Western Coral Snake
- December 13, 2023
- 0 comment
The Western Coral Snake, scientifically known as Micruroides euryxanthus, is a venomous snake native to the southwestern United States and Mexico. This slender serpent is characterized by its striking coloration, featuring vibrant bands of red, yellow, and black along its body.
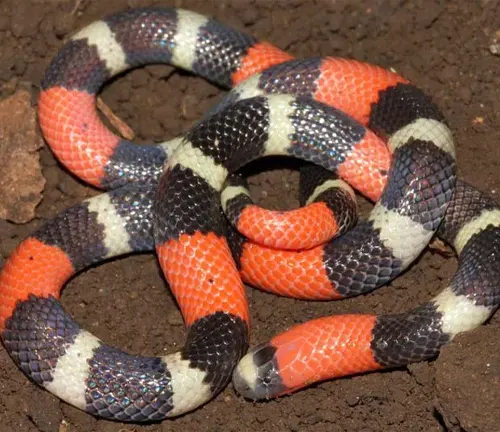
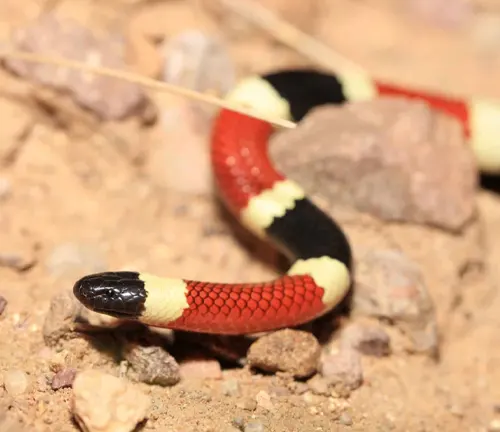


Often confused with non-venomous coral snake mimics, the Western Coral Snake can be distinguished by the order of its colored bands—red touching yellow, then black. Typically measuring around 18 to 30 inches in length, this species possesses a potent neurotoxic venom that affects the nervous system of its prey. Despite its venomous nature, the Western Coral Snake is considered relatively docile and rarely poses a threat to humans.
Its habitat preference includes desert scrub lands, grasslands, and woodlands, where it hunts small reptiles and amphibians. Conservation efforts are crucial for the Western Coral Snake, as its population faces threats from habitat loss and human encroachment. Studying and understanding this enigmatic species are essential for preserving the delicate balance of ecosystems it inhabits.
| Characteristic | Description |
|---|---|
| Scientific Name | Micruroides euryxanthus |
| Common Name | Western Coral Snake |
| Length | 18 to 30 inches |
| Coloration | Bands of red, yellow, and black |
| Color Pattern | Red touching yellow, then black (Warning colors) |
| Venom | Neurotoxic |
| Venom Potency | Potent, affecting the nervous system |
| Diet | Small reptiles and amphibians |
| Habitat | Desert scrublands, grasslands, woodlands |
| Behaviour | Generally docile, poses little threat to humans |
| Conservation Status | Faces threats from habitat loss and human impact |
| Range | Southwestern United States and Mexico |
Venomous or Not Venomous?
One of the captivating mysteries surrounding the Western Coral Snake is its venomous nature. Distinguished by the order of its coloured bands — red touching yellow, then black — the snake’s warning colours often prompt questions about its potential danger to humans. Exploring the intricacies of its venom and understanding its impact on the ecosystem contributes to a more nuanced perspective on this enigmatic species.
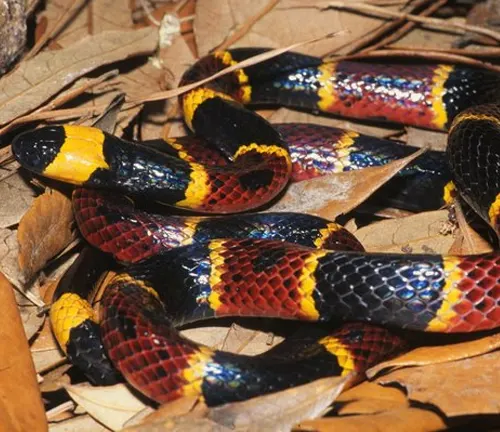

Ecological Importance
The Western Coral Snake plays a crucial role in maintaining ecological balance in its native habitat. As a predator, it helps control populations of small reptiles and amphibians, contributing to the overall health of the ecosystem. Studying its ecological importance sheds light on the intricate web of relationships within its habitat and the potential consequences of its decline.
Habitat
Adapting to a variety of environments, the Western Coral Snake can be found in desert scrublands, grasslands, and woodlands. Understanding its habitat preferences is essential for conservation efforts, as human activities continue to encroach upon these fragile ecosystems.
Behaviour
Contrary to its venomous reputation, the Western Coral Snake is generally docile and poses little threat to humans. Examining its behavior provides valuable insights into its role in the food chain, reproductive habits, and interactions with other species within its habitat.
Art And Culture
Beyond its ecological significance, the Western Coral Snake has also made its mark in art and culture. Its vibrant colors and distinctive pattern have inspired indigenous art and folklore, adding a cultural dimension to its biological importance.
Survival
Survival in the wild poses numerous challenges for the Western Coral Snake. From avoiding predators to securing prey, the strategies employed by this species for survival showcase the resilience and adaptability that enable its continued existence in diverse environments.
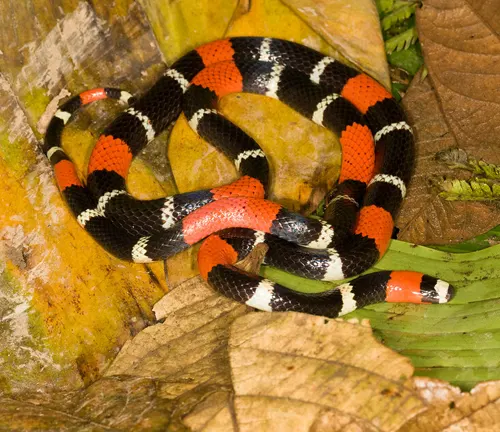

Conservation
The Western Coral Snake faces threats from habitat loss and human encroachment. Conservation efforts are crucial to ensuring the survival of this species and maintaining the delicate balance of ecosystems it inhabits. Collaborative initiatives involving scientists, conservationists, and local communities are essential for the preservation of this unique snake.
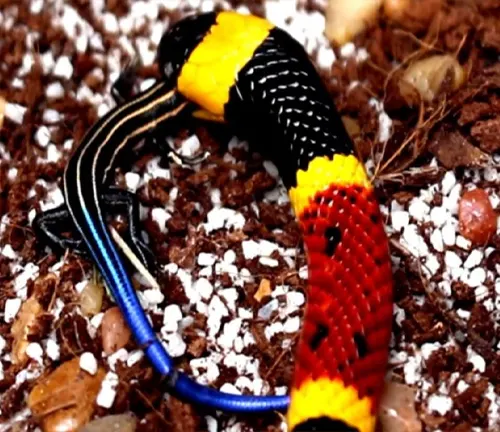

Common Food
The Western Coral Snake sustains itself by preying on small reptiles and amphibians. Exploring its diet provides valuable insights into the interconnections of species within its ecosystem and the role it plays in controlling certain populations.
Benefits
Understanding the benefits of the Western Coral Snake extends beyond its immediate ecosystem. As a subject of scientific study, it contributes to our understanding of venomous species and the potential applications of their venom in medical research. Unravelling the secrets of its biology may pave the way for advancements in antivenom development and other medical applications.
Different Species
Eastern Coral Snake
(Micrurus fulvius)
Found in the southeastern United States, this species has a similar coloration pattern to the Western Coral Snake. Its bands are arranged as red, yellow, and black, but the order is red touching black, then yellow.
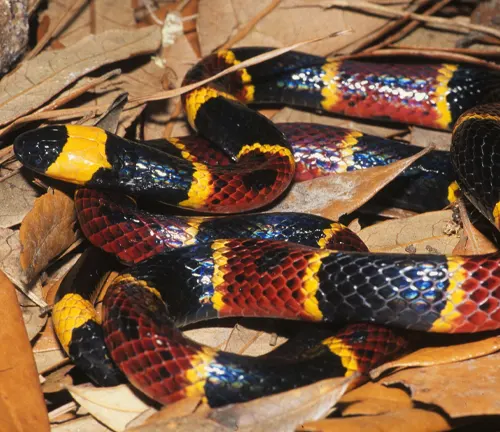
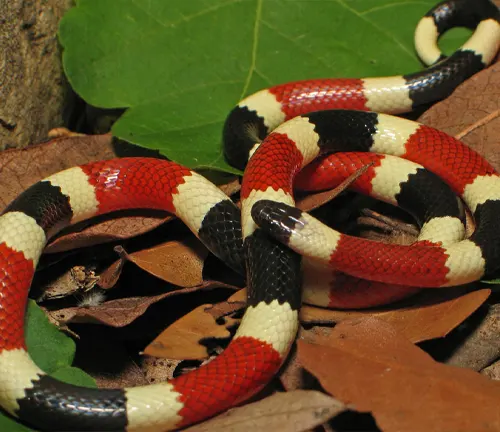


Arizona Coral Snake
(Micruroides sp.)
This species is closely related to the Western Coral Snake and is found in Arizona and Mexico. It shares similar characteristics, such as vibrant bands of red, yellow, and black.
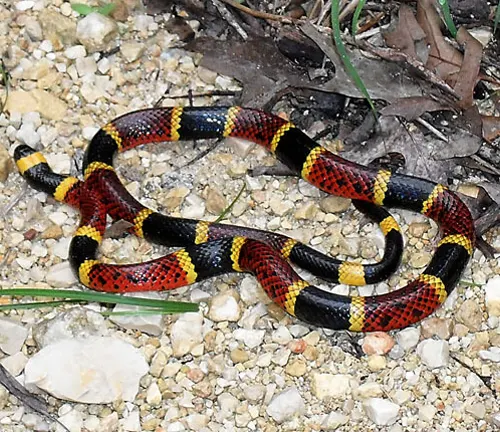
Texas Coral Snake
(Micrurus tener)
Inhabiting the southern United States and northeastern Mexico, the Texas Coral Snake has a distinctive coloration pattern with red touching yellow, then black. It is part of the same genus as the Eastern Coral Snake.

Conclusion
In conclusion, the Western Coral Snake stands as a testament to the intricate beauty of the natural world. From its captivating botanical appearance to its ecological significance and cultural impact, this species warrants careful consideration and conservation. By appreciating its role in the ecosystem and implementing measures to protect its habitat, we can ensure the continued existence of this remarkable snake for generations to come.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
- What is the Western Coral Snake?
The Western Coral Snake (Micruroides euryxanthus) is a venomous snake species found in the southwestern United States and Mexico. It is known for its distinctive coloration, featuring bands of red, yellow, and black. - How venomous is the Western Coral Snake?
The Western Coral Snake has potent neurotoxic venom, but it is generally considered docile and rarely poses a threat to humans. However, caution should be exercised when encountering any venomous snake in the wild. - What is the difference between the Western Coral Snake and non-venomous mimics?
The Western Coral Snake is often confused with non-venomous snakes that mimic its coloration. The key distinguishing feature is the order of the colored bands: red touching yellow, then black. - Where does the Western Coral Snake live?
The species inhabits a range of environments, including desert scrub lands, grasslands, and woodlands in the southwestern United States and Mexico. - Is the Western Coral Snake endangered?
While not currently classified as endangered, the Western Coral Snake faces threats from habitat loss and human encroachment. Conservation efforts are crucial to maintaining its populations. - What does the Western Coral Snake eat?
The diet of the Western Coral Snake primarily consists of small reptiles and amphibians. Its role as a predator contributes to the balance of its ecosystem. - How can one identify the Western Coral Snake?
Identification is based on its unique coloration pattern: red touching yellow, then black. This differs from the non-venomous mimics, which have variations in the order of these colours. - Is the Western Coral Snake aggressive towards humans?
Generally, the Western Coral Snake is considered docile and not aggressive towards humans. However, caution should always be exercised, and any encounter should be observed from a safe distance. - Are there other coral snake species in the same region?
Yes, there are related species, such as the Eastern Coral Snake and the Arizona Coral Snake, which share similar characteristics. Each species may have variations in color patterns. - What is the cultural significance of the Western Coral Snake?
The vibrant colors and distinctive pattern of the Western Coral Snake have inspired indigenous art and folklore, adding a cultural dimension to its biological importance.














Leave your comment