White Mulberry
- November 27, 2023
- 0 comment
White mulberry, scientifically known as Morus alba, is a deciduous tree native to China but has spread its roots across various regions, adapting to diverse climates. Revered for its significant cultural and historical importance, this tree has been cultivated for thousands of years, not only for its delicious fruits but also for its leaves, which serve as the primary food source for silkworms in the silk industry. The tree reaches a moderate height, with distinctive lobed leaves and a smooth, light-gray bark. One of its most notable features is its sweet, succulent berries that range in color from white to red or purple, depending on the ripeness. Rich in vitamins and antioxidants, these berries have found a place in traditional medicine and culinary practices.
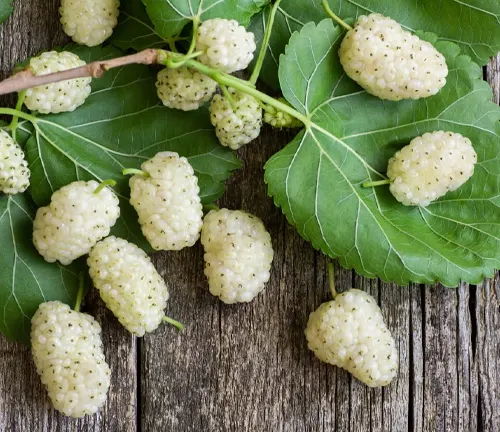
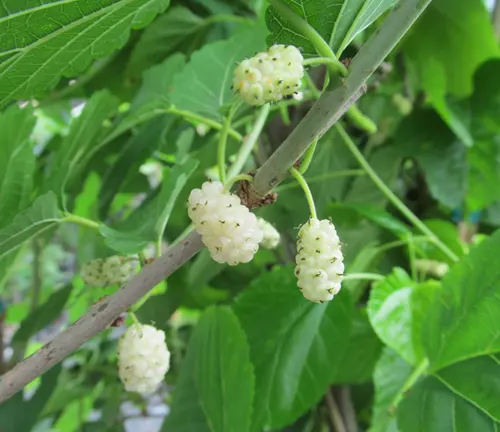


Beyond its culinary and medicinal uses, the white mulberry has garnered attention for its potential health benefits. Studies suggest that it may aid in managing blood sugar levels and possess anti-inflammatory properties. The leaves, in particular, have been explored for their role in controlling diabetes, leading to the development of mulberry leaf extracts as a supplement. Additionally, white mulberry trees are valued for their role in agroforestry, contributing to soil conservation and supporting biodiversity.
| Characteristic | Description |
|---|---|
| Scientific Name | Morus alba |
| Common Names | White Mulberry, Chinese Mulberry, Silkworm Mulberry |
| Family | Moraceae |
| Native Range | China |
| Height | Up to 20 meters (65 feet) |
| Leaves | Distinctive lobed, serrated edges |
| Bark | Smooth, light-gray |
| Fruit | Sweet, succulent berries; white to red or purple |
| Culinary Use | Berries are used in various dishes, jams, and desserts |
| Economic Significance | Leaves are a primary food source for silkworms |
| Medicinal Properties | Potential benefits include blood sugar management and anti-inflammatory effects |
| Health Benefits | Rich in vitamins and antioxidants |
| Agroforestry Role | Contributes to soil conservation and biodiversity |
| Cultural Significance | Important in traditional Chinese and silk industry history |
| Resilience | Adapts to diverse climates, widely cultivated |
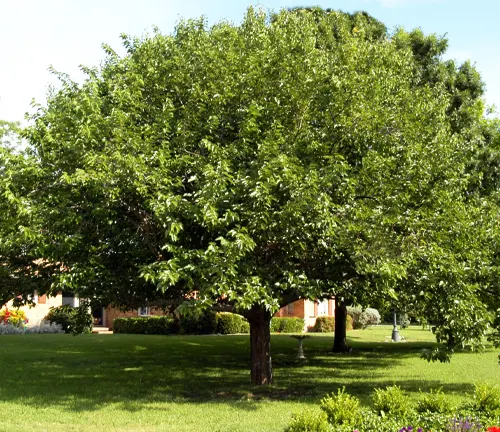
Brief Overview of the Tree
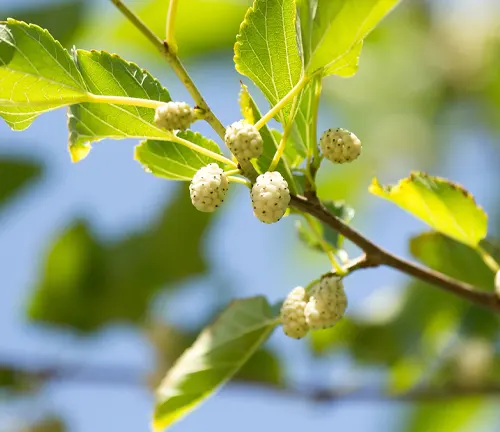

The White Mulberry, scientifically known as Morus alba, stands as a testament to nature’s resilience and human ingenuity. Originating in China, this deciduous tree has traversed through time, intertwining itself with cultural, culinary, and ecological narratives across the globe. From its lobed leaves to succulent berries, the White Mulberry weaves a story of versatility and significance.
Attributes and Characteristics
Standing at a moderate height, the White Mulberry boasts distinctive leaves and smooth, light-gray bark. Its berries, ranging in color from white to red or purple, add a touch of sweetness to the tree’s visual allure. These attributes, coupled with its adaptability to diverse climates, make it a prized addition to landscapes worldwide.
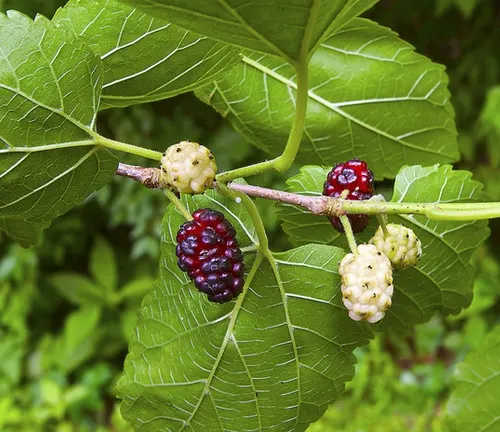

Natural Setting
The White Mulberry finds its roots in China but has gracefully embraced various regions, thriving in both urban and rural landscapes. Its ability to flourish in different environments speaks to its adaptability and makes it a symbol of natural beauty in diverse settings.

Soil Type
This resilient tree is not overly finicky about soil type, showcasing its versatility. It can tolerate a range of soil conditions, making it accessible for cultivation in various locations.
Soil Preferences
While it can tolerate different soil types, the White Mulberry prefers well-drained soil. Providing this type of soil ensures optimal growth and development.
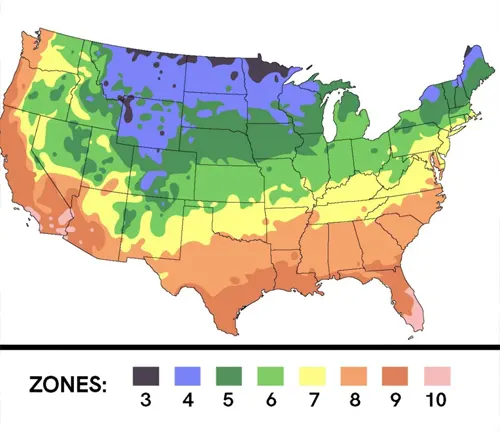
Hardiness Zone
Adaptable to a variety of climates, the White Mulberry typically thrives in hardiness zones 4 to 8, showcasing its ability to withstand a spectrum of temperature ranges.
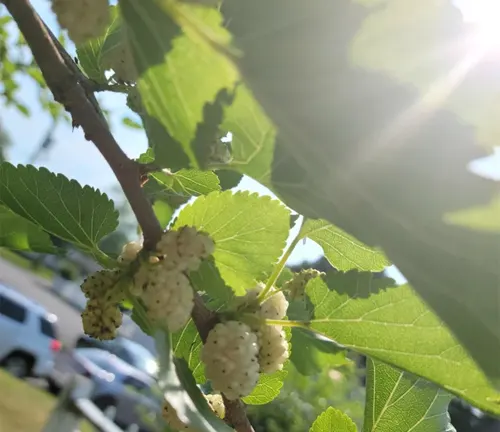

Sun Preference
With a preference for full sun, the White Mulberry flourishes when exposed to direct sunlight. This makes it an ideal choice for sunny landscapes and gardens.
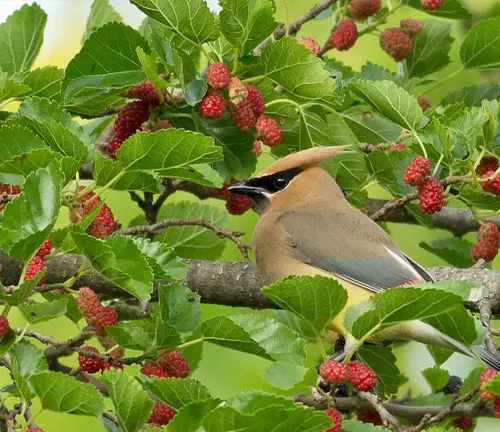
Wildlife Value
Beyond its aesthetic appeal, the White Mulberry serves as a valuable resource for wildlife. The berries attract various birds and insects, contributing to the biodiversity of the ecosystem.
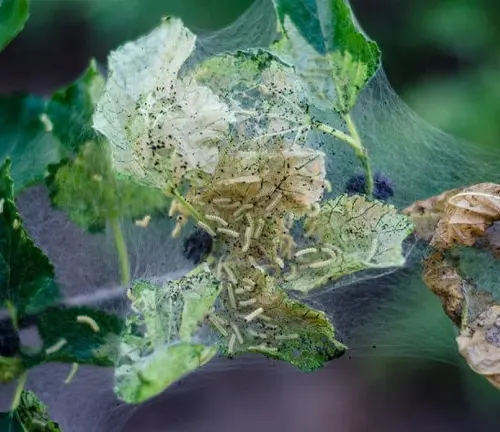


Common Pests & Diseases
While generally hardy, White Mulberries can face challenges from pests like aphids and diseases such as powdery mildew. Vigilance and proper care help mitigate these issues.
Care
Caring for a White Mulberry involves providing well-drained soil, regular watering, and occasional pruning to maintain its health and shape. These simple practices ensure a thriving tree.
Health
Studies suggest that White Mulberry may offer health benefits, including potential blood sugar management and anti-inflammatory properties. The berries, rich in vitamins and antioxidants, contribute to overall well-being.
Safety
While the White Mulberry is generally safe, caution is advised as unripe fruits may cause stomach upset. As with any plant, it’s essential to be aware of individual sensitivities.
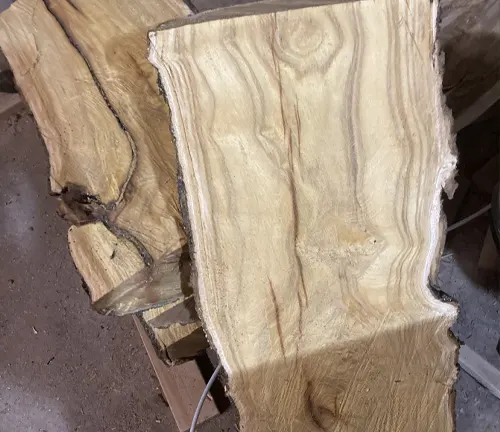
Wood Products
The wood of the White Mulberry, known for its durability, has been historically used in crafting tools, furniture, and even as a preferred material for making bows.
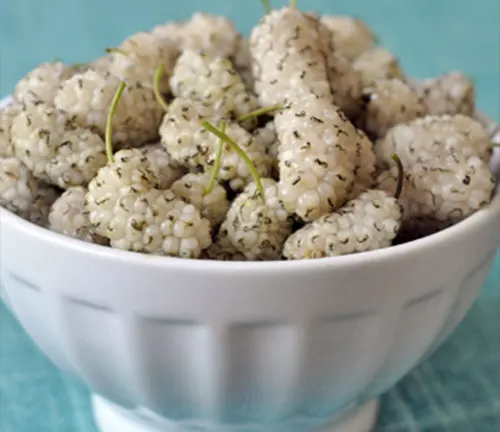


Edible or Not
Both the berries and leaves of the White Mulberry are edible. The berries are enjoyed in various culinary delights, while the leaves, a primary food source for silkworms, have been used in traditional medicine.
Benefits
Beyond its culinary uses, White Mulberry offers a range of benefits, from potential medicinal applications to its role in supporting biodiversity and soil conservation.

Enhancing the Quality of Life
The White Mulberry, with its aesthetic appeal and contributions to health and ecology, enhances the quality of life for those who cultivate and appreciate its presence.
Contribution to the Environment
As a tree that adapts to various climates and contributes to soil conservation, the White Mulberry stands as a positive force in environmental sustainability.
Disadvantages
While its benefits are numerous, the White Mulberry can pose challenges, such as attracting certain pests. Understanding these disadvantages allows for informed cultivation.
Longevity
With proper care, White Mulberry trees can live for several decades, becoming enduring symbols in the landscapes they inhabit.

Fun Facts
Did you know that the White Mulberry played a crucial role in the silk industry, with its leaves being the primary food source for silkworms? This fun fact adds an extra layer to the rich tapestry of its history and significance.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
- What is White Mulberry?
White Mulberry (Morus alba) is a deciduous tree native to China, known for its lobed leaves and sweet, succulent berries. It has cultural, culinary, and medicinal significance. - Where is White Mulberry commonly found?
While native to China, White Mulberry has been cultivated worldwide and adapts to diverse climates, making it common in various regions. - What are the uses of White Mulberry?
White Mulberry has multiple uses, including culinary applications with its edible berries and leaves, as well as historical significance in the silk industry. - Are White Mulberry berries edible?
Yes, White Mulberry berries are edible and are used in various culinary dishes, jams, and desserts. - Are White Mulberry leaves edible?
Yes, White Mulberry leaves are edible, and historically, they have been used as the primary food source for silkworms in the silk industry. - What are the potential health benefits of White Mulberry?
Studies suggest potential health benefits, including blood sugar management and anti-inflammatory properties, primarily attributed to compounds in the leaves. - How do you care for a White Mulberry tree?
White Mulberry trees require well-drained soil, regular watering, and occasional pruning. Full sun exposure is preferable for optimal growth. - What pests and diseases affect White Mulberry trees?
Common pests include aphids, and diseases such as powdery mildew can affect White Mulberry trees. Vigilance and proper care can help mitigate these issues. - Can White Mulberry wood be used for crafting?
Yes, White Mulberry wood is durable and has been historically used for crafting tools, furniture, and bows. - Is White Mulberry safe?
Generally, White Mulberry is safe. However, caution is advised, as unripe fruits may cause stomach upset, and individuals should be aware of any personal sensitivities. - How long does a White Mulberry tree live?
With proper care, White Mulberry trees can live for several decades, contributing to the landscape over an extended period. - What is the ecological contribution of White Mulberry?
White Mulberry contributes to the environment by supporting biodiversity, attracting wildlife with its berries, and aiding in soil conservation. - What is the significance of White Mulberry in history?
White Mulberry has played a crucial role in Chinese traditions and the silk industry, making it a historically significant and culturally relevant tree. - Can White Mulberry be grown in different climates?
Yes, White Mulberry is adaptable to various climates and is cultivated in a range of regions globally. - Any interesting facts about White Mulberry?
Yes, an interesting fact is that White Mulberry leaves are the primary food source for silkworms, contributing to the production of silk.














Leave your comment