Ginseng
- December 20, 2023
- 0 comment
Ginseng, a perennial plant revered for its medicinal properties, has a rich history deeply embedded in traditional medicine across various cultures. Belonging to the genus Panax, which means “all-healing” in Greek, ginseng is renowned for its purported adaptogenic qualities, believed to enhance the body’s resilience to stress and promote overall well-being.
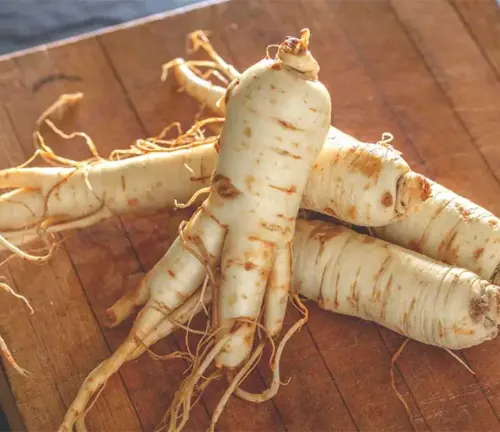
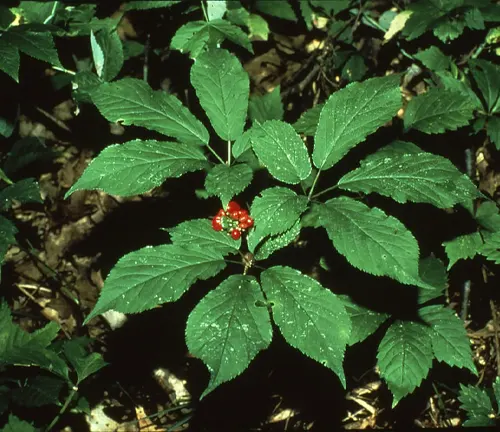


The plant’s distinct, forked root, resembling the human body, is the primary source of its therapeutic compounds. Ginsenosides, the active constituents found in ginseng, are thought to contribute to its wide-ranging health benefits. Throughout centuries, ginseng has been a staple in traditional Chinese medicine, where it is esteemed as a potent tonic for vitality and longevity. Beyond Asia, ginseng has gained global popularity, finding its place in herbal remedies and dietary supplements.
While research on the exact mechanisms and efficacy of ginseng is ongoing, its reputation as an herbal powerhouse persists, with claims of potential benefits ranging from improved cognitive function to enhanced immune response. As ginseng continues to captivate the interest of both traditional healers and modern scientists, its allure as a natural remedy remains deeply rooted in cultural traditions and a quest for holistic health.
| Attribute | Details |
|---|---|
| Scientific Name | Panax spp. (Various species) |
| Plant Family | Araliaceae |
| Common Types | Panax ginseng (Asian or Korean Ginseng), Panax quinquefolius (American Ginseng), Panax notoginseng (Chinese or Sanchi Ginseng) |
| Habitat | Deciduous forests, cool and shaded areas |
| Root Description | Forked, often resembling the human figure |
| Active Compounds | Ginsenosides (Panaxosides) |
| Traditional Uses | Adaptogen, tonic for vitality, stress relief, immune support |
| Cultural Significance | Traditional Chinese Medicine, Korean and Native American herbal practices |
| Harvesting | Typically harvested after 6 years for optimal potency |
| Preparations | Dried root, capsules, extracts, teas |
| Potential Benefits | Adaptogenic properties, cognitive support, immune modulation, anti-inflammatory effects |
| Research Areas | Ongoing studies on specific health benefits, dosage, and safety |
| Cautions | Consultation with healthcare professionals advised, potential interactions with medications |
| Global Popularity | Widely used in herbal remedies and dietary supplements |
| Cultivation | Requires specific growing conditions, often cultivated in Asia, North America, and parts of Europe |
| Commercial Varieties | Various ginseng products available, including red and white ginseng (steamed and dried, respectively) |
| Market Presence | Found in health food stores, pharmacies, and traditional medicine markets worldwide |
Unveiling the Intricacies of Ginseng
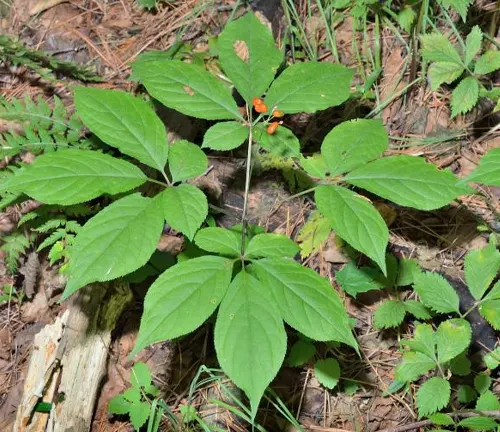

In the heart of shaded woodlands, the botanical brilliance of ginseng unfolds. Belonging to the genus Panax, this perennial plant boasts a rich tapestry of species, with Panax ginseng, Panax quinquefolius, and Panax notoginseng standing out among the most revered. From its distinctive forked root to the intricate composition of ginsenosides, ginseng’s botanical profile is a testament to nature’s sophistication.
Ginseng’s Enchanting Habitat
Nestled in deciduous forests, ginseng exudes woodland elegance. Its preference for cool, shaded environments creates a harmonious relationship with the forest floor. As this herbaceous perennial graces the forest with its presence, it becomes a symbol of natural beauty and resilience, embodying the essence of its Greek-derived genus name, “Panax,” meaning “all-healing.”
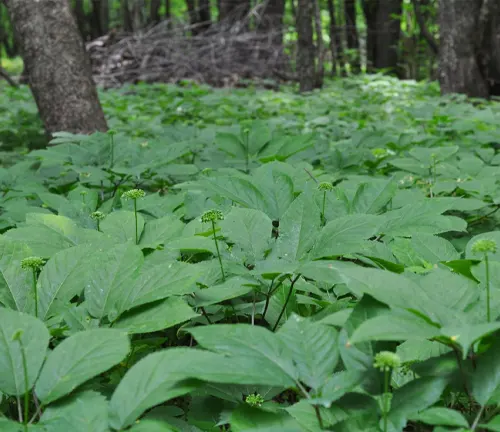

Ginseng’s Role in Forest Ecosystems
Beyond its aesthetic allure, ginseng holds ecological importance. As a shade-loving plant, it contributes to the diversity and balance of forest ecosystems. Ginseng’s growth habit and interaction with surrounding flora create a delicate web of ecological relationships, emphasizing the interconnected ness of plant life in the woodland environment.
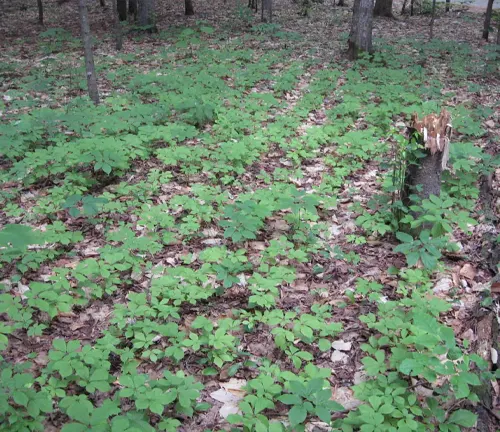

Nurturing Nature’s Gift
The cultivation of ginseng is an art in itself, requiring specific conditions and patience. As demand for this herbal treasure grows, so does the need for responsible cultivation practices. Conservation efforts play a pivotal role in ensuring the sustainability of wild ginseng populations, promoting ethical harvesting, and encouraging cultivation practices that respect the delicate balance of nature.
Ginseng as Nature’s Guardian
Ginseng not only graces the forest with its presence but also serves as nature’s guardian through soil stabilisation. Its extensive root system helps prevent soil erosion, offering a natural solution to maintaining the integrity of woodland landscapes. This role showcases the plant’s contribution to environmental stability, making it a silent yet powerful ally in the forest ecosystem.
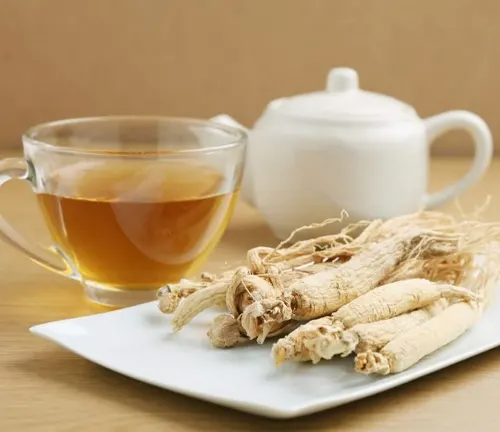


A Journey Through Ginseng’s Many Facets
In traditional practices and modern applications alike, ginseng finds itself woven into the fabric of diverse cultures. From traditional Chinese medicine to Native American herbal remedies, ginseng has transcended borders and centuries. Dried roots, capsules, extracts, and teas showcase the adaptability of this herb, making it accessible to a global audience seeking natural wellness.
Exploring the Potential of Ginseng
The allure of ginseng extends far beyond its cultural significance. Research continues to unveil its potential benefits, ranging from adaptogenic properties that enhance resilience to stress, to cognitive support and immune modulation. As the scientific community delves deeper, ginseng’s multifaceted nature emerges, offering promise for holistic health and well-being.
Navigating the Intricacies of Ginseng
Embarking on a journey into the biological marvel that is ginseng, we delve into the intricate world of this perennial herb. From its scientific classification to the compounds that make it a botanical treasure, ginseng’s biological makeup unveils the secrets behind its revered status in traditional medicine and global herbal practices.
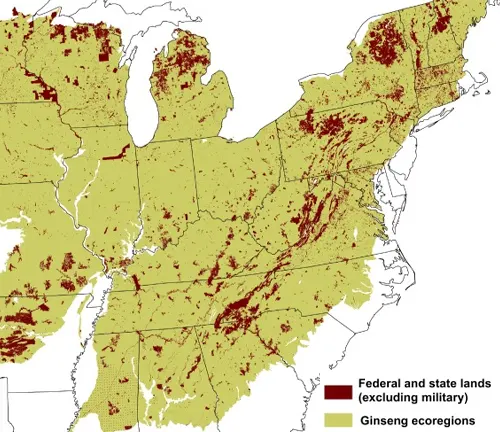
Tracing Ginseng’s Natural Abode
In the shaded realms of deciduous forests and cool woodlands, ginseng establishes its natural abode. Unraveling the habitat map of ginseng reveals not just a plant but a guardian of the forest floor. The exploration of its preferred ecosystems sheds light on the symbiotic relationships that shape ginseng’s growth and contribute to its unique qualities.
Decrypting the Chemistry of Ginseng
As we navigate the biological landscape of ginseng, the focus turns to its key components. Ginsenosides, the active compounds within the plant, take center stage. We delve into the nuanced world of these chemical entities, exploring their diverse structures and understanding how they underpin the various health benefits attributed to ginseng.
Balancing the Benefits and Risks of Ginseng
In the pursuit of holistic well-being, it becomes crucial to scrutinize not only the positive aspects but also the potential side effects of ginseng. From interactions with medications to considerations for specific health conditions, we navigate the delicate balance between reaping the benefits of this herbal marvel and being mindful of its possible repercussions.
Different Species
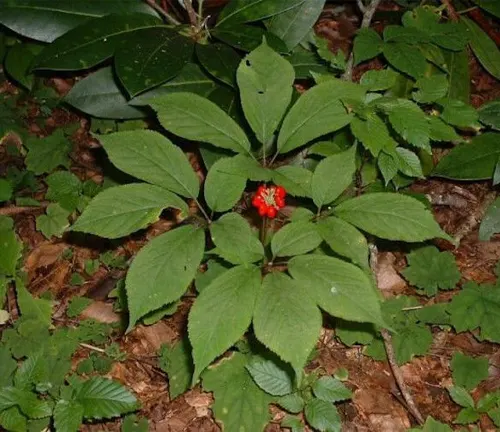

Panax ginseng
(Asian Ginseng or Korean Ginseng)
Originating from the mountains of Eastern Asia, particularly Korea and China.
Renowned for its adaptogenic properties and traditionally used in Chinese medicine.
The root is often harvested after 6 years for maximum potency.
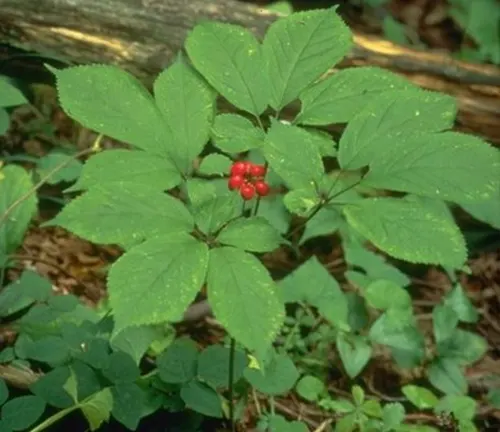
Panax quinquefolius
(American Ginseng)
Native to North America, primarily found in the deciduous forests of the United States and Canada.
Historically used by Native American tribes and later adopted into Western herbalism.
Known for a milder flavor compared to Asian ginseng.
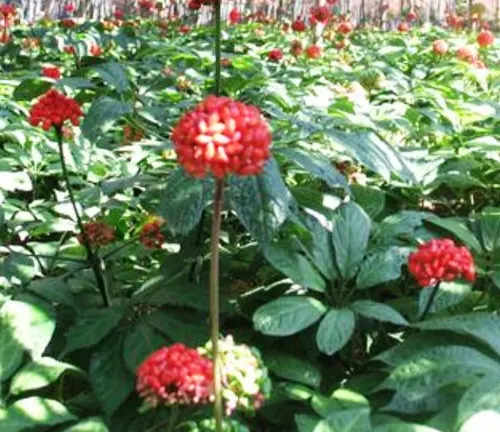


Panax notoginseng
(Chinese or Sanchi Ginseng)
Indigenous to China and other parts of Asia.
Traditionally used in Chinese medicine for its potential cardiovascular benefits.
Often referred to as “Sanchi” or “Tianqi” in traditional Chinese medicine.
Panax japonicus
(Japanese Ginseng)
Found in Japan, Korea, and parts of China.
Shares some botanical characteristics with Panax ginseng but is considered a separate species.
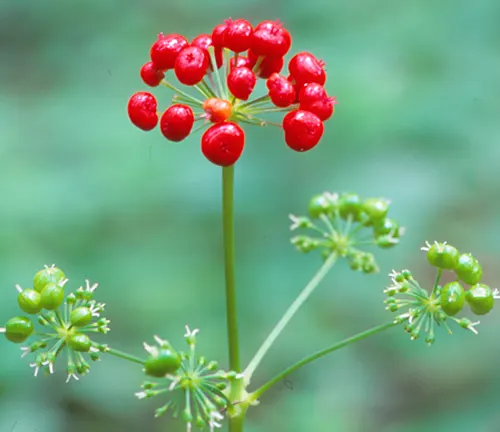
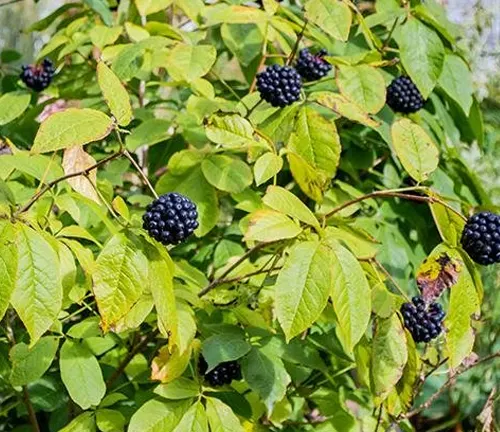


Eleutherococcus senticosus
(Siberian Ginseng)
Despite its name, Siberian ginseng is not a true ginseng but is often referred to as such due to similar adaptogenic properties.
Native to Russia, China, Japan, and Korea.
Traditionally used in Russian and Chinese herbal medicine.
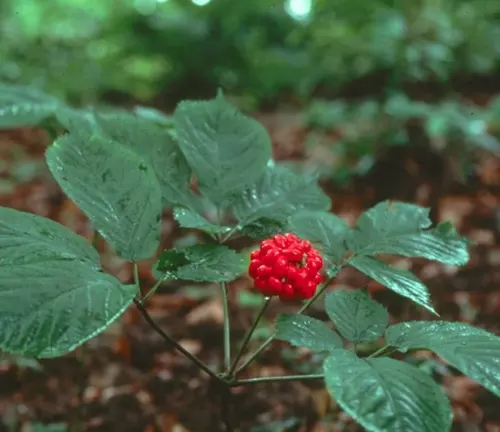
Panax vietnamensis
(Vietnamese Ginseng)
Indigenous to Vietnam.
Considered a rare and valuable species with potential medicinal properties similar to other ginseng varieties.
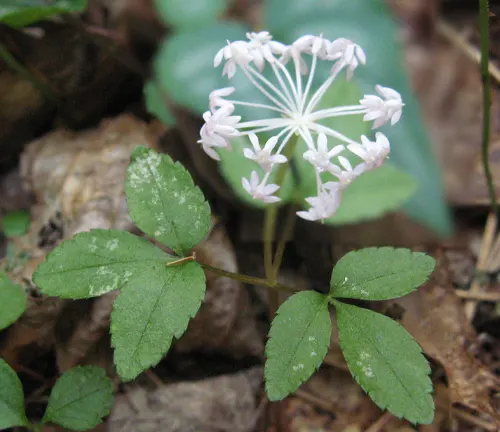


Panax trifolius
(Dwarf Ginseng)
Native to North America.
Smaller in size compared to other ginseng species and has three leaflets instead of five.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1. What is ginseng?
Ginseng is a perennial plant with fleshy roots belonging to the genus Panax. It is known for its use in traditional medicine and is believed to have various health benefits.
2. What are the common species of ginseng?
Common species include Panax ginseng (Asian or Korean Ginseng), Panax quinquefolius (American Ginseng), Panax notoginseng (Chinese or Sanchi Ginseng), and others.
3. What are ginsenosides?
Ginsenosides are the active compounds in ginseng responsible for its medicinal properties. They are believed to contribute to adaptogenic and health-promoting effects.
4. What is the traditional use of ginseng?
Ginseng has a long history of use in traditional Chinese medicine, Korean medicine, and Native American herbal practices. It is often used as a tonic for vitality, adaptogen, and for its potential cognitive and immune support.
5. How is ginseng cultivated?
Ginseng cultivation requires specific conditions, including shaded environments and well-drained soil. The root is typically harvested after several years to reach optimal potency.
6. Are there different forms of ginseng products?
Yes, ginseng is available in various forms, including dried roots, capsules, extracts, teas, and even as an ingredient in certain foods and beverages.
7. What are the potential health benefits of ginseng?
Research suggests potential benefits, including adaptogenic properties, cognitive support, immune modulation, and anti-inflammatory effects. However, the scientific evidence is still evolving.
8. Are there any side effects or interactions with medications?
Ginseng may interact with certain medications, and excessive consumption can lead to side effects. It’s important to consult with a healthcare professional, especially for individuals with pre-existing health conditions.
9. Can anyone use ginseng?
While ginseng is generally considered safe for many individuals, pregnant or nursing women, children, and individuals with certain health conditions should consult a healthcare provider before using ginseng.
10. Is wild ginseng sustainable?
Wild ginseng populations face conservation concerns due to over harvesting. Sustainable cultivation practices are encouraged to preserve wild populations and meet the demand for ginseng products.














Leave your comment