Scarlet Macaw
- December 7, 2023
- 0 comment
The Scarlet Macaw (Ara macao) is easily identifiable by its brilliant red, blue, and yellow plumage, a distinctive long tail, and a powerful beak. These birds are not only visually stunning but also showcase high levels of intelligence and social behavior. Stands as one of the most captivating and vibrant members of the parrot family. Known for its dazzling plumage and intelligent demeanor, these birds are native to the rainforests of Central and South America.
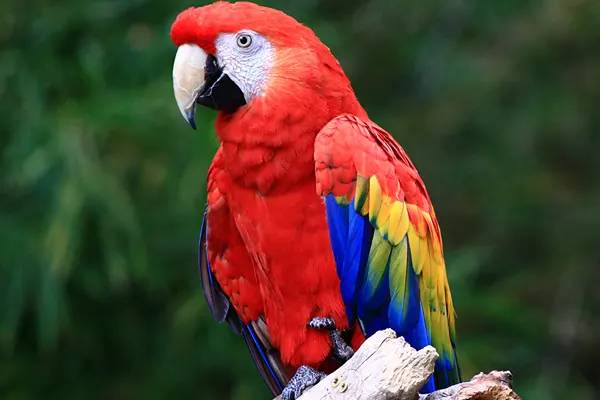

Scarlet Macaw
- Lifespan: 40 to 50 Years
- Habitat: Lush rainforests, tropical and subtropical forests.
- Diet: Fruits, Nuts, Seeds, and Berries, Flowers, Leaves, and even Insects.
- Size: 81 to 99 cm
- Weight: 2 to 3.5 lbs
- Wingspan: 91 cm from tip to tip
- Conservation Status: Least Concern, Relatively Stable
- Population Trend: Local populations may face threats and declines due to habitat destruction, illegal pet trade, and other human-induced factors.
Scarlet Macaws have a rich evolutionary history dating back millions of years. Their origins can be traced to the ancient rainforests, where they evolved unique adaptations to thrive in diverse environments. Scarlet Macaws exhibit diversity not only in appearance but also in their habitats and behaviors. From the Amazon rainforest to the Andes Mountains, different subspecies have adapted to specific niches.
Species Type
The Scarlet Macaw (Ara macao) belongs to the species Ara, which is a genus of large, colorful macaws within the family Psittacidae. Psittacidae is a family of parrots, and within this family, the genus Ara includes several distinct species of macaws, each characterized by its own unique features and range.
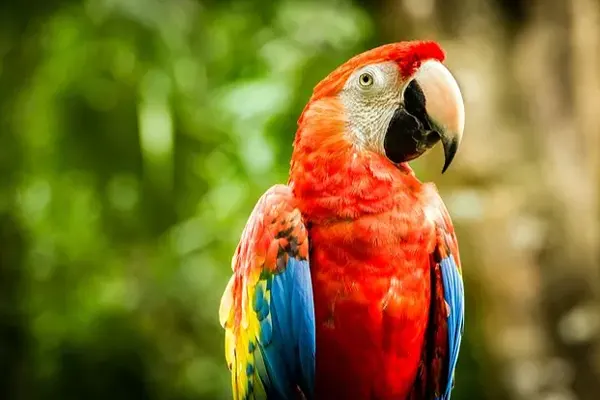
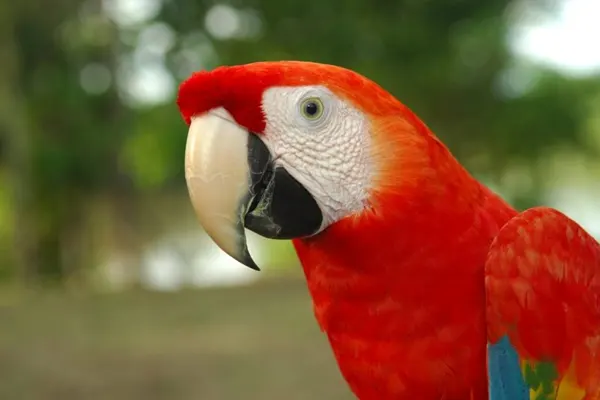


Males may be slightly larger than females, but this difference is often challenging to discern without direct comparison. Males might have slightly larger and broader heads compared to females, but this distinction may not be easily noticeable without close examination.
Feather Coloration
Scarlet Red: The dominant color that gives the Scarlet Macaw its name is the brilliant scarlet red that covers a significant portion of its body. This intense red hue is most prominent on the wings, back, and tail feathers. Complementing the scarlet red, the wings of the Scarlet Macaw feature a deep royal blue color. This blue extends to the primary and secondary flight feathers, creating a striking contrast against the red plumage.
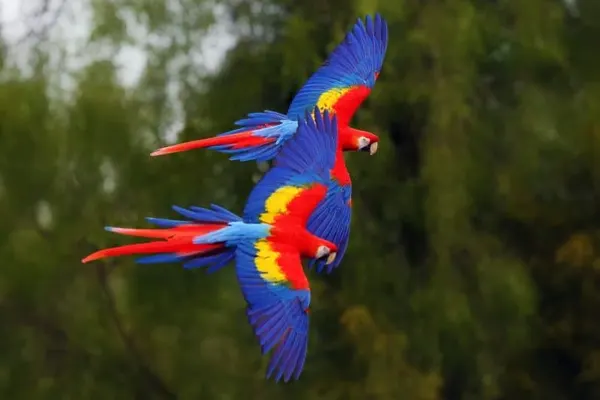


- Green Accents: While not as conspicuous as the red, blue, and yellow, the feathers on the upper surface of the wings and the back often exhibit a greenish tint. This green adds a subtle yet significant element to the macaw’s overall color palette.
- Black Feather Tips: The wingtips and tail feathers often have black accents, providing further contrast to the vibrant primary colors. These black-tipped feathers contribute to the intricate and detailed appearance of the Scarlet Macaw.
- Color Variations: While the standard coloration described above is characteristic of Scarlet Macaws, there can be some variations in individual birds. Factors such as age, diet, and genetics can influence the intensity and brightness of the colors.
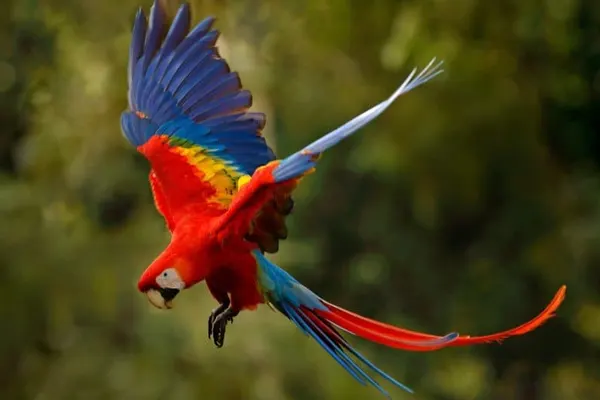
Flight Characteristics
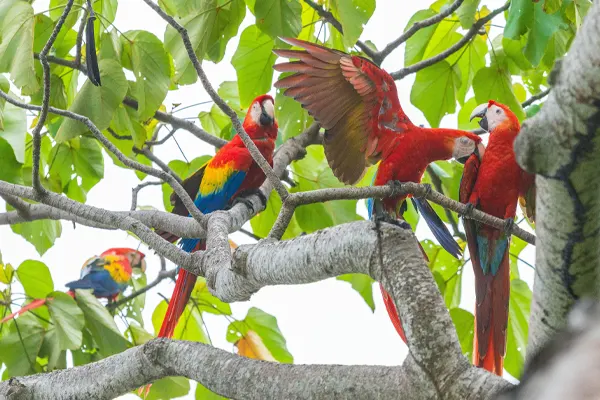
Scarlet Macaws are powerful fliers with strong and well-developed wing muscles. Their flight is characterized by steady, direct wing beats, allowing them to cover considerable distances in search of food, water, and suitable habitats. Scarlet Macaws are highly social birds and often fly in pairs or small groups. This social behavior extends to their flight, where they maintain close proximity to one another. This not only fosters social bonds but also provides safety in numbers.
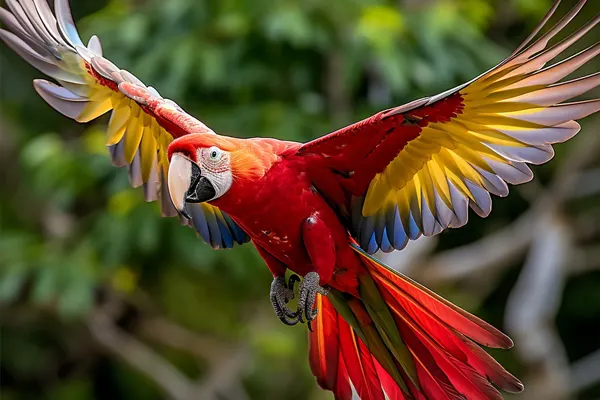

- Efficient Gliding: Scarlet Macaws are capable of gliding over long distances with minimal wing flapping. This energy-efficient gliding is particularly useful during periods of extended flight, helping them conserve energy while covering vast areas in search of resources.
- Precision Landing: When approaching a perch or nesting site, Scarlet Macaws display remarkable precision in their landing. Their strong wings and tail feathers allow them to make controlled descents, ensuring a safe and accurate landing on branches or other surfaces.
Migration Patterns
Scarlet Macaws (Ara macao) are not typically known for long-distance migrations like some bird species. Instead, they are known for their relatively sedentary lifestyle within their preferred habitats, particularly the tropical rainforests of Central and South America. These macaws tend to establish territories and remain within the regions that provide the necessary resources for their survival.
Scarlet Macaws are considered resident birds, meaning they do not undertake regular seasonal migrations. They are known to inhabit specific territories throughout the year.
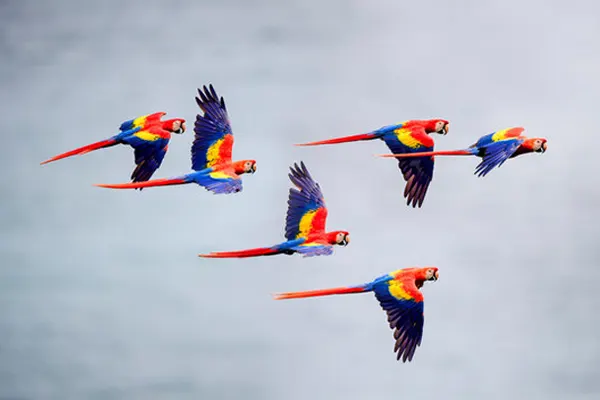
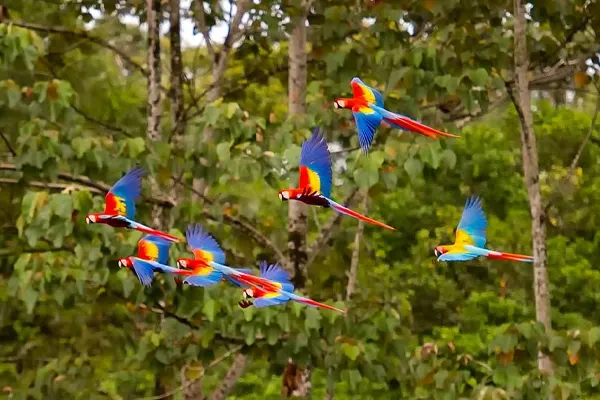


Scarlet Macaws are primarily non-migratory birds with a tendency to establish and defend territories within their preferred habitats. While some local movements and dispersal may occur, their overall lifestyle revolves around the abundant and diverse resources found in the tropical rainforests they call home.
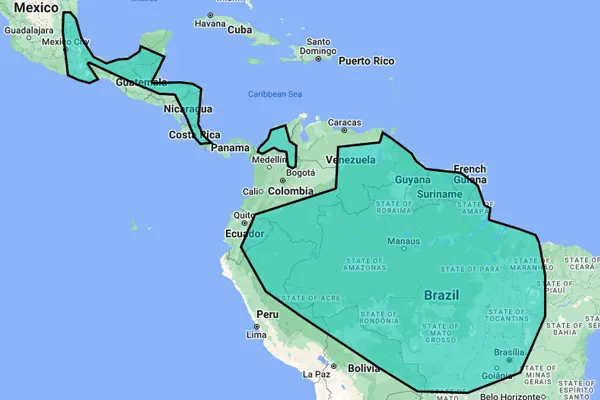
Habitat & Distribution
The Scarlet Macaw (Ara macao) is predominantly found in the lush and diverse ecosystems of tropical rainforests in Central and South America. These vibrant birds exhibit a strong preference for habitats characterized by dense canopies, varied tree species, and proximity to water sources. They thrive in both lowland and montane rainforests, showcasing their adaptability to different altitudes within their range.
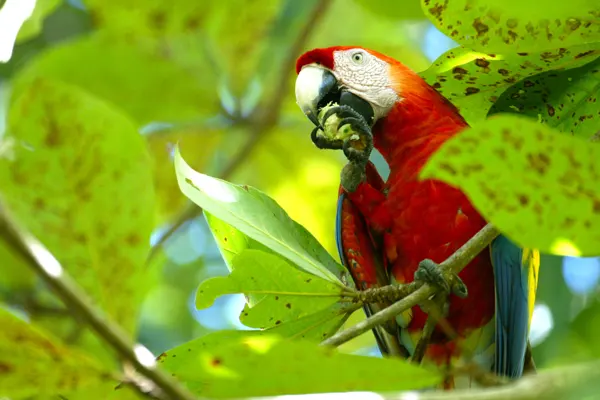
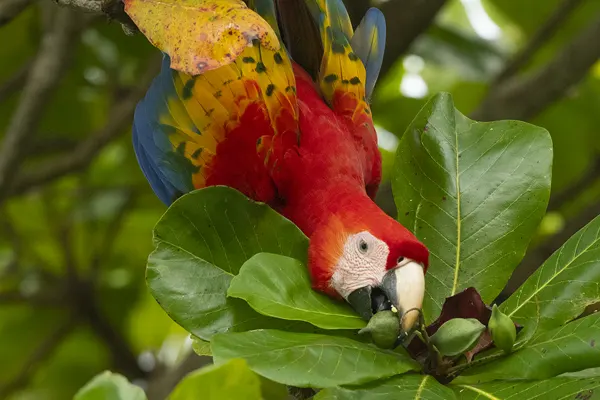


- Central America: Scarlet Macaws are found in parts of Mexico, particularly in the Yucatán Peninsula. They extend through Central America, inhabiting regions in Belize, Guatemala, Honduras, Nicaragua, Costa Rica, and Panama.
- South America: In South America, their range covers a significant portion of the Amazon Rainforest, extending into countries such as Colombia, Venezuela, Ecuador, Peru, and Brazil. Within these countries, they inhabit various habitats, from lowland rainforests to mountainous regions.
Behavioral Traits
The Scarlet Macaw (Ara macao) exhibits a range of behavioral traits that contribute to its adaptability in its native habitats. These behaviors, shaped by both instinct and learned responses, play a crucial role in their daily lives, social interactions, and survival strategies. Understanding these behavioral traits is essential for conservation efforts, as it helps create effective strategies for the protection and preservation of Scarlet Macaw populations in their natural habitats.
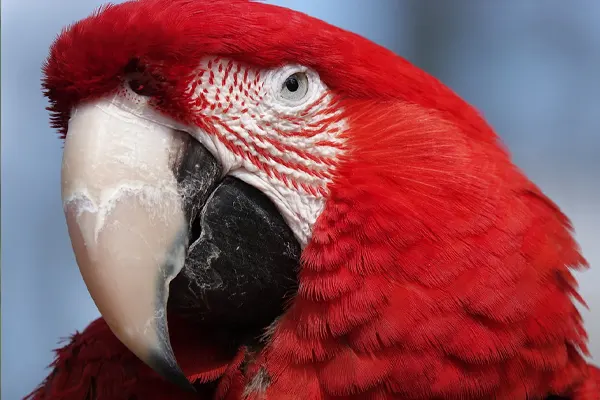

- Intelligence: Like many parrot species, Scarlet Macaws are intelligent birds. They demonstrate problem-solving skills, learn through observation, and can be trained to perform various tasks. Their intelligence contributes to their ability to adapt to changing environmental conditions.
- Playful Behavior: Scarlet Macaws exhibit playful behaviors, including flying acrobatics, hanging upside down, and playing with objects. Play is not only a form of entertainment but also contributes to the development of physical and cognitive skills.
Role in Ecosystem
Scarlet Macaws are efficient seed dispersers. As they feed on fruits, nuts, and seeds, they inadvertently scatter seeds across the landscape. This behavior aids in the regeneration of plant species, contributing to the diversity and structure of the forest. By dispersing seeds, Scarlet Macaws contribute to the maintenance of plant diversity. The seeds they disperse may germinate and grow into new plants, ensuring the continued existence of various tree and plant species in the ecosystem.
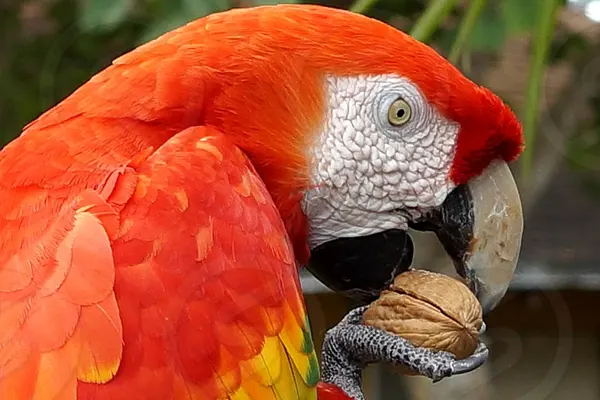

- Habitat Modification: The act of excavating nesting cavities in trees can lead to the creation of new microhabitats. The abandoned nest sites may be used by other bird species, insects, or small mammals, contributing to increased biodiversity in the area.
- Pollination: While not primary pollinators, Scarlet Macaws can contribute to the pollination of certain plant species. As they feed on nectar-containing flowers, pollen can adhere to their feathers and be transferred between flowers, facilitating the reproductive processes of these plants.
- Prey for Predators: Scarlet Macaws serve as a food source for various predators, including large birds of prey and mammals. Their presence in the food web provides sustenance for these predators, influencing the dynamics of predator-prey relationships.
- Indicator of Ecosystem Health: The presence and behavior of Scarlet Macaws can serve as indicators of the overall health of their ecosystems. Population declines or behavioral changes may signify ecological imbalances, prompting researchers and conservationists to investigate and address underlying issues.
Dietary Habits
The diverse dietary habits of Scarlet Macaws highlight their adaptability to the varied environments they inhabit, from the rainforests of Central and South America to drier habitats. Their foraging behaviors also play a crucial role in the ecological processes of their ecosystems, contributing to seed dispersal and the maintenance of plant diversity. Conservation efforts that protect their habitats and ensure the availability of their natural food sources are essential for the well-being of Scarlet Macaw populations.
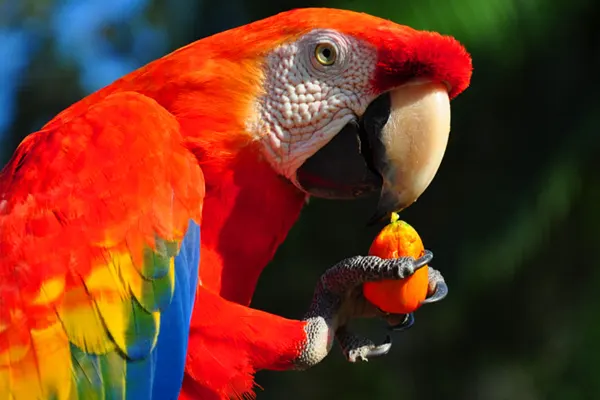
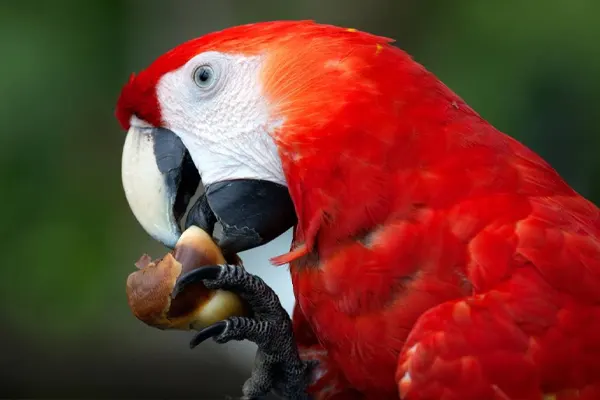


- Fruits: The primary component of the Scarlet Macaw’s diet is fruits. They feed on a wide variety of fruits from different tree species, including figs, palm fruits, and berries. The macaw’s strong, hooked beak is well-suited for breaking open the tough outer shells of fruits to access the nutritious pulp and seeds.
- Nuts and Seeds: Scarlet Macaws are known for their ability to crack open hard nuts and seeds using their powerful beaks. They favor seeds from various tree species, and their foraging behaviors contribute to seed dispersal in their habitats. Some of the seeds they consume may pass through their digestive system, facilitating the germination of new plants.
- Flowers and Nectar: Scarlet Macaws may feed on flowers, extracting nectar from certain species. While they are not primary pollinators, their visits to flowers may contribute to the transfer of pollen between plants.
Interesting Facts
Beyond their visually stunning plumage, Scarlet Macaws are known for their vibrant personalities. These intelligent birds are quick learners and can mimic human speech with surprising accuracy. Their playful and inquisitive nature makes them popular choices as pets, but it’s important to note that they require extensive care and attention due to their social and intellectual needs. In the wild, their expressive behaviors and vocalizations contribute to the lively atmosphere of the tropical rainforests they call home. The Scarlet Macaw’s animated personality adds another layer of fascination to its already captivating presence in the natural world.
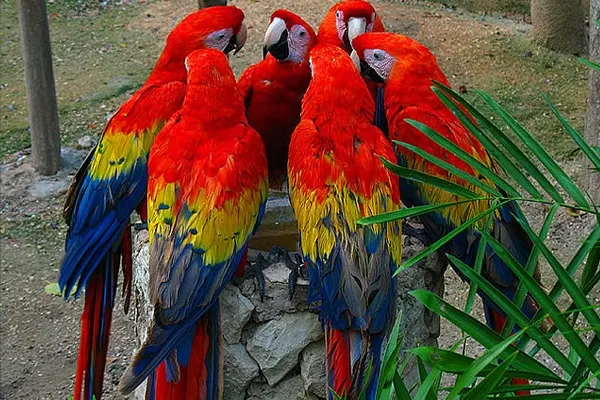

- Intelligent and Social: Like many parrot species, Scarlet Macaws are highly intelligent and social birds. They exhibit complex behaviors, engage in problem-solving activities, and form strong bonds with their mates and flock members.
- Monogamous Pair Bonds: Scarlet Macaws are known to form monogamous pair bonds that can last for life. Mated pairs engage in mutual grooming, share parental responsibilities, and often display affectionate behaviors.
- Distinct Vocalizations: Scarlet Macaws are vocal birds with a diverse range of calls, squawks, and screams. Their loud vocalizations serve various purposes, including communication with flock members, mate recognition, and territory marking.
- Strong Beak: Equipped with a powerful and hooked beak, Scarlet Macaws can easily crack open hard nuts and seeds. This adaptation allows them to access a variety of food sources in their natural habitats.
Nesting Habits
Scarlet Macaws exhibit a preference for nesting in tree cavities, particularly large, mature trees. They seek out specific types of trees, often favoring those with softer wood that is easier to excavate. The selection of nesting sites is a critical aspect of their reproductive strategy. The timing of nesting varies among populations, but in general, Scarlet Macaws tend to breed during the dry season when food resources are more abundant. The specific timing can be influenced by factors such as climate and food availability in their habitat.
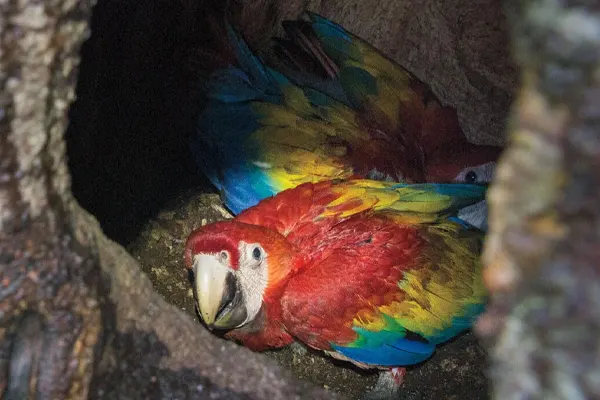


- Parental Care: Once the eggs hatch, the parents continue their cooperative efforts in caring for the chicks. They feed the chicks regurgitated food, consisting of predigested fruits and nuts, providing essential nutrients for their growth.
- Fledging and Independence: Scarlet Macaw chicks fledge, or develop the ability to fly, approximately 90 to 100 days after hatching. After fledging, the young birds may stay with their parents for some time, learning essential skills such as foraging and flying before becoming fully independent.
- Nesting Success and Site Reuse: The success of Scarlet Macaw nesting can be influenced by various factors, including the availability of suitable nesting sites and the abundance of food resources. In some cases, the same nesting sites may be reused in subsequent breeding seasons.
Melodious Song & Vocalizations
Scarlet Macaws (Ara macao) are not known for melodious songs in the traditional sense, they are highly vocal birds with a diverse range of calls, squawks, and screams. Their vocalizations serve various purposes and play a crucial role in communication within their social groups.
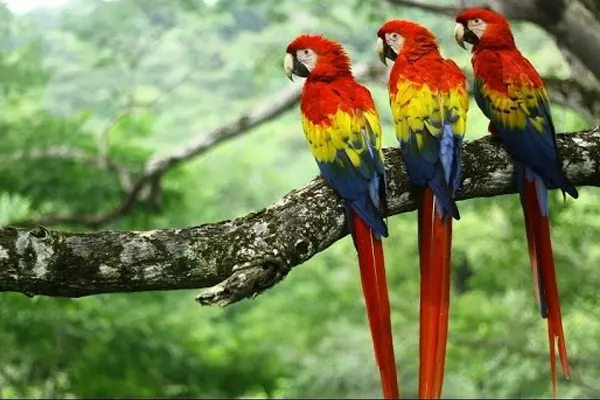

- Loud and Distinctive Calls: Scarlet Macaws are known for their loud and distinctive calls that can be heard over long distances. These calls are used for communication between individuals within the flock and serve to maintain contact, especially when flying or foraging in different areas.
- Contact Calls: The macaws use contact calls to stay in touch with their mate or other members of their social group. These calls help maintain cohesion within the flock, allowing individuals to communicate their location and well-being to one another.
- Mate Recognition: During the breeding season, Scarlet Macaws engage in specific vocalizations as part of their courtship behavior. These calls help in mate recognition and reinforce the bond between paired individuals.
- Territorial Calls: Scarlet Macaws are territorial birds, and their vocalizations play a role in marking and defending their territory. They may use loud calls and squawks to signal their presence and deter potential intruders.
Ecological Significance
The Scarlet Macaw (Ara macao) holds significant ecological importance within its native habitats, contributing to various ecological processes and maintaining the health and balance of ecosystems. Conserving Scarlet Macaw populations and their habitats is essential not only for the well-being of the species itself but also for the overall health and functioning of the diverse ecosystems they inhabit. Efforts to protect these birds contribute to the preservation of biodiversity and the ecological services provided by their unique behaviors.
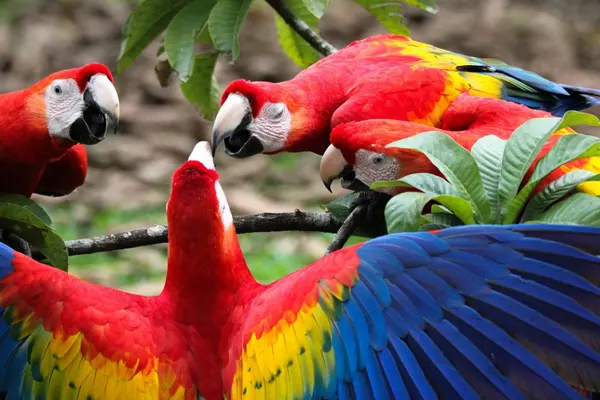

- Nutrient Cycling: The organic matter in the feces of Scarlet Macaws, which contains nutrients from the fruits and seeds they consume, contributes to nutrient cycling in the ecosystem. This process helps maintain soil fertility and supports the growth of vegetation.
- Keystone Species: Scarlet Macaws are considered keystone species, meaning they have a disproportionately large impact on their ecosystem relative to their abundance. Changes in their population or behavior can have cascading effects on other species and ecosystem dynamics.
- Biodiversity Maintenance: Through their interactions with the environment, Scarlet Macaws contribute to the overall maintenance of biodiversity. The interconnected relationships between these birds and various plant and animal species help sustain the complexity and resilience of their habitats.
Conservation Status
The Least Concern status indicates that, at the global level, the Scarlet Macaw is not currently facing a high risk of extinction. However, this general status may not reflect localized threats or population declines in specific regions. It’s important to note that conservation statuses can change over time as new data becomes available. Despite the overall Least Concern status, Scarlet Macaw populations face various threats and conservation challenges that vary across their range.
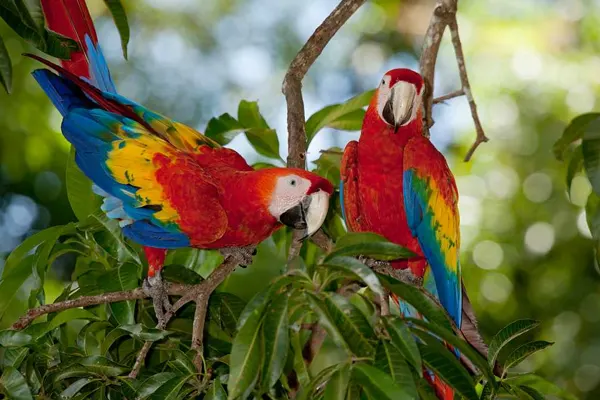
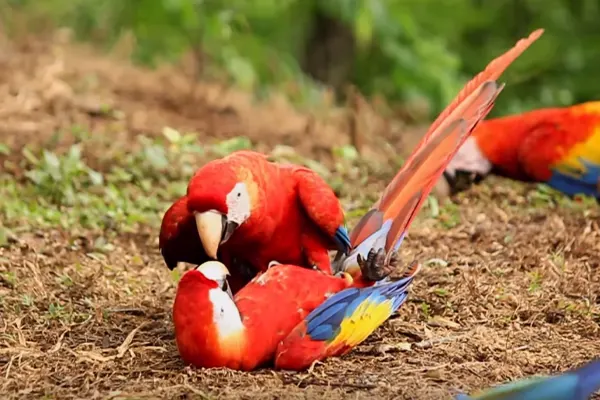


Conservation efforts for Scarlet Macaws involve habitat protection, anti-poaching measures, community engagement, and education. Establishing protected areas, enforcing wildlife protection laws, and promoting sustainable practices are essential components of conservation strategies.
- Illegal Pet Trade: The Scarlet Macaw is often targeted for the illegal pet trade due to its vibrant plumage and popularity in aviculture. Capture for the pet trade can have severe consequences for wild populations.
- Hunting: In some regions, Scarlet Macaws are hunted for their feathers, meat, or as a perceived threat to crops. Hunting can have detrimental effects on local populations, particularly when combined with other threats.
Research and Ongoing Studies
Researchers utilize technology such as GPS tracking, camera traps, and remote sensing to monitor Scarlet Macaw movements, assess habitat changes, and gather data on population trends. Technological advancements contribute to more effective and non-invasive monitoring methods.
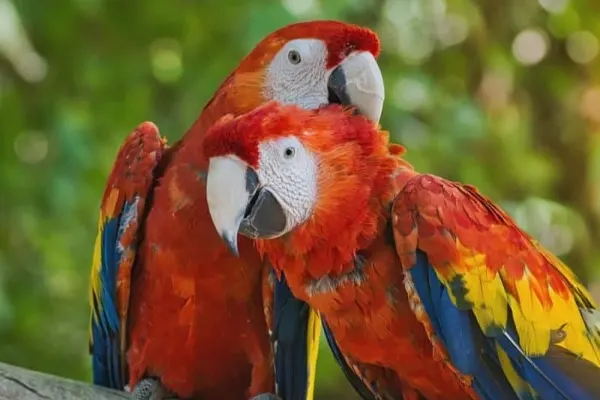

- Behavioral Ecology: Researchers are studying the behavioral ecology of Scarlet Macaws, including aspects such as nesting behavior, foraging strategies, vocalizations, and social dynamics within their flocks. Understanding these behaviors provides insights into their adaptation to their natural environment.
- Breeding and Reproduction: Studies focus on the reproductive biology of Scarlet Macaws, including nesting success, mate selection, and factors influencing breeding outcomes. Research in this area contributes to conservation efforts by identifying critical breeding habitats and potential threats to successful reproduction.
- Habitat Use and Selection: Ongoing studies investigate Scarlet Macaw habitat preferences, patterns of habitat use, and the impact of habitat fragmentation on their populations. This research aids in identifying key areas for habitat conservation and restoration.
- Genetics and Population Dynamics: Genetic studies help researchers understand the genetic diversity and population structure of Scarlet Macaw populations. This information is crucial for developing effective conservation strategies, particularly in addressing issues related to inbreeding and population declines.
Educational and Ecotourism
The presence of Scarlet Macaws (Ara macao) in their native habitats provides valuable educational and ecotourism opportunities, contributing to both conservation efforts and local economies. Scarlet Macaw habitats often overlap with indigenous communities. Ecotourism programs may integrate cultural experiences, allowing visitors to learn about traditional practices, folklore, and the coexistence of local communities with these iconic birds.
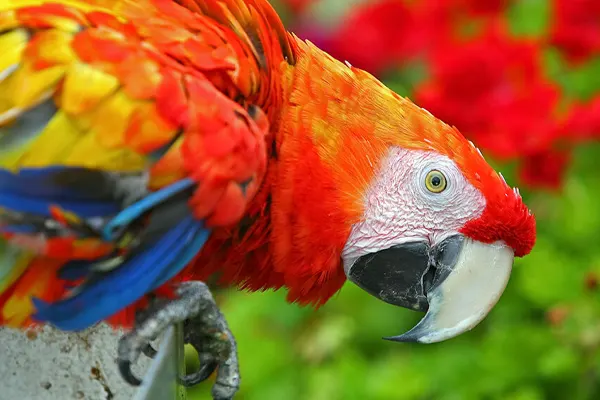

- Birdwatching Tours: Scarlet Macaws are popular attractions for birdwatchers. Guided birdwatching tours allow enthusiasts to observe these colorful birds in their natural habitats, often with the assistance of experienced naturalists who can provide information about their behavior and ecology.
- Photography Safaris: Ecotourism operators offer photography safaris focused on capturing the beauty of Scarlet Macaws and other wildlife. This not only provides memorable experiences for visitors but also creates opportunities to showcase the importance of conservation through visual storytelling.
- Community-Based Ecotourism: Initiatives involve local communities in providing guided tours, accommodations, and cultural experiences. Revenue generated from ecotourism activities can contribute to community livelihoods, providing economic incentives for conservation.
- Wildlife Sanctuaries and Reserves: Establishing wildlife sanctuaries and reserves that prioritize Scarlet Macaw conservation can attract ecotourists. These protected areas offer a chance to observe these birds while supporting their preservation in a controlled and sustainable manner.
Conclusion
The Scarlet Macaw (Ara macao) stands as a remarkable and iconic species, captivating both researchers and enthusiasts alike with its vibrant plumage, complex behaviors, and crucial ecological role. As we delve into the various aspects of the Scarlet Macaw’s life, it becomes evident that these birds are not only aesthetically captivating but also play a vital role in the ecosystems they inhabit.
From their diverse dietary habits and nesting behaviors to their vocalizations and cultural significance, Scarlet Macaws exemplify the intricate web of life within tropical rainforests. Their adaptability to various environments, from lush forests to drier habitats, showcases the resilience of this species in the face of environmental challenges.
However, the Scarlet Macaw is not without its share of threats. Habitat loss, illegal trade, and climate change pose significant risks to their populations. The delicate balance between human activities and the conservation of these magnificent birds requires thoughtful and concerted efforts.














Leave your comment