattlesnake serves as a warning signal to potential threats. It’s a way for the snake to communicate its presence and deter predators or humans from approaching.
4. Do Timber Rattlesnakes make good pets?
Keeping Timber Rattlesnakes as pets is not recommended. They have specific habitat and dietary requirements that are challenging to meet in captivity. Additionally, it may be illegal to keep them as pets in some regions.
5. What is the ecological role of Timber Rattlesnakes?
Timber Rattlesnakes play a crucial role in controlling rodent populations, contributing to the overall health and balance of their ecosystems.
6. How can I avoid snakebites when hiking in areas with Timber Rattlesnakes?
To reduce the risk of snakebites, stay on designated trails, wear sturdy boots, and be cautious when reaching into areas where a snake could be hidden. Be aware of your surroundings and listen for rattling sounds.
7. Are Timber Rattlesnakes endangered?
Timber Rattlesnakes face conservation concerns due to habitat loss, road mortality, and illegal collection. While they may not be classified as endangered, various populations are considered threatened, and conservation efforts are underway.
8. What should I do if bitten by a Timber Rattlesnake?
Seek immediate medical attention if bitten by a Timber Rattlesnake. Do not attempt to suck out the venom or apply a tourniquet. Keeping calm and getting to a healthcare facility as quickly as possible is crucial.
9. Can Timber Rattlesnakes be found in urban areas?
While Timber Rattlesnakes prefer natural habitats, instances of them being found in suburban or urban areas are possible, especially if those areas are near suitable habitats.
10. How can I contribute to Timber Rattlesnake conservation?
Support conservation organisations working to protect snake habitats, follow responsible outdoor practices to minimise impact, and participate in educational programs to raise awareness about the importance of these species in the ecosystem.














Leave your comment