How to Grow Coffee Plant: Sustainable Farming Practices
- March 19, 2024
- 1 comment
Dive into the world of home gardening with our detailed guide on how to grow coffee plants. From the initial planting to the joy of harvest, we’ll walk you through every step, ensuring you can savor the unparalleled taste of your own coffee. Perfect for those who love both gardening and a great cup of joe.

Benefits of Coffee Plant
| Benefit | Description |
|---|---|
| Improved cognitive function | Coffee contains caffeine, which can enhance alertness, concentration, and cognitive performance. |
| Increased metabolism | Caffeine stimulates the central nervous system, potentially boosting metabolic rate and aiding in weight management. |
| Antioxidant properties | Coffee is rich in antioxidants, such as chlorogenic acid, which may help reduce oxidative stress and lower the risk of chronic diseases. |
| Reduced risk of certain diseases | Regular coffee consumption has been associated with a decreased risk of diseases such as Parkinson’s, Alzheimer’s, type 2 diabetes, and certain cancers. |
| Enhanced physical performance | Caffeine can improve physical performance by increasing adrenaline levels and mobilizing fatty acids, potentially leading to better exercise outcomes. |
| Mood elevation | Coffee consumption has been linked to improved mood and a reduced risk of depression, attributed to its impact on neurotransmitters like dopamine and serotonin. |
| Lower risk of liver diseases | Studies suggest that moderate coffee intake may protect against liver conditions such as cirrhosis, liver fibrosis, and liver cancer. |
| Potential protection against heart disease | Moderate coffee consumption has been associated with a reduced risk of heart failure, stroke, and other cardiovascular conditions. |
| Improved longevity | Some research indicates that moderate coffee drinkers may have a lower risk of premature death compared to non-coffee drinkers. |
List on How To Grow Coffee Plant
- Choosing the Right Variety
- Acquiring Seeds or Seedlings
- Ideal Growing Conditions
- Soil and Container
- Watering and Fertilizing
- Pruning and Maintenance
- Harvesting Coffee Cherries
- Processing and Roasting
Choosing the Right Variety
Before you embark on your coffee-growing journey, it’s essential to choose the right variety of coffee plant. The two most common species used for coffee production are Coffea arabica and Coffea canephora (also known as Coffea robusta).
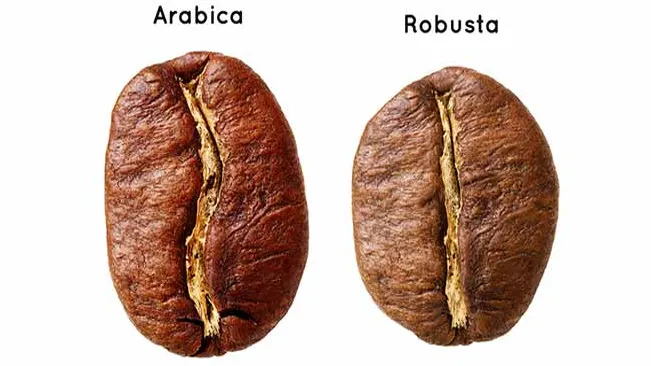
Coffea arabica

- Flavor Profile: Arabica coffee is renowned for its complex and nuanced flavors, often exhibiting floral, fruity, and acidic notes. It’s prized for its smoothness and well-balanced taste.
- Growing Conditions: Arabica plants thrive in mild climates with consistent temperatures ranging from 15°C to 24°C (59°F to 75°F). They prefer higher elevations, typically between 600 to 2000 meters above sea level, where they receive ample rainfall and well-drained soil.
- Suitability for Home Growing: Arabica plants are well-suited for home cultivation, especially in regions with mild climates. With proper care and attention to their specific environmental needs, you can successfully grow arabica coffee plants in your garden or even indoors.
Coffea canephora (Robusta)

- Flavor Profile: Robusta coffee is characterized by its strong, bold flavor profile, often described as earthy, woody, and with a more pronounced bitterness compared to arabica. It’s commonly used in espresso blends for its robust taste.
- Growing Conditions: Robusta plants are hardier and more tolerant of a wide range of growing conditions compared to arabica. They thrive in warmer climates with temperatures ranging from 24°C to 30°C (75°F to 86°F). Robusta plants can tolerate lower elevations and are more resistant to pests and diseases.
- Suitability for Home Growing: While robusta plants are less common in home gardens due to their preference for warmer climates, they can still be grown successfully in suitable regions. However, they may require more attention to pest management and soil quality.
Acquiring Seeds or Seedlings
Once you’ve decided on the variety, you’ll need to acquire either seeds or seedlings to start your coffee plant. You can purchase coffee seeds online or from specialty nurseries. Alternatively, you can try germinating seeds from fresh coffee cherries, though this process can be more challenging. If you opt for seedlings, make sure they are healthy and well-established.
- Purchasing Seeds Online or from Specialty Nurseries:
- Many online retailers and specialty nurseries offer coffee seeds for sale. When purchasing seeds, ensure they are from a reputable source to guarantee quality and viability.
- Look for seeds of the specific coffee variety you desire, whether it’s Arabica, Robusta, or another type. Different varieties have distinct flavors, growing conditions, and characteristics.
- Check for any instructions provided by the seller regarding seed germination and care. Some seeds may require specific conditions or treatments to improve germination rates.
- Germinating Seeds from Fresh Coffee Cherries:
- If you have access to fresh coffee cherries, you can attempt to extract and germinate the seeds, also known as coffee beans.
- Begin by removing the outer pulp and mucilage from the coffee cherry to reveal the seeds inside. This process typically involves fermentation and washing to clean the seeds thoroughly.
- Once cleaned, the seeds can be dried and then planted in suitable growing medium to initiate germination. However, this method can be more challenging and time-consuming compared to purchasing seeds.
- Choosing Healthy Seedlings:
- Alternatively, you can opt to purchase seedlings from nurseries or coffee farms. Seedlings are young coffee plants that have already been germinated and are ready for transplanting.
- When selecting seedlings, choose ones that are healthy, vigorous, and free from any signs of disease or pest damage.
- Check the root system to ensure it is well-developed and not pot-bound, which can hinder the plant’s growth once transplanted.
- Consider the growing conditions in your area and choose seedlings that are suitable for your climate and soil type. Some varieties may be better suited to specific environments than others.
Ideal Growing Conditions

- Sunlight: Coffee plants require ample sunlight, but direct sunlight can be too intense. Opt for a location with indirect sunlight or partial shade to prevent leaf scorching and ensure optimal growth.
- Temperature: Maintain temperatures between 60°F and 70°F (15°C to 25°C) for optimal growth. While coffee plants can tolerate slight fluctuations, consistent temperatures within this range promote healthy development.
- Moisture: Adequate moisture is crucial for coffee plants. Keep the soil consistently moist but not waterlogged. Ensure proper drainage to prevent waterlogging, which can lead to root rot.
- Air Circulation: Good air circulation is essential for preventing fungal diseases and ensuring overall plant health. Avoid placing coffee plants in stagnant air or overly humid conditions.
- Soil: Use well-draining, nutrient-rich soil with a slightly acidic pH (around 6.0 to 6.5) for coffee plants. A mix of peat moss, compost, and perlite or sand works well. Regularly check soil moisture levels and adjust watering accordingly.
- Fertilization: Coffee plants benefit from regular fertilization during the growing season (spring and summer). Use a balanced fertilizer specifically formulated for houseplants or acid-loving plants. Follow the manufacturer’s instructions for application rates and frequency.
- Pruning: Prune coffee plants to maintain their shape and encourage bushier growth. Remove any dead or diseased branches, as well as any growth that appears weak or spindly.
- Pest and Disease Control: Monitor coffee plants for pests such as aphids, mealybugs, and spider mites. Treat infestations promptly with insecticidal soap or neem oil. Additionally, watch for signs of fungal diseases like powdery mildew or leaf rust and take preventive measures such as improving air circulation and avoiding overwatering.
Soil and Container
Soil
Coffee plants thrive in well-draining, slightly acidic soil conditions. Here are some key points to consider regarding soil for your coffee plant:

- Drainage: Ensure that the soil you use provides adequate drainage. Coffee plants do not tolerate waterlogged conditions, which can lead to root rot. A mixture of potting soil, perlite, and peat moss can help achieve good drainage.
- Acidity: Coffee plants prefer slightly acidic soil with a pH ranging between 6.0 and 6.5. You can adjust the pH level of your soil using amendments if necessary. Soil pH testing kits are readily available at garden centers and can help you monitor and adjust the acidity levels as needed.
- Nutrient content: While coffee plants don’t require exceptionally nutrient-rich soil, it’s essential to provide them with a balanced mix of nutrients. You can achieve this by incorporating organic matter, such as compost, into the soil mix. Additionally, using a slow-release fertilizer formulated for acid-loving plants can help ensure your coffee plant receives adequate nutrition.
- Consistency: Maintain consistent moisture levels in the soil, avoiding both waterlogged and dry conditions. Water your coffee plant when the top inch of soil feels dry to the touch, but be careful not to overwater.
Container
Choosing the right container for your coffee plant is equally important. Here are some considerations when selecting a container:

- Size: Start with a small to medium-sized container for young coffee plants, allowing room for growth. As the plant grows, you may need to gradually increase the size of the container to accommodate its expanding root system. A container that is too small can restrict root growth and lead to stunted development.
- Drainage: Opt for a container with sufficient drainage holes at the bottom to prevent water from pooling around the roots. Proper drainage is crucial for preventing root rot and other moisture-related issues.
- Material: Choose a durable and weather-resistant material for your container, such as plastic, ceramic, or terracotta. Each material has its advantages, so select one that suits your preferences and the overall aesthetic of your space.
- Portability: Consider the weight of the container, especially if you plan to move your coffee plant indoors or outdoors seasonally. Lightweight containers made of materials like plastic are easier to maneuver than heavier options like ceramic or stone.
Watering and Fertilizing
Watering
Coffee plants thrive when their soil is consistently moist but not waterlogged. Adequate watering is crucial for their health and productivity. Here are some guidelines for watering your coffee plant:

- Consistent Moisture: Keep the soil consistently moist, especially during the growing season. Aim to water the plant whenever the top inch of soil feels dry to the touch.
- Avoid Overwatering: While it’s essential to keep the soil moist, be cautious not to overwater your coffee plant. Waterlogging can lead to root rot and other issues. Ensure proper drainage in the pot or planting area to prevent water from pooling around the roots.
- Monitor Environmental Factors: Factors such as temperature, humidity, and sunlight intensity can affect the plant’s water needs. During hot and dry periods, you may need to water more frequently, while cooler or humid conditions may require less frequent watering.
- Use Room Temperature Water: Use room temperature water when watering your coffee plant, as cold water can shock the roots. Avoid using water that’s too hard or contains high levels of minerals, as it may adversely affect the plant’s health.
- Watering Frequency: Depending on environmental conditions and the size of the plant, you may need to water your coffee plant every few days to once a week. Adjust the frequency based on the plant’s needs, always aiming for consistent moisture.
Fertilizing
Coffee plants have specific nutritional requirements, and regular fertilization is necessary to ensure healthy growth and optimal coffee bean production. Here’s how to fertilize your coffee plant effectively:

- Choose the Right Fertilizer: Use a balanced fertilizer formulated for acid-loving plants, as coffee plants prefer slightly acidic soil. Look for a fertilizer with a balanced ratio of nitrogen (N), phosphorus (P), and potassium (K), along with micronutrients.
- Frequency of Fertilization: During the growing season, which typically coincides with spring and summer, fertilize your coffee plant every two to four weeks. This frequent feeding provides the plant with essential nutrients to support vigorous growth and flower and fruit development.
- Application Method: Apply the fertilizer according to the manufacturer’s instructions. It’s usually recommended to dilute the fertilizer with water to prevent burning the plant’s roots. Alternatively, you can incorporate slow-release fertilizer pellets into the soil, ensuring a steady supply of nutrients over time.
- Avoid Overfertilizing: While fertilization is crucial, be careful not to overdo it. Too much fertilizer can lead to salt buildup in the soil, which can harm the plant. Always follow the recommended dosage and avoid fertilizing during the plant’s dormant period in fall and winter.
- Monitor Plant Response: Pay attention to how your coffee plant responds to fertilization. Healthy growth, vibrant foliage, and the development of flowers and fruits indicate that the plant is receiving adequate nutrients. Adjust your fertilization regimen based on the plant’s performance and any signs of nutrient deficiencies or excesses.
Pruning and Maintenance
Regular pruning is essential to encourage bushy growth and prevent your coffee plant from becoming leggy. Prune away any dead or diseased branches, and pinch off the tips of new growth to promote branching. Keep an eye out for pests such as aphids or mealybugs, and treat them promptly with insecticidal soap or neem oil.

- Encouraging Bushy Growth: Regular pruning helps stimulate bushy growth in coffee plants. By trimming away dead or diseased branches and pinching off the tips of new growth, you encourage the plant to produce more lateral branches, resulting in a fuller and more robust appearance.
- Preventing Legginess: Without proper pruning, coffee plants can become leggy, with long, spindly stems and sparse foliage. This not only affects the aesthetic appeal of the plant but can also compromise its health and productivity. Pruning helps maintain a compact and well-proportioned growth habit, ensuring that the plant remains healthy and vigorous.
- Removing Dead or Diseased Branches: Dead or diseased branches not only detract from the appearance of the plant but can also serve as entry points for pests and diseases. Regularly inspect your coffee plant for any signs of damage or decay, and promptly prune away any affected branches to prevent further spread.
- Promoting Air Circulation: Proper pruning helps improve air circulation within the plant canopy, reducing the risk of fungal diseases such as powdery mildew and rust. Thinning out crowded branches allows sunlight to penetrate more evenly, promoting photosynthesis and overall plant health.
- Pest and Disease Management: Pruning also facilitates pest and disease management by allowing for better access to the plant’s foliage. Keep a vigilant eye out for common coffee pests such as aphids or mealybugs, and promptly remove any infested branches. Treatments such as insecticidal soap or neem oil can be effective in controlling pest populations while minimizing harm to the plant.
- Pruning Techniques: When pruning your coffee plant, use clean, sharp pruning shears to make clean cuts and minimize damage to the plant tissue. Focus on removing dead, damaged, or overgrown branches, and aim to maintain a balanced and symmetrical shape. Additionally, pinch off the tips of new growth to encourage branching and promote a bushy appearance.
- Seasonal Maintenance: While coffee plants can be pruned year-round, it’s generally best to perform major pruning during the plant’s dormant season, typically in late winter or early spring. This allows the plant to recover and regrow vigorously during the growing season.
Harvesting Coffee Cherries
Waiting for Maturity

- Growing coffee plants requires patience as it can take several years for a coffee plant to mature and produce cherries. The process begins with nurturing the plant until it reaches the stage of flowering, typically occurring after three to five years of growth. These small, delicate white flowers are the precursor to the coffee cherries.
Formation of Coffee Cherries

- After successful flowering, the plant will start to develop coffee cherries. These cherries initially appear green and gradually transition through various stages of ripening. As they mature, they change color, transitioning from green to yellow, then to orange, and finally to a deep, vibrant red when fully ripe.
Assessing Ripeness

- Proper timing is crucial when harvesting coffee cherries. Ripe cherries contain the highest concentration of sugars and flavors, leading to better-quality coffee beans. Farmers carefully inspect the color and firmness of the cherries to determine their ripeness. Fully ripe cherries are plump, brightly colored, and slightly soft to the touch.
Hand Harvesting

- In many coffee-growing regions, harvesting is done by hand to ensure only ripe cherries are picked. Skilled workers meticulously traverse the coffee plantation, selectively picking the ripe cherries while leaving unripe ones on the plant to continue maturing. Hand harvesting is labor-intensive but allows for better quality control.
Processing the Cherries

- Once harvested, the cherries undergo processing to extract the coffee beans within. There are different methods of processing, including the wet (washed) process and the dry (natural) process. In the wet process, the cherries are pulped to remove the outer skin and then fermented to loosen the pulp further. In the dry process, the cherries are dried whole before the beans are extracted.
Processing and Roasting
Processing Coffee Beans

- Harvesting: Coffee cherries are typically harvested when they reach peak ripeness, which varies depending on the coffee variety and growing conditions. Harvesting can be done by hand or using machines.
- Removal of Pulp: After harvesting, the outer pulp of the coffee cherry needs to be removed to access the beans inside. This can be done through various methods, including wet processing (fermentation and washing) or dry processing (natural sun-drying).
- Fermentation (if applicable): In wet processing, the beans are fermented to break down the mucilage layer surrounding them. This step can influence the flavor profile of the coffee.
- Drying: Once the pulp is removed, the beans need to be dried to reduce moisture content. This can be done by spreading them out in the sun or using mechanical dryers.
- Hulling: After drying, the outer parchment layer of the beans is removed through hulling, revealing the green coffee beans inside.
Roasting Coffee Beans

- Green Beans: The dried and hulled coffee beans are referred to as green beans. Before they can be brewed, they must undergo the roasting process.
- Roasting: Roasting coffee beans involves applying heat to the green beans, which causes them to undergo physical and chemical transformations. During roasting, the beans change color, lose moisture, and develop complex flavors and aromas.
- Roast Levels: Roasting levels can vary from light to dark, with each level producing different flavor profiles. Lighter roasts tend to preserve more of the bean’s original characteristics, while darker roasts develop richer, bolder flavors with caramelized sugars.
- Cooling and Packaging: After roasting, the beans are cooled to stop the roasting process and prevent over-roasting. Once cooled, they are often packaged in airtight bags to preserve freshness and flavor.
Conclusion
Growing your own coffee plant at home is a rewarding experience that allows you to connect more deeply with the origins of your favorite beverage. By following these simple steps and providing your coffee plant with the care it needs, you can enjoy the satisfaction of nurturing it from seed to cup. So why not give it a try and embark on your own coffee-growing adventure today? Who knows, you might just discover a newfound appreciation for the art of coffee cultivation.
FAQs (Frequently Asked Questions)
- What type of climate do coffee plants require to thrive?
- Coffee plants typically thrive in tropical climates with consistent temperatures between 60°F to 70°F (15°C to 25°C). They also require high humidity and moderate rainfall.
- Coffee plants typically thrive in tropical climates with consistent temperatures between 60°F to 70°F (15°C to 25°C). They also require high humidity and moderate rainfall.
- Can I grow coffee plants indoors?
- Yes, you can grow coffee plants indoors, but they require specific conditions such as bright, indirect sunlight, consistent warmth, and high humidity. Providing these conditions can be challenging but not impossible.
- Yes, you can grow coffee plants indoors, but they require specific conditions such as bright, indirect sunlight, consistent warmth, and high humidity. Providing these conditions can be challenging but not impossible.
- How long does it take for a coffee plant to produce beans?
- Coffee plants typically start producing beans after about three to five years of growth. However, it may take longer depending on factors like the plant’s health, growing conditions, and variety.
- Coffee plants typically start producing beans after about three to five years of growth. However, it may take longer depending on factors like the plant’s health, growing conditions, and variety.
- What kind of soil is best for growing coffee plants?
- Coffee plants prefer well-draining, slightly acidic soil with a pH range of 6.0 to 6.5. A mix of peat moss, perlite, and compost can create an ideal growing medium.
- Coffee plants prefer well-draining, slightly acidic soil with a pH range of 6.0 to 6.5. A mix of peat moss, perlite, and compost can create an ideal growing medium.
- How often should I water my coffee plant?
- Coffee plants prefer consistently moist soil but not waterlogged. Watering frequency will depend on factors like climate, pot size, and soil type. Generally, aim to water when the top inch of soil feels dry.
- Coffee plants prefer consistently moist soil but not waterlogged. Watering frequency will depend on factors like climate, pot size, and soil type. Generally, aim to water when the top inch of soil feels dry.
- Do coffee plants require fertilization?
- Yes, coffee plants benefit from regular fertilization during the growing season (spring and summer). Use a balanced fertilizer formulated for acid-loving plants, and follow the manufacturer’s instructions for application.
- Yes, coffee plants benefit from regular fertilization during the growing season (spring and summer). Use a balanced fertilizer formulated for acid-loving plants, and follow the manufacturer’s instructions for application.
- How do I propagate coffee plants?
- Coffee plants can be propagated from seeds or cuttings. Seeds should be fresh and planted in a well-draining soil mix. Cuttings can be taken from healthy, mature plants and rooted in water or a rooting medium.
- Coffee plants can be propagated from seeds or cuttings. Seeds should be fresh and planted in a well-draining soil mix. Cuttings can be taken from healthy, mature plants and rooted in water or a rooting medium.
- Should I prune my coffee plant?
- Pruning coffee plants can help maintain their shape, remove dead or diseased branches, and promote airflow and light penetration. Prune sparingly and avoid heavy pruning, especially on young plants.
- Pruning coffee plants can help maintain their shape, remove dead or diseased branches, and promote airflow and light penetration. Prune sparingly and avoid heavy pruning, especially on young plants.
- What pests and diseases are common in coffee plants?
- Common pests that affect coffee plants include coffee berry borers, aphids, and scale insects. Diseases such as coffee leaf rust and coffee berry disease can also pose threats. Regular inspection and prompt treatment are essential for prevention and control.
- Common pests that affect coffee plants include coffee berry borers, aphids, and scale insects. Diseases such as coffee leaf rust and coffee berry disease can also pose threats. Regular inspection and prompt treatment are essential for prevention and control.
- When is the best time to harvest coffee beans?
- Coffee beans are typically harvested when they are ripe, which varies depending on the coffee variety and growing conditions. In general, harvesting occurs once the coffee cherries turn from green to red, although some varieties may be ripe when they are yellow or orange. Harvesting usually takes place once a year, but it can vary depending on the region and climate.

Kristine Moore
Forestry AuthorI'm Kristine Moore, a seasoned garden landscaping professional with over 30 years of experience. My extensive career has been dedicated to transforming outdoor spaces into stunning, sustainable landscapes. With a deep understanding of horticulture, design principles, and environmental stewardship, I have become a respected figure in the field, known for creating harmonious, visually appealing, and eco-friendly gardens. My commitment to excellence and continuous learning in landscaping trends and techniques has solidified my reputation as an expert in garden design and implementation.













Very educating
Titus machanga
March 25, 2024 7:15 am