Macaques Monkey
- January 16, 2024
- 0 comment
Macaques monkeys, belonging to the genus Macaca, represent a captivating and diverse group of primates that inhabit various regions across the globe. These intelligent and social animals are characterized by their distinctive physical features, ranging from the expressive faces of rhesus macaques to the adaptable long-tailed macaques found in Southeast Asia. Living in groups called troops, macaques exhibit intricate social structures and hierarchies, engaging in complex communication through vocalizations, facial expressions, and body language. Their diet is remarkably varied, including fruits, leaves, insects, and small vertebrates, showcasing their adaptability to different environments.
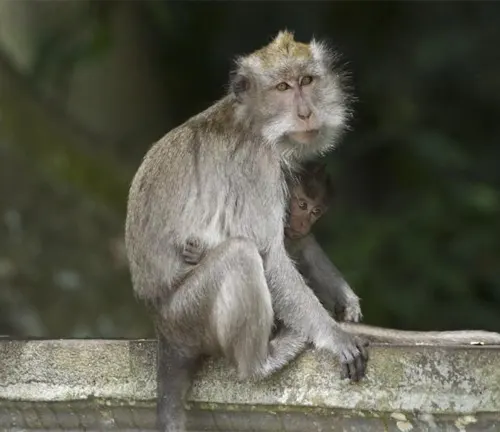

Macaques have played a role in scientific research, particularly in fields like neuroscience, owing to their genetic and physiological similarities to humans. Despite their significance, macaques face challenges such as habitat loss, climate change, and ethical concerns related to captivity and scientific experiments. Conservation efforts are crucial to preserving these primates, ensuring their survival and the intricate balance they bring to their ecosystems. Beyond their ecological importance, macaques hold cultural significance, making appearances in literature, art, and folklore across various societies. Understanding the enigmatic world of macaques is not only an exploration of the animal kingdom but also a call to appreciate and protect these fascinating creatures for generations to come.
| Characteristic | Details |
|---|---|
| Genus | Macaca |
| Distribution | Varied, spanning Asia, Africa, and parts of Europe |
| Social Structure | Living in groups (troops) with intricate hierarchies |
| Physical Characteristics | Diverse, including red faces (rhesus), short tails (pig-tailed), and expressive features |
| Habitat | Diverse environments from rainforests to arid plains |
| Diet | Omnivores, consuming fruits, leaves, insects, and small vertebrates |
| Communication | Vocalizations, facial expressions, and body language for social interaction |
| Lifespan | Typically 20 to 30 years, varying by species |
| Adaptations | Tailored to survive in different habitats, exhibiting behavioral and physical adaptations |
| Scientific Research | Valuable subjects in neuroscience and behavioral studies due to genetic and physiological similarities |
| Challenges | Habitat loss, climate change, ethical concerns in captivity and research |
| Conservation | Essential for protecting vulnerable populations and preserving biodiversity |
| Cultural Significance | Found in literature, art, and folklore, symbolizing various qualities in different societies |
Macaques Monkey: Exploring the Enigmatic Primates
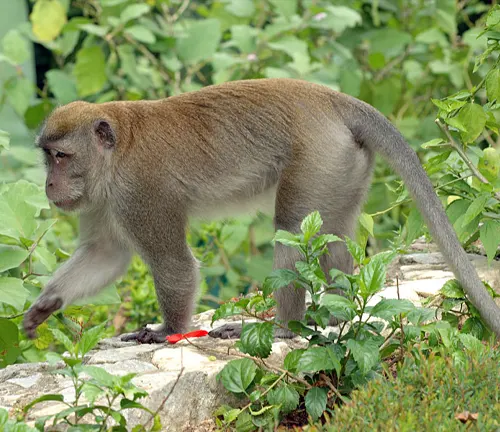

Macaques monkeys, with their fascinating characteristics and diverse species, hold a unique place in the animal kingdom. From their physical features to social behaviors, these primates captivate researchers and enthusiasts alike. In this article, we delve into the world of macaques, uncovering their classification, habitat, behavior, and the intricate web of interactions they share with humans.
Macaques monkeys, scientifically known as Macaca, belong to the Old World monkey family. These primates are distributed across various regions, showcasing remarkable adaptability to diverse environments.
Despite their commonality, macaques play a crucial role in maintaining ecological balance, contributing to the overall health of their habitats.
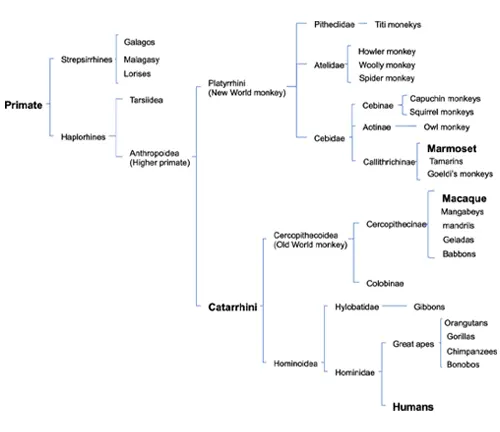
Classification and Species
Different Species of Macaques
The Macaca genus includes several species, each exhibiting unique characteristics. Understanding their classification provides insights into the diversity of these primates.
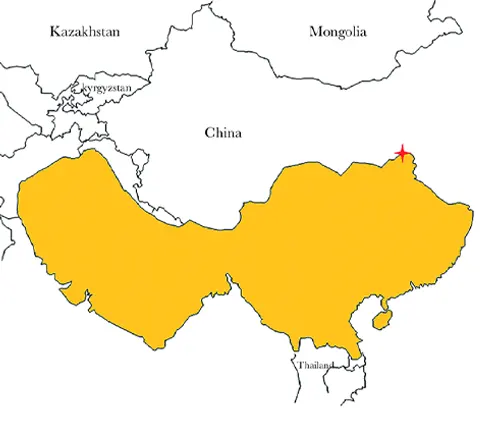
Geographic Distribution
Macaques are not confined to specific continents; their distribution spans Asia, Africa, and parts of Europe, showcasing their adaptability to different climates and terrains.
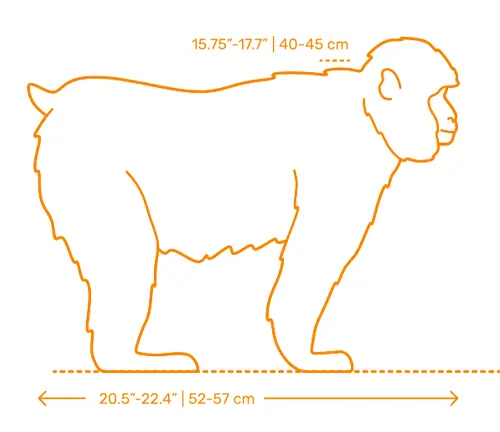
Physical Characteristics
Size and Weight
Macaques exhibit a wide range of sizes, from the petite crab-eating macaque to the robust Tibetan macaque. Understanding their physical attributes sheds light on their evolutionary adaptations.
Notable Features
Distinct facial expressions, prehensile tails, and a variety of fur colors contribute to the visual appeal of macaques, making them easily distinguishable within their species.
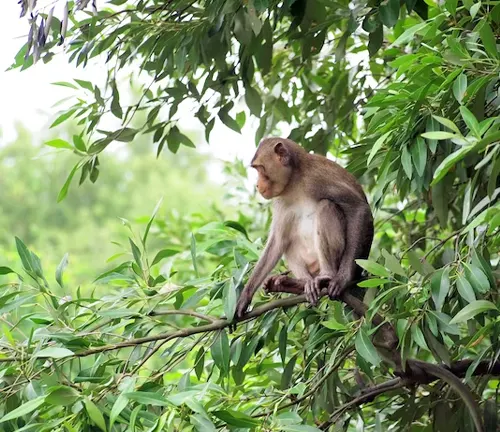
Habitat and Behavior
Natural Habitat
Macaques inhabit diverse environments, ranging from dense rainforests to arid plains. Exploring their natural habitats unveils the challenges they face in the wild.
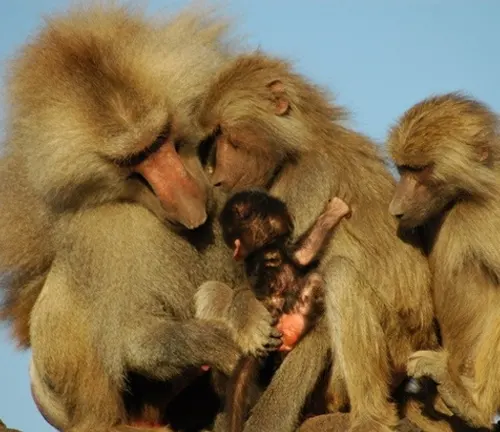


Social Behavior and Hierarchies
Known for their intricate social structures, macaques establish hierarchies that dictate group dynamics. Observing these behaviors provides valuable insights into their cooperative and competitive nature.
Diet and Feeding Habits
Varied Diet
Macaques are omnivores with a diverse diet that includes fruits, leaves, insects, and small vertebrates. Examining their feeding habits showcases their adaptability to different food sources.
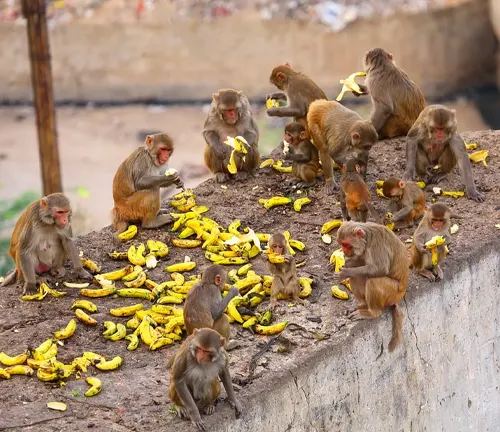

Hunting and Foraging
The hunting and foraging techniques employed by macaques vary across species. Some rely on group efforts, while others exhibit individual prowess in securing sustenance.
Reproduction and Life Cycle
Mating Rituals
Macaques engage in intricate mating rituals, showcasing behaviors that strengthen social bonds. Understanding their reproductive processes provides a glimpse into their complex social structures.
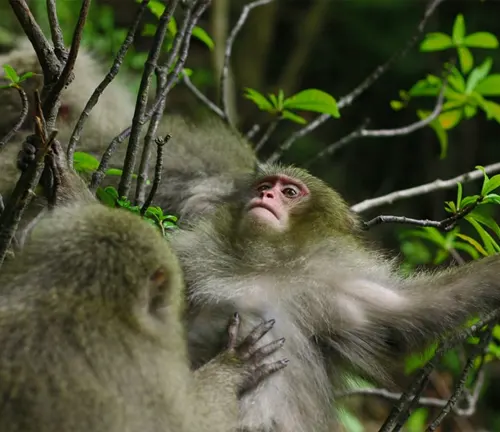
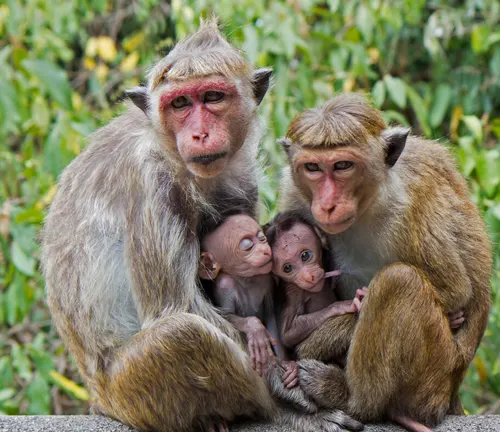


Gestation and Infancy
The gestation period and infancy of macaques involve unique challenges. Exploring these aspects sheds light on the vulnerabilities faced by the young members of their species.
Interactions with Humans
Historical Significance
Throughout history, macaques have held cultural and symbolic importance in various societies. Their roles in folklore and traditions contribute to the rich tapestry of human-animal interactions.
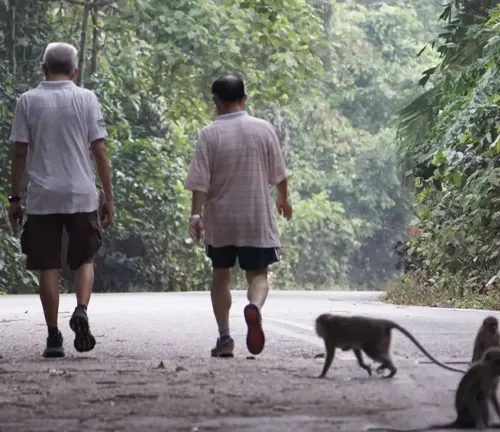

Conservation Efforts
As human activities impact macaque populations, conservation efforts become imperative. Examining ongoing initiatives helps raise awareness about the importance of preserving these primates.
Challenges and Threats
Environmental Threats
Macaques face challenges from habitat loss, climate change, and other environmental factors. Understanding these threats underscores the urgency of conservation efforts.
Human-Related Challenges
Interaction with humans poses additional challenges, from poaching to the impact of urbanization. Examining these challenges encourages a holistic approach to macaque conservation.
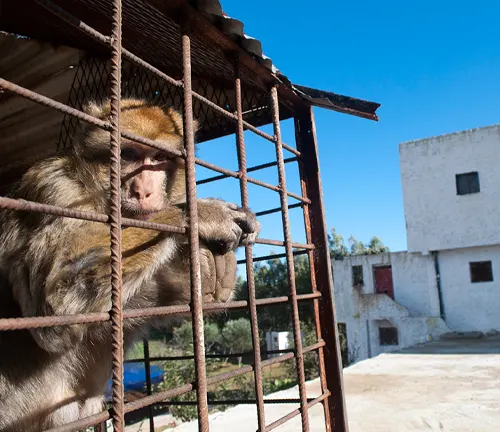

Unique Adaptations
Survival Strategies
Macaques exhibit unique adaptations that contribute to their survival in diverse environments. Studying these strategies provides valuable insights for wildlife conservation.
Evolutionary Adaptations
The evolutionary history of macaques has shaped their current characteristics. Exploring their adaptations over time enhances our understanding of their place in the animal kingdom.
Different Species
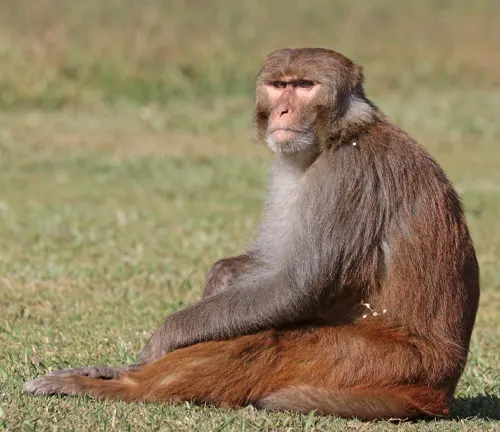
Rhesus Macaque
(Macaca mulatta)
Found in South, Central, and Southeast Asia, known for their distinctive red faces and reclusive behavior.
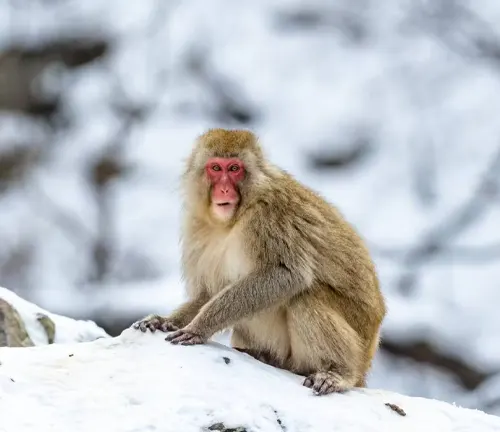


Japanese Macaque
(Macaca fuscata)
Native to Japan, these macaques are famous for their adaptation to snowy environments and the use of hot springs during winter.
Long-tailed Macaque
(Macaca fascicularis)
Widely distributed in Southeast Asia, these macaques are known for their social structures and adaptability to different habitats.
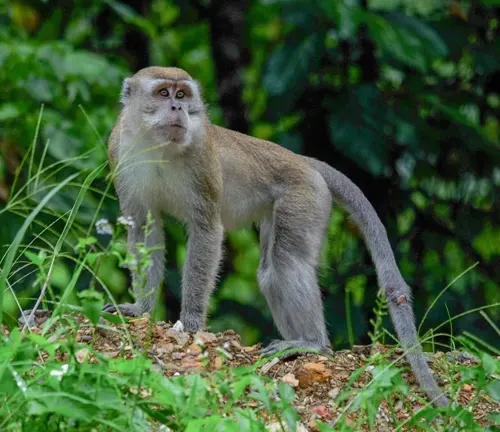
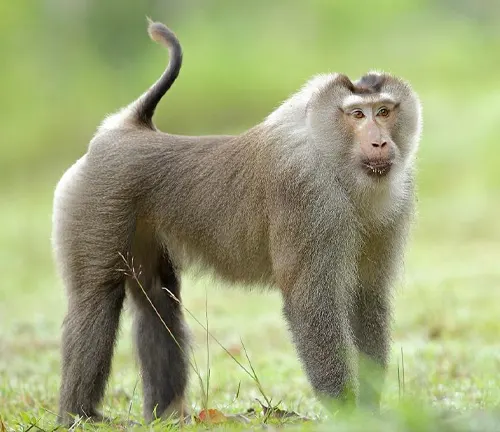


Pig-tailed Macaque
(Macaca nemestrina)
Found in Southeast Asia, these macaques are recognized by their short tails and social behaviors, living in groups called troops.
Assam Macaque
(Macaca assamensis)
Native to Southeast Asia, these macaques are known for their reddish-brown fur and inhabit tropical forests.
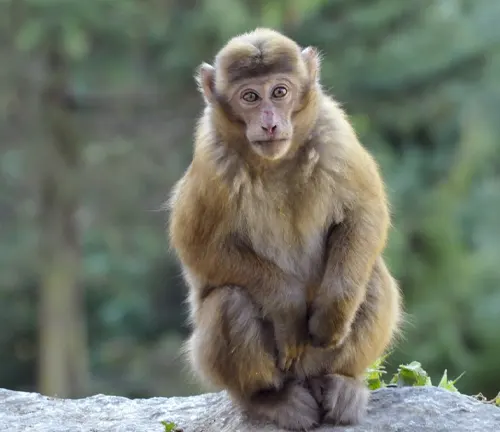
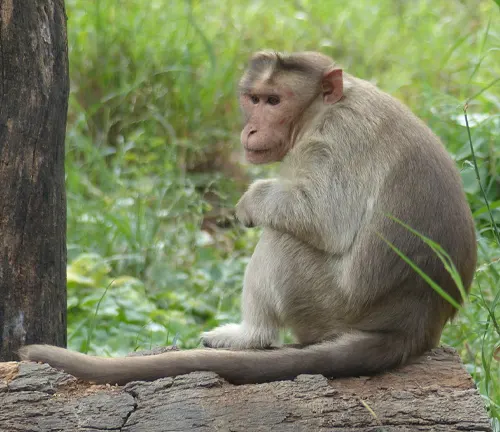


Bonnet Macaque
(Macaca radiata)
Indigenous to South India, these macaques have a cap-like crown of hair on their heads and are often found in urban areas.
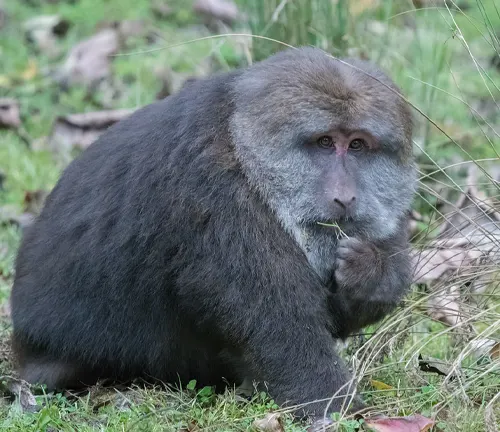
Tibetan Macaque
(Macaca thibetana)
Inhabiting the Tibetan plateau and parts of China, these macaques are adapted to cold climates and mountainous regions.
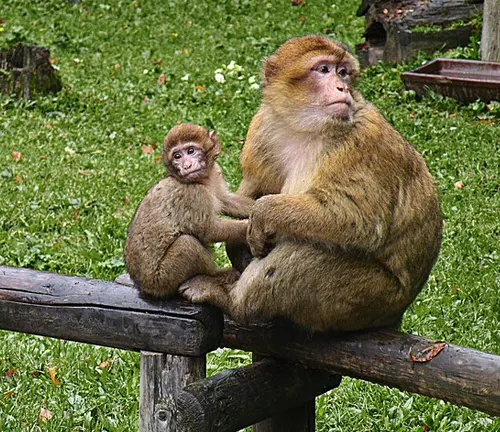


Barbary Macaque
(Macaca sylvanus)
Native to the Atlas Mountains in North Africa, these macaques are the only ones found outside of Asia and are known for their distinct appearance.
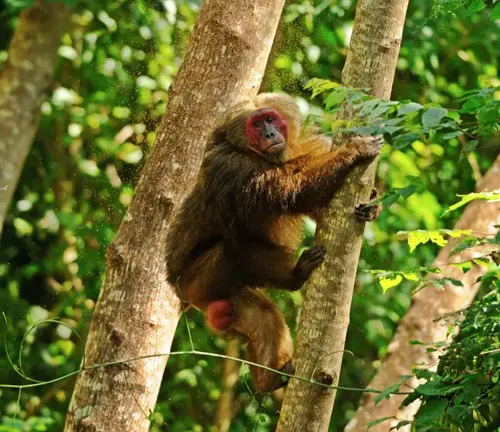
Stump-tailed Macaque
(Macaca arctoides)
Found in Southeast Asia, these macaques have short tails and live in various habitats, including tropical rainforests.
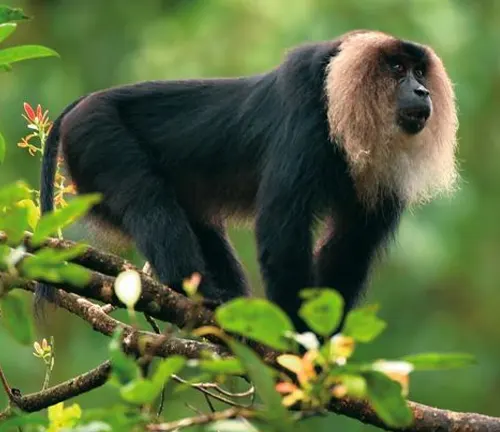


Lion-tailed Macaque (Macaca silenus)
Endemic to the Western Ghats of South India, these macaques are recognized by their distinctive manes and limited distribution.
Frequently Asked Question
- Are macaques endangered?
While some species of macaques are endangered due to habitat loss and other threats, not all are facing the same level of risk. Conservation efforts are essential to protect vulnerable populations. - Can macaques be kept as pets?
Keeping macaques as pets is not recommended. They have complex needs and social structures that are challenging to replicate in a domestic setting. Additionally, it raises ethical concerns about wildlife captivity. - Do macaques live in groups?
Yes, macaques are social animals that often live in groups called troops. These groups have hierarchical structures, and social interactions play a crucial role in their daily lives. - What is the lifespan of macaques?
The lifespan of macaques varies among species but generally ranges from 20 to 30 years. Factors such as habitat, diet, and the presence of predators can influence their life expectancy. - How do macaques communicate?
Macaques communicate using a combination of vocalizations, facial expressions, and body language. These forms of communication help them convey information about their intentions, emotions, and social status. - What do macaques eat?
Macaques are omnivores with a varied diet. They consume fruits, leaves, insects, small vertebrates, and, in some cases, even human food. Their diet depends on the species and the availability of food in their habitats. - Are macaques used in scientific research?
Yes, macaques have been used in scientific studies, particularly in fields such as neuroscience and behavioral research. Their genetic and physiological similarities to humans make them valuable subjects for certain experiments. - How do macaques adapt to different environments?
Macaques have evolved various adaptations to thrive in diverse habitats. These adaptations include physical features, behavioral strategies, and social structures that help them survive in environments ranging from tropical rainforests to mountainous regions. - Why are macaques important in popular culture?
Macaques often hold cultural significance and symbolism in various societies. They appear in literature, art, and folklore, representing different qualities and themes depending on the cultural context. - How can individuals contribute to macaque conservation?
Individuals can support macaque conservation by contributing to reputable conservation organizations, spreading awareness about the challenges macaques face, and advocating for ethical treatment and preservation of their natural habitats.














Leave your comment