Antilopine Kangaroo
- January 22, 2024
- 0 comment
The Antilopine Kangaroo, scientifically known as Macropus antilopinus, is a remarkable marsupial species native to the northern regions of Australia. This unique kangaroo species stands out for its impressive size, with males reaching up to 1.8 meters (6 feet) in length and weighing around 70 kilograms (154 pounds), while females are slightly smaller, averaging 35 kilograms (77 pounds). Sporting a reddish-brown fur coat, Antilopine Kangaroos are well-adapted to their tropical savanna and woodland habitat, providing excellent camouflage amidst the vegetation. Notably, they possess large, rounded ears that enhance their sense of hearing, a crucial asset for detecting potential predators in their environment.
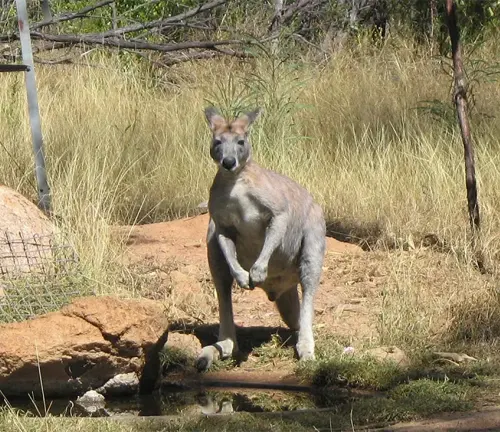

These kangaroos are herbivorous, primarily feeding on grasses, shrubs, and leaves, and possess an efficient digestive system to extract nutrients from their plant-based diet. Despite their solitary nature, they may form small groups, particularly during the wet season when food becomes more abundant. What makes their reproductive behavior fascinating is their ability to delay the development of embryos until environmental conditions are favorable, ensuring the survival of their young even in challenging circumstances. Although facing threats like habitat destruction and hunting, Antilopine Kangaroos are currently classified as a species of “Least Concern” on the IUCN Red List, emphasizing the importance of ongoing conservation efforts to protect these intriguing marsupials in their native Australian habitat.
| Characteristic | Description |
|---|---|
| Scientific Name | Macropus antilopinus |
| Size | Males: Up to 1.8 meters (6 feet); Females: Average 35 kilograms (77 pounds) |
| Appearance | Reddish-brown fur coat with large, rounded ears |
| Habitat | Northern Australia – Tropical savannas and woodlands |
| Diet | Herbivorous – Grasses, shrubs, leaves, vegetation |
| Predators | Dingoes, eagles, and occasionally large reptiles like crocodiles |
| Social Structure | Generally solitary, but may form small groups during the wet season |
| Reproductive Behavior | Embryo development delayed until favorable conditions |
| Gestation Period | Approximately 33-38 days |
| Lifespan (Wild) | 6-8 years |
| Conservation Status | “Least Concern” on the IUCN Red List |
| Conservation Efforts | Habitat preservation, population monitoring, research |
| Adaptation to Climates | Thrives in tropical savannas and various climates in northern Australia |
| Ecological Role | Influences plant growth through grazing and contributes to nutrient cycling |
| Seasonal Adaptations | May migrate for food or adjust feeding patterns |
| Social Behavior | Typically solitary, but can be seen in small groups |
| Jumping Ability | Excellent jumpers, capable of covering long distances |
| Main Threats | Habitat destruction and hunting |
| Captivity for Research | Some individuals kept for research and con |
Australia’s Enigmatic Marsupial

In the vast and diverse continent of Australia, one can find an array of unique and fascinating wildlife. From the adorable koalas to the intimidating crocodiles, Australia’s fauna is truly extraordinary. Among the lesser-known but equally intriguing inhabitants of this continent is the Antilopine Kangaroo. In this article, we will delve into the world of this enigmatic marsupial, exploring its characteristics, habitat, behavior, and conservation status.
Physical Characteristics
Size and Appearance
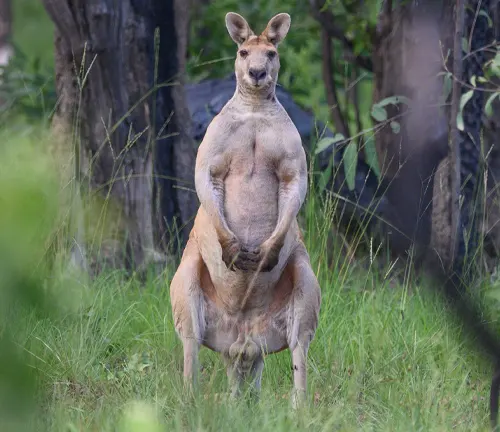
Antilopine Kangaroos are one of the largest kangaroo species, with males reaching up to 1.8 meters (6 feet) in length and weighing around 70 kilograms (154 pounds). Females are slightly smaller, with an average weight of 35 kilograms (77 pounds). They are characterized by their reddish-brown fur, which provides excellent camouflage in their natural habitat.


Unique Features
One of the most distinctive features of the Antilopine Kangaroo is its long, slender legs and relatively short tail. These adaptations allow them to move swiftly and gracefully through their environment. Additionally, they have large, rounded ears, which enhance their sense of hearing, a crucial asset for detecting predators.
Habitat and Distribution
Antilopine Kangaroos are primarily found in the tropical savannas and woodlands of northern Australia. Their distribution extends across the Northern Territory, northern Queensland, and Western Australia. These kangaroos are well-suited to this habitat, as it provides them with ample food resources and protection.
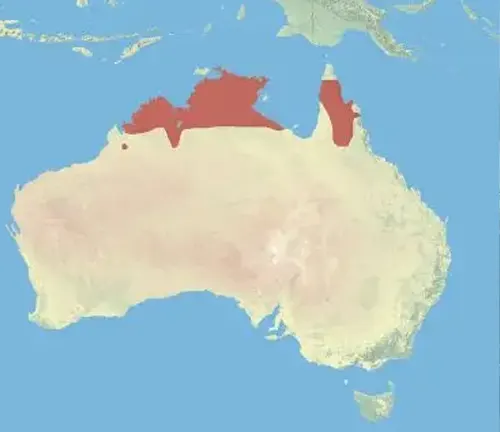
Behavior and Lifestyle
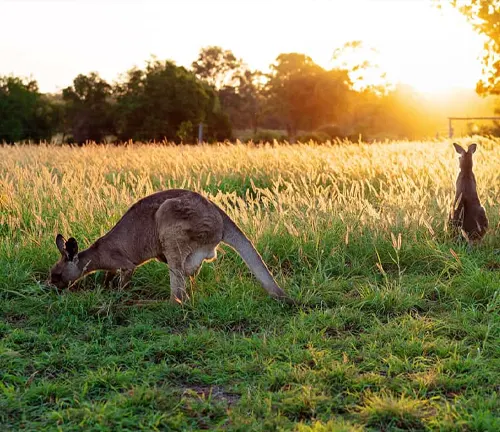

Feeding Habits
Like other kangaroo species, Antilopine Kangaroos are herbivorous, primarily feeding on grasses, shrubs, and leaves. Their digestive system is adapted to efficiently extract nutrients from plant material, allowing them to thrive in their arid environment.
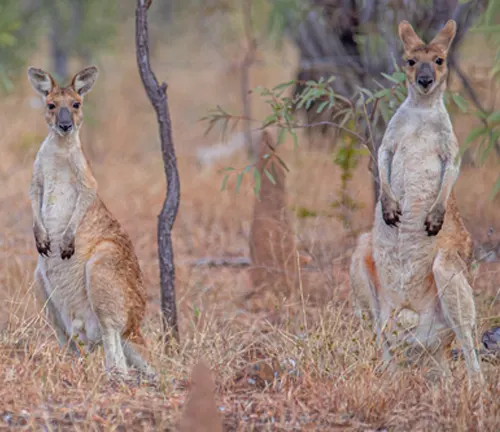
Social Structure
Antilopine Kangaroos are generally solitary animals, unlike the more social Eastern Grey Kangaroos. However, they may form small groups, especially during the wet season when food is more abundant. These groups are usually composed of females and their young.
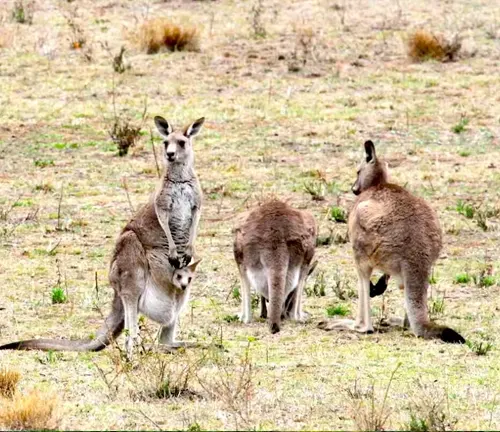
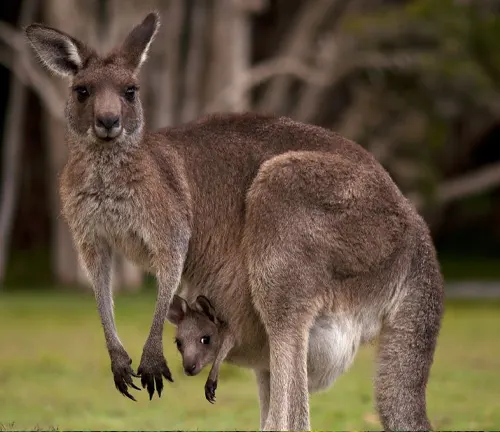


Reproduction
The reproductive cycle of Antilopine Kangaroos is intriguing. Females have the ability to delay the development of their embryos until environmental conditions are favorable for raising young. This unique adaptation ensures the survival of their offspring even in challenging circumstances.
Conservation Status
Despite their adaptation to their natural habitat, Antilopine Kangaroos face various threats, including habitat destruction and hunting. In some areas, their populations have declined due to land development and increased human activity. Consequently, they are classified as a species of “Least Concern” on the International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN) Red List. Nonetheless, continuous monitoring and conservation efforts are essential to protect their populations.
Different Species
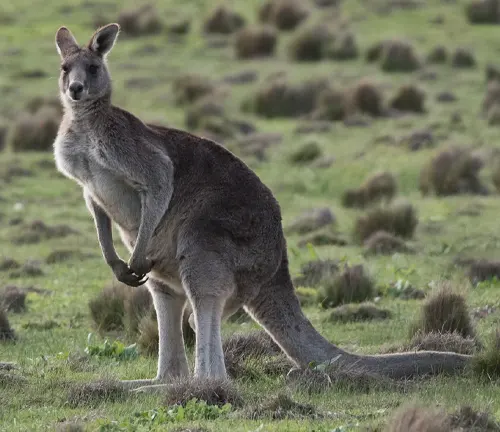
Eastern Grey Kangaroo
(Macropus giganteus)
The Eastern Grey Kangaroo is one of the largest marsupials and is known for its silver-grey fur and powerful build. It is found on the eastern coast of Australia.
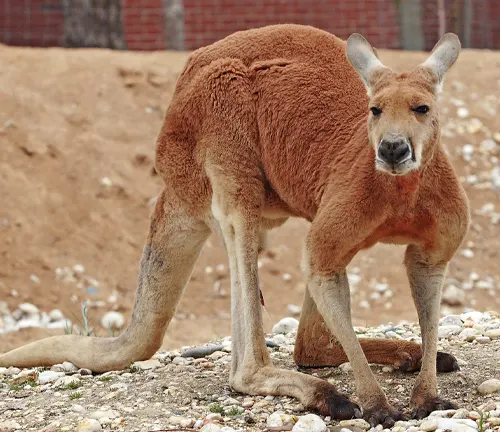


Red Kangaroo
(Macropus rufus)
The Red Kangaroo is the largest marsupial and is known for its distinctive red-brown fur. It inhabits arid and semi-arid regions of Australia.
Western Grey Kangaroo
(Macropus fuliginosus)
This species is found in southwestern and western Australia and is smaller than the Eastern Grey Kangaroo. It has a grey coat and is often seen in grasslands.
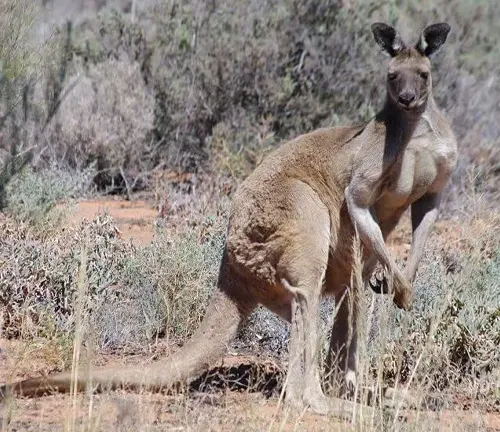
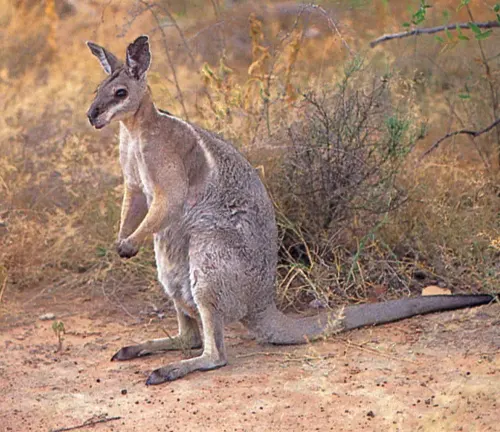


Wallaby
Wallabies are smaller relatives of kangaroos and belong to the same genus, Macropus. There are several species of wallabies, including the Agile Wallaby, Red-Necked Wallaby, and Swamp Wallaby, each with its unique characteristics and distribution.
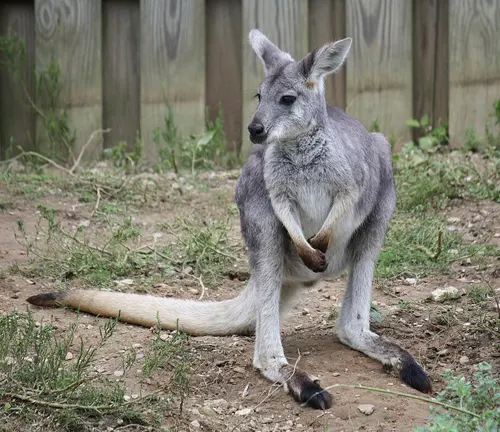
Wallaroo
Wallaroos are intermediate in size between kangaroos and wallabies. They include species like the Common Wallaroo (Macropus robustus) and the Black Wallaroo (Macropus bernardus).

Frequently Asked Question (FAQs)
- What is the scientific name of the Antilopine Kangaroo?
- The scientific name of the Antilopine Kangaroo is Macropus antilopinus.
- Where can you find Antilopine Kangaroos in the wild?
- Antilopine Kangaroos are primarily found in northern Australia, including regions in the Northern Territory, northern Queensland, and Western Australia.
- How big do Antilopine Kangaroos grow?
- Antilopine Kangaroos can reach impressive sizes, with males growing up to 1.8 meters (6 feet) in length and weighing around 70 kilograms (154 pounds). Females are slightly smaller, with an average weight of 35 kilograms (77 pounds).
- Are Antilopine Kangaroos herbivores?
- Yes, Antilopine Kangaroos are herbivores, meaning they primarily feed on plant material.
- What is the primary diet of Antilopine Kangaroos?
- The primary diet of Antilopine Kangaroos consists of grasses, shrubs, leaves, and other vegetation found in their natural habitat.
- Do Antilopine Kangaroos have any natural predators?
- Yes, Antilopine Kangaroos have natural predators, including dingoes, large birds of prey like eagles, and occasionally, large reptiles such as crocodiles.
- How do Antilopine Kangaroos defend themselves from predators?
- Antilopine Kangaroos rely on their speed and agility to evade predators. They are known for their powerful hind legs, which allow them to make rapid escapes by hopping away from threats.
- Are Antilopine Kangaroos solitary animals or do they live in groups?
- Antilopine Kangaroos are generally solitary animals, although they may form small groups, especially during the wet season when food is more abundant. These groups typically consist of females and their young.
- What is the reproductive behavior of Antilopine Kangaroos?
- The reproductive behavior of Antilopine Kangaroos includes delayed implantation, which allows females to postpone the development of embryos until favorable environmental conditions for raising young are met.
- How long is the gestation period of Antilopine Kangaroos?
- The gestation period for Antilopine Kangaroos is approximately 33-38 days.
- What is the lifespan of Antilopine Kangaroos in the wild?
- In the wild, Antilopine Kangaroos typically have a lifespan of 6-8 years.
- Are Antilopine Kangaroos considered endangered or threatened?
- Antilopine Kangaroos are currently classified as a species of “Least Concern” on the International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN) Red List, indicating that they are not considered endangered or threatened.
- What are the major conservation efforts in place to protect Antilopine Kangaroos?
- Conservation efforts aimed at protecting Antilopine Kangaroos include habitat preservation, monitoring of populations, and research to better understand their ecological needs.
- Do Antilopine Kangaroos adapt to different climates within their range?
- Antilopine Kangaroos are adapted to the tropical savannas and woodlands of northern Australia, which includes a range of climates from semi-arid to wetter regions.
- What role do Antilopine Kangaroos play in their ecosystem?
- Antilopine Kangaroos play a vital role in their ecosystem by influencing plant growth through grazing and contributing to nutrient cycling.
- How do Antilopine Kangaroos cope with the seasonal changes in their habitat?
- During seasonal changes, Antilopine Kangaroos may migrate to areas with more abundant food resources or adjust their feeding patterns to cope with fluctuations in their environment.
- Are Antilopine Kangaroos social animals, or do they prefer solitude?
- While generally solitary, Antilopine Kangaroos may form small groups, especially during certain times of the year.
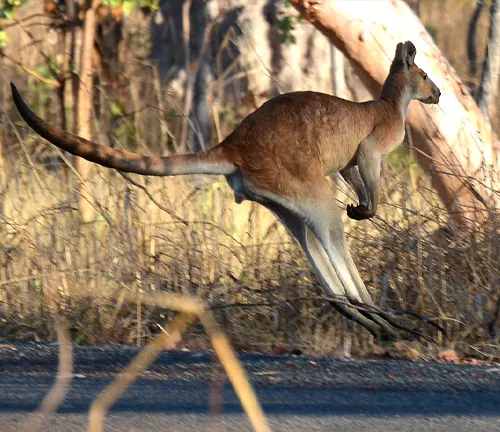
- Can Antilopine Kangaroos jump high like other kangaroo species?
- Yes, like other kangaroo species, Antilopine Kangaroos are skilled jumpers and can cover large distances in a single leap when they need to escape or travel.
- What are the main threats to the Antilopine Kangaroo’s survival in the wild?
- Main threats include habitat destruction due to land development and increased human activity, as well as hunting in some areas.
- Are Antilopine Kangaroos kept in captivity for conservation or research purposes?
- Yes, some Antilopine Kangaroos are kept in captivity for conservation and research purposes to better understand their biology and contribute to their preservation in the wild.














Leave your comment