Peppermint Plant
- December 27, 2023
- 0 comment
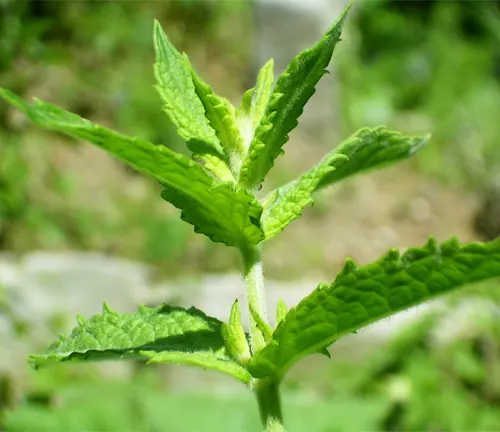
The peppermint plant, scientifically known as Mentha × piperita, is a well-loved and versatile herb that has been cherished for centuries for its aromatic leaves and numerous medicinal properties. Native to Europe and Asia, peppermint is a hybrid of watermint and spearmint, characterized by its distinctively refreshing scent and flavor. This hardy perennial herb boasts square stems, serrated dark green leaves, and spikes of small pink or lavender flowers.
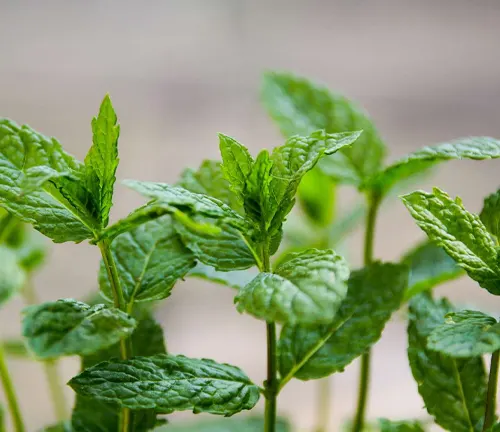

Renowned for its culinary uses, peppermint is a key ingredient in various dishes, teas, and desserts, imparting a cool, minty taste. Beyond its culinary applications, the plant has gained recognition for its therapeutic benefits, with essential oils extracted from its leaves used in aromatherapy and traditional medicine. Peppermint is celebrated for its ability to alleviate digestive issues, soothe headaches, and provide relief from respiratory discomfort.
Its natural menthol content contributes to its cooling sensation, making it a popular choice in topical creams and ointments. Whether enjoyed as a flavorful addition to culinary creations or harnessed for its holistic properties, the peppermint plant continues to be a cherished herb that transcends both the culinary and wellness realms.
| Characteristic | Description |
|---|---|
| Scientific Name | Mentha × piperita |
| Family | Lamiaceae |
| Type | Perennial herb |
| Native Region | Europe and Asia |
| Height | 30 to 90 cm (12 to 35 inches) |
| Leaves | Dark green, serrated, and aromatic |
| Flowers | Spikes of small pink or lavender flowers |
| Flavor | Cool, minty |
| Aroma | Refreshing |
| Culinary Uses | Flavoring in dishes, teas, and desserts |
| Medicinal Uses | Alleviates digestive issues, soothes headaches |
| Essential Oil Content | Contains menthol for aromatherapy and topical use |
| Growing Conditions | Prefers moist, well-drained soil; thrives in sunlight |
| Hardy Zones | Typically zones 3 to 11, depending on specific variety |
Exploring the Peppermint Plant
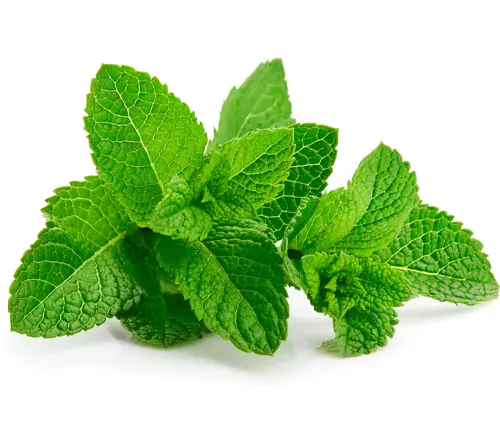

The Peppermint plant, scientifically known as Mentha × piperita, stands as a botanical beauty that has captivated human senses for centuries. In this exploration, we delve into the distinctive features that define this herb, from its square stems to the serrated leaves and the delicate spikes of pink or lavender flowers. Unveiling the secrets of its origins in Europe and Asia, we uncover the fascinating hybridization of watermint and spearmint that gives Peppermint its unique and aromatic character.
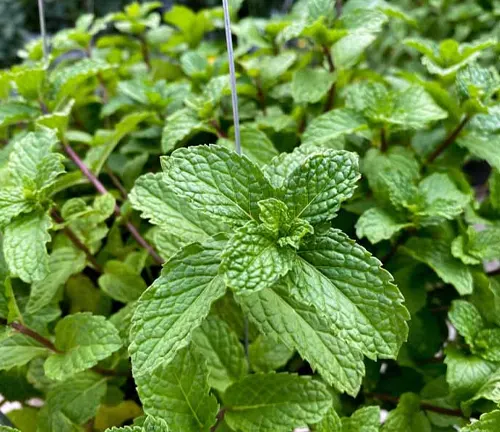
A Closer Look at Peppermint’s Aesthetic Appeal
Beyond its botanical allure, the Peppermint plant exudes woodland elegance. With a height ranging from 30 to 90 cm, this perennial herb graces landscapes with its dark green foliage and adds a touch of sophistication. Whether cultivated in gardens or found in the wild, Peppermint’s presence introduces a subtle charm, complemented by its refreshing aroma. Join us in appreciating the visual splendor that the Peppermint plant brings to diverse environments.
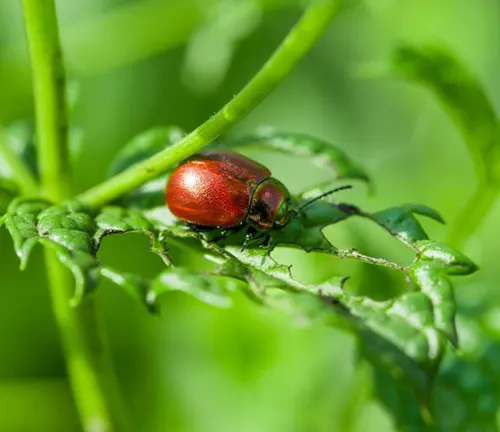


Peppermint’s Role in the Natural World
The ecological significance of the Peppermint plant extends beyond its aesthetic appeal. As a member of the Lamiaceae family, Peppermint contributes to biodiversity by providing habitat and sustenance for various insects. Its role in supporting pollinators adds a layer of importance to its presence in ecosystems. Join us in exploring how this unassuming herb plays a part in the delicate balance of the natural world.
Nurturing Peppermint for Future Generations
Understanding the cultivation of Peppermint is essential for both enthusiasts and conservationists. Unveiling the optimal growing conditions, we explore how this herb thrives in well-drained soil and sunlight. However, as demand for Peppermint rises, conservation efforts become crucial. Discover the measures taken to preserve the genetic diversity of Peppermint and ensure its continued presence in our gardens and ecosystems.
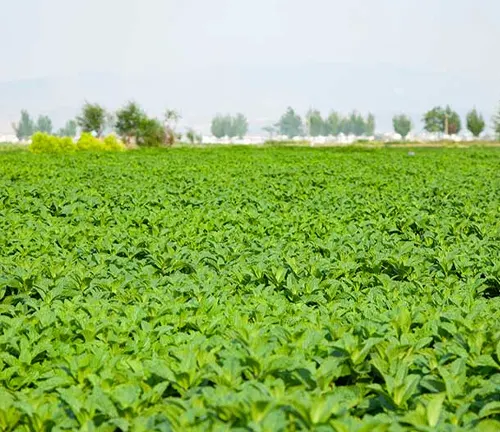
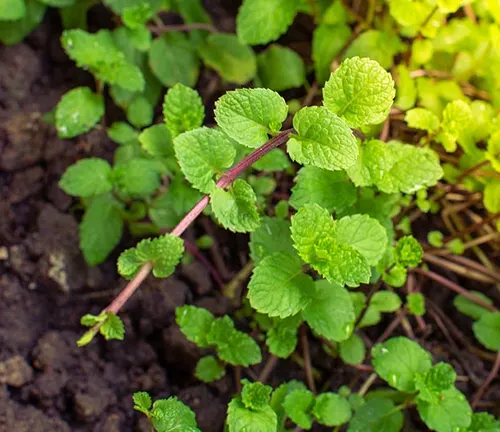


Peppermint’s Underground Impact
Peppermint not only graces us with its above-ground beauty but also plays a significant role in soil stabilization. Its extensive root system helps prevent soil erosion, making it a valuable ally in maintaining the integrity of landscapes. Join us in exploring the underground impact of Peppermint and how its growth patterns contribute to the overall health of the soil.
From Culinary Delights to Aromatic Bliss
Peppermint’s versatility shines through in its common uses. From flavoring dishes and teas to enhancing desserts, this herb has a cherished place in kitchens around the world. Delve into the culinary realm as we uncover the delightful ways Peppermint enriches our palates. Additionally, we explore its role in aromatherapy, where the essential oils extracted from its leaves add a touch of aromatic bliss to our lives.


Unveiling Peppermint’s Medicinal and Therapeutic Wonders
The Peppermint plant extends its influence beyond the culinary and aromatic realms, showcasing a range of medicinal and therapeutic benefits. Explore how Peppermint has been used for centuries to alleviate digestive issues, soothe headaches, and provide relief from respiratory discomfort. With its natural menthol content, Peppermint becomes a source of comfort in topical applications, contributing to its enduring popularity in the realm of holistic well-being.
Mapping Its Natural Habitat
The Peppermint plant, scientifically known as Mentha × piperita, thrives in a variety of habitats, contributing to its widespread cultivation and popularity. In this exploration, we delve into the habitat map of Peppermint, uncovering the diverse environments where this aromatic herb establishes its roots. From its native regions in Europe and Asia to its adaptability in gardens and wild landscapes, the Peppermint plant reveals its remarkable versatility.
A Symphony of Aromatic Elements
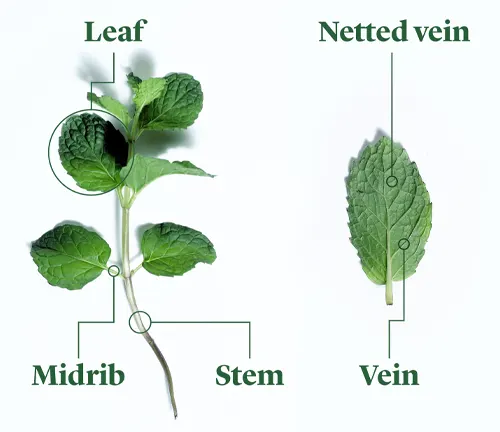
Central to the allure of the Peppermint plant are its components, each playing a unique role in crafting its distinctive aroma and flavor. From the essential oils that carry the essence of menthol to the square stems, serrated leaves, and delicate flowers, Peppermint weaves a symphony of aromatic elements. Join us in unraveling the botanical composition that makes Peppermint a cherished herb in culinary, medicinal, and aromatic realms.
Navigating Peppermint’s Potential Impact
While Peppermint is celebrated for its myriad benefits, it’s essential to explore the potential side effects associated with its consumption. In this segment, we navigate through considerations related to Peppermint, touching upon aspects such as its menthol content, potential interactions with medications, and sensitivity in certain individuals. Understanding the nuanced impact of Peppermint allows us to appreciate its virtues while being mindful of its potential effects.
Different Species
Spearmint
(Mentha spicata)
While spearmint is one of the parent plants in the creation of peppermint, it is a distinct species with its own unique flavor. Spearmint is known for its bright, sweet, and slightly minty taste, often used in culinary applications and beverages.
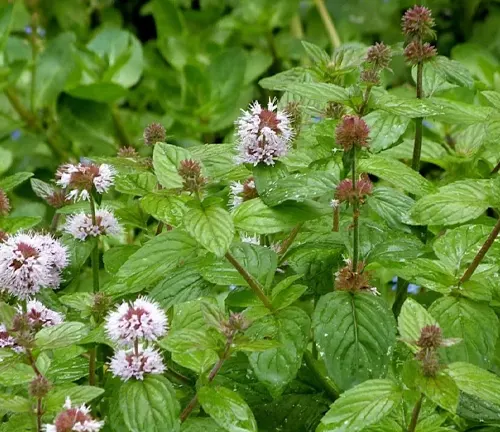


Watermint
(Mentha aquatica)
Watermint is the other parent plant in the formation of peppermint. It has a milder flavor compared to peppermint and is often found in damp or wet habitats. Watermint is less commonly used in culinary applications but has historical uses in traditional medicine.
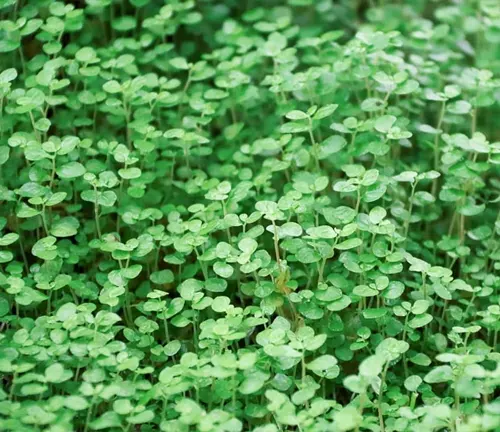
Corsican Mint
(Mentha requienii)
Also known as “miniature mint” or “micro mint,” Corsican Mint has a distinct fragrance and flavor. It is low-growing and is often used as a ground cover in gardens. The leaves have a strong minty aroma and are sometimes used in culinary dishes.
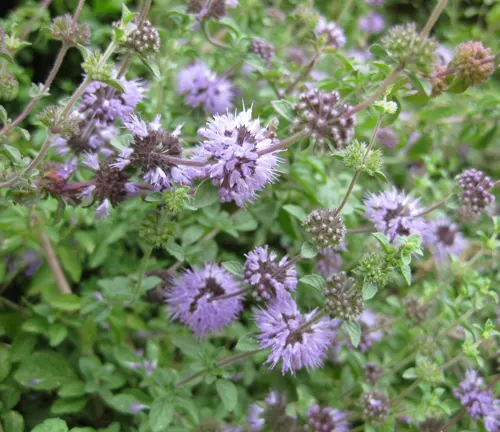


Pennyroyal
(Mentha pulegium)
Pennyroyal is a species of mint known for its strong, pungent aroma. It has a long history of use in traditional medicine and is sometimes used as a flavoring agent. However, it should be used with caution due to its potent nature.
Apple Mint
(Mentha suaveolens)
Apple Mint, also known as Pineapple Mint, has a fruity and slightly sweet flavor. It is often used in salads, beverages, and desserts, providing a refreshing twist to traditional minty flavors.
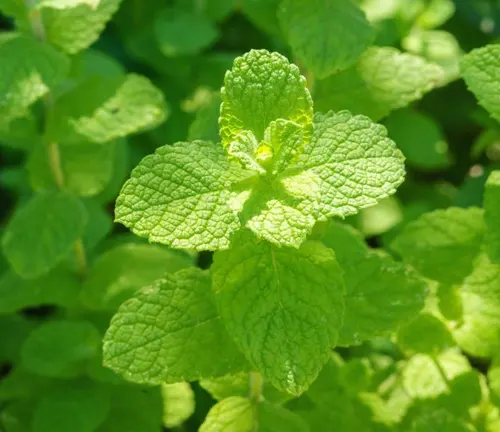
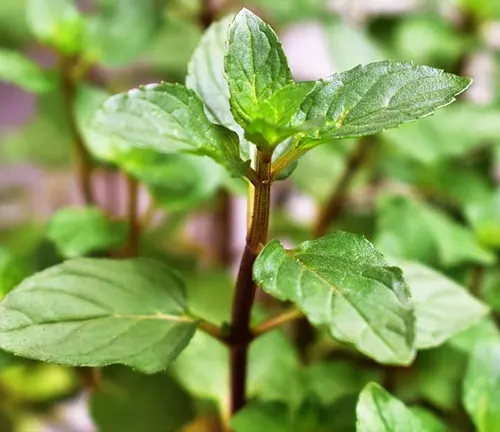


Chocolate Mint
(Mentha × piperita f. citrata ‘Chocolate’)
While not a distinct species, Chocolate Mint is a cultivar of peppermint that deserves mention. It has a chocolate-mint flavor and is often used in desserts and teas.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
- What is Peppermint?
Peppermint is a hybrid mint plant, scientifically known as Mentha × piperita, resulting from the crossbreeding of watermint and spearmint. It is well-known for its refreshing aroma and flavor. - How is Peppermint Different from Spearmint?
Peppermint has a more intense and mentholated flavor compared to spearmint. The leaves of peppermint are often darker in color, and the plant has a higher menthol content, giving it a cooler taste. - What Are the Botanical Features of Peppermint?
Peppermint is characterized by square stems, serrated dark green leaves, and spikes of small pink or lavender flowers. It is a hardy perennial herb that can reach a height of 30 to 90 cm. - Where is Peppermint Native?
Peppermint is not native to a specific region but is believed to have originated in Europe and Asia. It is now cultivated globally in various temperate climates. - How is Peppermint Used in Cooking?
Peppermint is used to flavor a variety of dishes, beverages, and desserts. It adds a cool and minty taste to salads, teas, chocolates, and more. - What Are the Medicinal Uses of Peppermint?
Peppermint has been traditionally used to alleviate digestive issues, soothe headaches, and provide relief from respiratory discomfort. Its essential oil is used in aromatherapy. - Can Peppermint Be Grown at Home?
Yes, peppermint can be easily grown at home. It thrives in well-drained soil with exposure to sunlight. However, it can be invasive, so it’s often grown in containers to control its spread. - How Do You Propagate Peppermint?
Peppermint can be propagated through cuttings or by dividing established plants. It roots easily, and new plants can be started in soil or water. - What Are Some Popular Peppermint Varieties?
Popular peppermint varieties include ‘Black Mitcham’ known for its robust flavor, ‘Candymint’ with a sweet taste, and ‘Chocolate Mint’ with a chocolate-mint flavor. - Are There Any Side Effects to Consuming Peppermint?
While generally safe, excessive consumption of peppermint may lead to heartburn in some individuals. The menthol content can also cause sensitivity in certain people. It’s advisable to consult a healthcare professional if you have specific concerns.














Leave your comment