Arctic Fox
- January 11, 2024
- 0 comment
The Arctic Fox, scientifically known as Vulpes lagopus, is a captivating species uniquely adapted to the extreme conditions of the Arctic regions in the Northern Hemisphere. Renowned for its stunning, snow-white fur, this small mammal undergoes a seasonal molt, transitioning to a brownish-gray coat during the summer for effective camouflage. With a compact size and remarkable agility, Arctic Foxes navigate challenging terrain with ease. Their hunting techniques are a testament to their resourcefulness, relying on acute senses to locate prey beneath the snow.
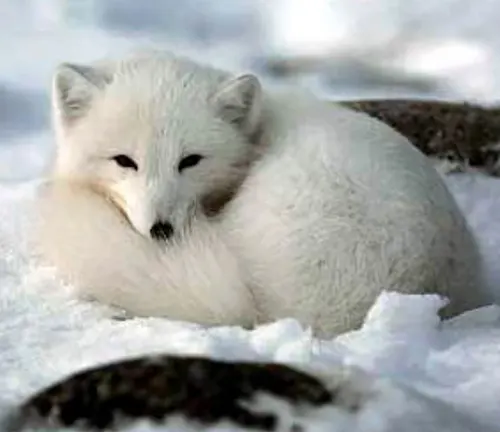

The Arctic Fox follows a distinct mating season, forming strong bonds with mates and sharing parental responsibilities. Despite their resilience, Arctic Fox populations face threats from natural predators, human-induced challenges, and the impacts of climate change. This species plays a crucial role in maintaining ecological balance in the Arctic ecosystem. Beyond its biological significance, the Arctic Fox holds symbolic value in various cultures and has found its place in folklore and mythology. Conservation efforts are underway to protect this species, emphasizing the importance of raising awareness and engaging individuals in safeguarding the Arctic Fox for future generations.
| Specification | Details |
|---|---|
| Scientific Name | Vulpes lagopus |
| Common Names | Arctic Fox, White Fox, Snow Fox |
| Size | Small and compact |
| Fur Color | Snow-white in winter, brownish-gray in summer |
| Fur Adaptations | Seasonal molt for camouflage and thermoregulation |
| Habitat | Arctic tundra and coastal areas |
| Native Regions | Arctic regions of North America, Europe, Asia |
| Hunting Techniques | Opportunistic predator with acute senses |
| Social Structure | Unique communal behaviors within a pack |
| Mating Season | Distinct mating season with strong mate bonds |
| Parental Responsibilities | Shared responsibilities in rearing offspring |
| Threats | Natural predators, human-induced challenges, climate change |
| Ecological Role | Maintains ecological balance in the Arctic ecosystem |
| Cultural Significance | Symbolic value in various cultures, folklore, and mythology |
| Conservation Status | Vulnerable, facing threats to population stability |
| Conservation Efforts | Ongoing initiatives to protect and preserve the species |
Arctic Fox: Unveiling the Secrets of the Frosty Wilderness
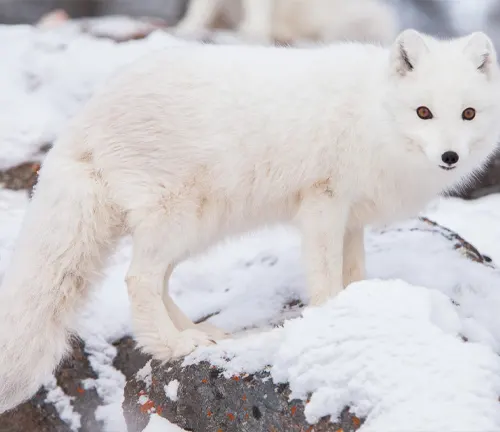

The Arctic Fox, also known as the “White Fox” or “Snow Fox,” is a fascinating creature that calls the frigid Arctic regions home. In this article, we delve into the various facets of the Arctic Fox’s life, from its unique adaptations to the challenges it faces in a changing environment.
The Arctic Fox (Vulpes lagopus) is a small mammal native to the Arctic regions of the Northern Hemisphere. Renowned for its stunning white coat, this fox has evolved remarkable features to survive in some of the harshest climates on Earth.
One of the distinctive features of the Arctic Fox is its dense fur coat, which changes color with the seasons to provide effective camouflage. Their small size, keen hunting skills, and ability to endure extreme temperatures make them well-adapted to their challenging environment.
Habitat and Distribution
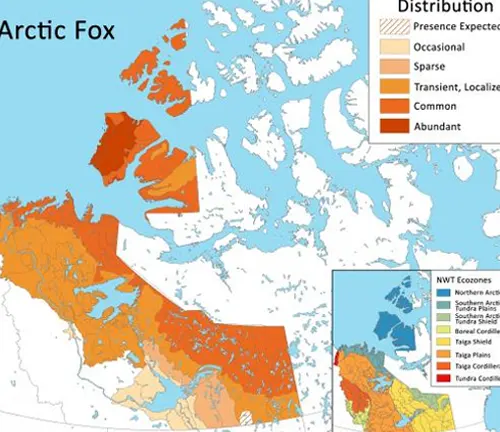
Arctic Fox’s Native Regions
The Arctic Fox predominantly inhabits the tundra and coastal areas of the Arctic region, including parts of North America, Europe, and Asia. Its distribution is closely tied to the availability of prey and suitable denning sites.
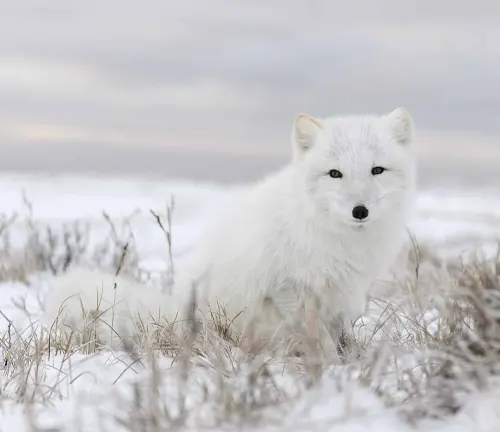
Seasonal Changes and Challenges
Surviving the harsh Arctic winters requires the Arctic Fox to undergo significant changes in behavior and physiology. Exploring how these changes occur offers valuable insights into the adaptability of this species.

Physical Characteristics
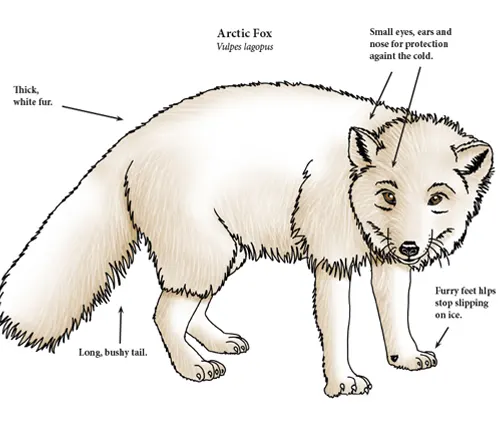
Fur Adaptations
The Arctic Fox’s fur undergoes a seasonal molt, transforming from a snow-white winter coat to a brownish-gray summer coat. This adaptation not only provides camouflage but also aids in thermoregulation, crucial for survival in the Arctic’s ever-changing climate.
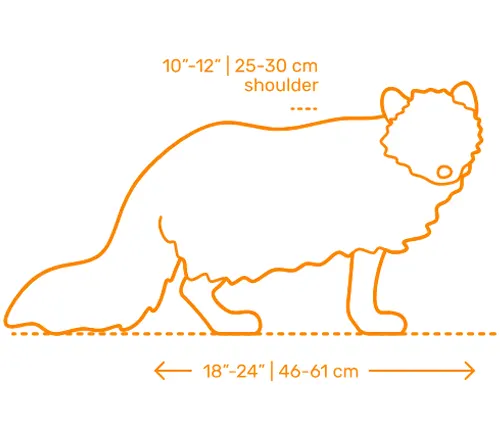
Size and Weight
Despite their small size, Arctic Foxes exhibit remarkable strength and agility. Understanding their physical characteristics provides a glimpse into the evolutionary traits that enable them to navigate the challenging Arctic terrain.
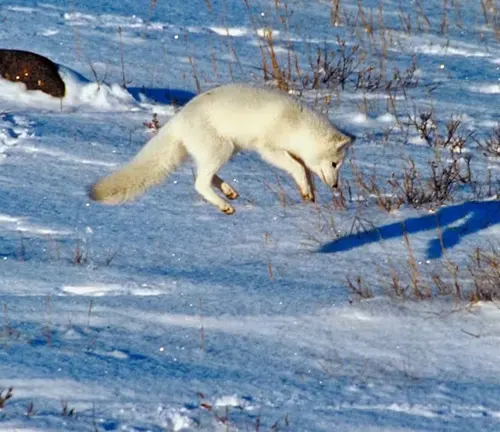
Behavior and Lifestyle
Hunting Techniques
Arctic Foxes are opportunistic predators, relying on their acute senses to locate prey beneath the snow. Examining their hunting techniques sheds light on their resourcefulness in securing sustenance in the vast Arctic landscape.

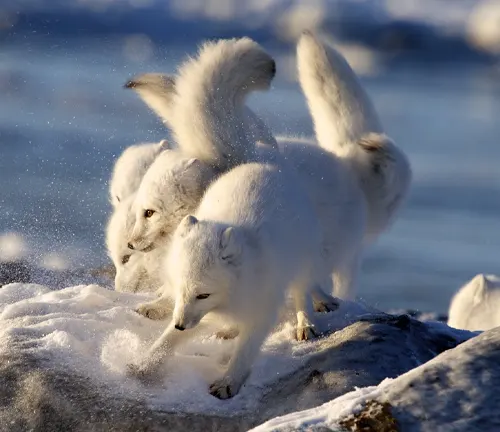
Social Structure
Unlike many other fox species, Arctic Foxes display a unique social structure. Investigating their communal behaviors and interactions reveals the intricacies of their relationships within the pack.
Reproduction
Mating Habits
The Arctic Fox follows a distinct mating season, during which pairs form strong bonds. Exploring their mating habits unveils the strategies employed by these creatures to ensure successful reproduction in a challenging environment.

Rearing of Offspring
The responsibilities of parenting are shared within Arctic Fox families. Examining the nurturing behaviors and protective instincts sheds light on the family dynamics of this captivating species.
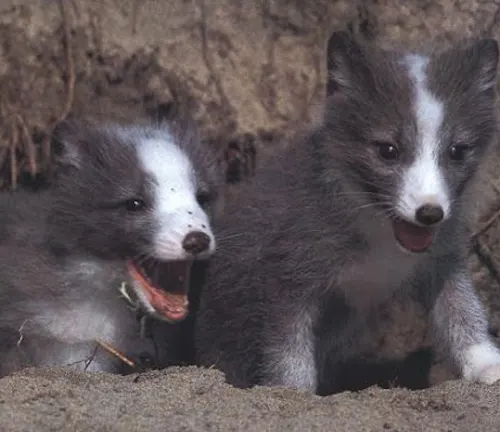

Threats and Conservation
Natural Predators
While Arctic Foxes have adapted to evade some predators, natural threats persist. Understanding the dynamics between Arctic Foxes and their predators contributes to a comprehensive view of their ecological role.
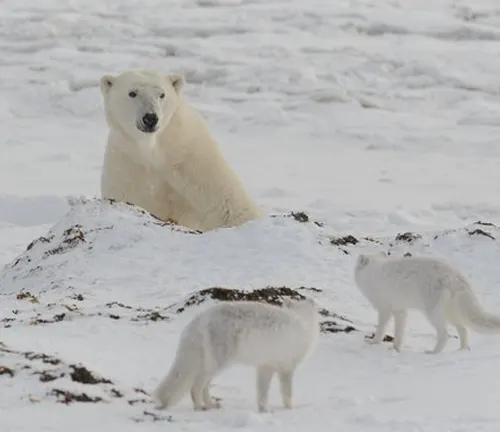

Human-Induced Threats
As human activities encroach upon Arctic habitats, the Arctic Fox faces new challenges. Examining the impact of anthropogenic factors on their survival underscores the importance of conservation efforts.

Conservation Efforts
Efforts to preserve the Arctic Fox involve both local initiatives and international collaborations. Delving into these conservation strategies provides valuable insights into the global commitment to safeguarding this species.
The Role of Arctic Fox in Ecosystem
Ecological Importance
Arctic Foxes play a crucial role in maintaining ecological balance. Exploring their impact on local ecosystems offers a deeper understanding of their significance beyond their charismatic appearance.
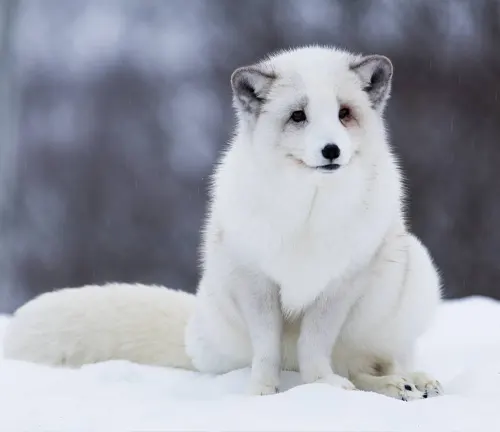

Interactions with Other Species
Examining the interactions between Arctic Foxes and other species within their habitat provides a holistic perspective on the intricate web of relationships that sustains Arctic ecosystems.
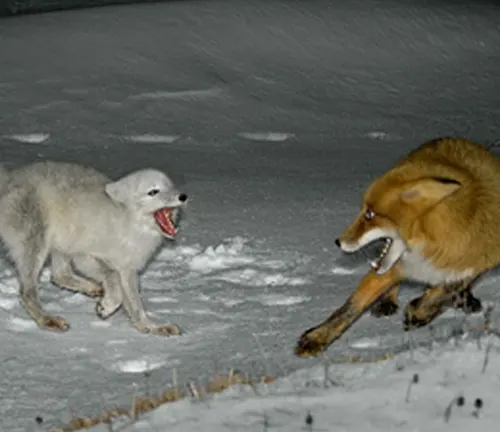

Arctic Fox in Popular Culture
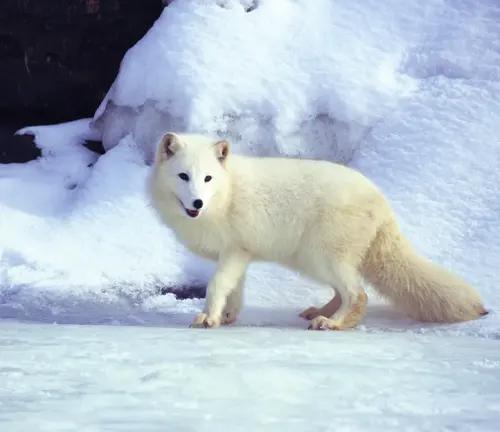

Symbolism
The Arctic Fox holds symbolic significance in various cultures. Unraveling the symbolism attached to this creature provides cultural context to its representation in folklore, mythology, and modern symbolism.
Folklore and Mythology
Throughout history, the Arctic Fox has been woven into the fabric of folklore and mythology. Exploring these narratives unveils the cultural richness associated with this enigmatic creature.
Captive Breeding and Domestication
Challenges and Benefits
Efforts to breed Arctic Foxes in captivity pose both challenges and benefits. Investigating these aspects offers insights into the complexities of conserving this species in controlled environments.
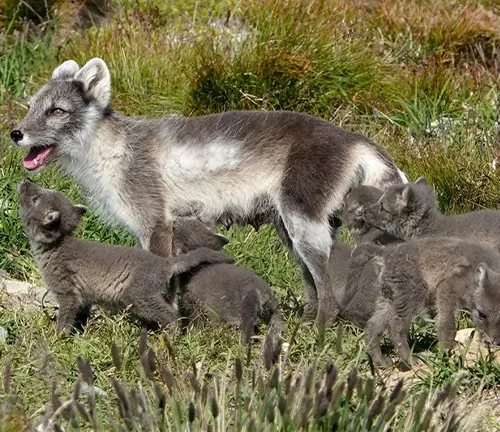

Legal Considerations
The legal frameworks surrounding the captive breeding and domestication of Arctic Foxes vary. Examining these regulations sheds light on the ethical considerations and responsibilities associated with keeping them in captivity.
Climate Change Impact
Adaptation Challenges
As the Arctic climate undergoes rapid changes, Arctic Foxes face new challenges. Understanding the impact of climate change on their habitat and behaviors highlights the urgency of conservation efforts.
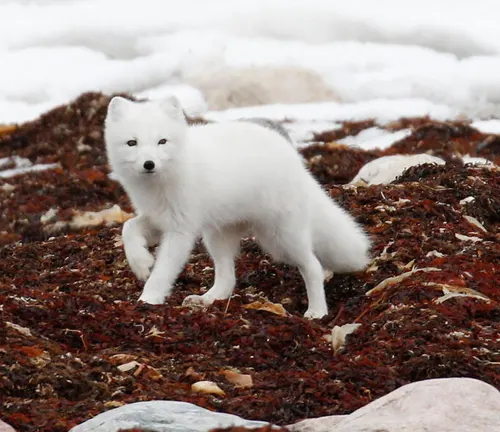

Research and Studies
Ongoing research and studies on the effects of climate change on Arctic Fox populations provide a glimpse into the scientific endeavors aimed at understanding and mitigating these challenges.
Arctic Fox as a Species at Risk
Vulnerable Status
Despite their resilience, Arctic Fox populations face threats that push them towards vulnerability. Exploring the factors contributing to their vulnerable status sheds light on the urgency of conservation measures.
Contributing Factors
Human activities, habitat loss, and climate change are among the key factors contributing to the precarious situation of Arctic Fox populations. Investigating these factors provides a comprehensive understanding of the challenges they face.
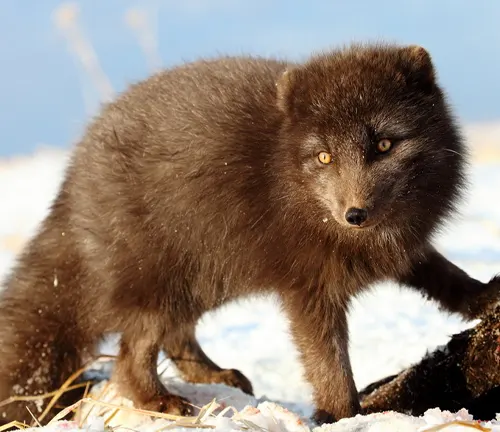
Different Species
Vulpes lagopus lagopus
(European Arctic Fox)
Found in the Arctic regions of Europe, including Scandinavia and Russia. This subspecies exhibits adaptations to the specific environmental conditions of the European Arctic.
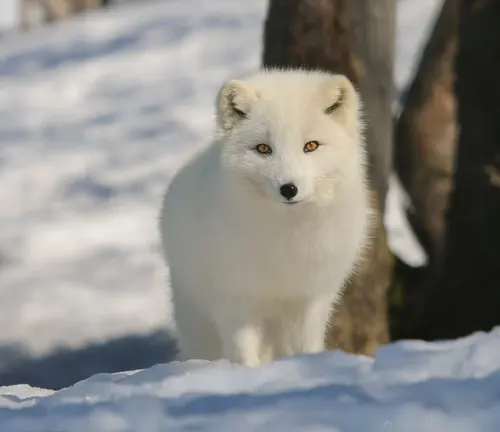

Vulpes lagopus pribilofensis
(Pribilof Islands Arctic Fox)
Inhabiting the Pribilof Islands in the Bering Sea, this subspecies has adapted to the unique island ecosystem. The Pribilof Islands Arctic Fox is known for its distinct characteristics.
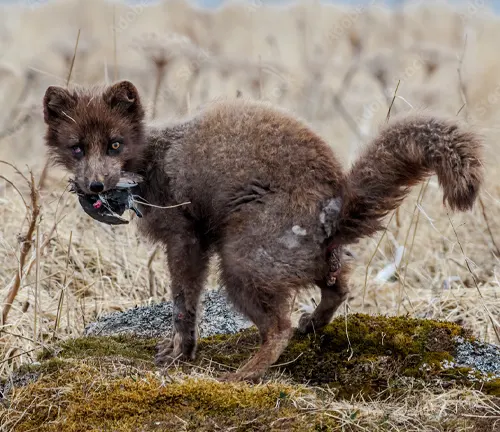

Vulpes lagopus semenovi
(Siberian Arctic Fox)
Native to Siberia and parts of Russia, the Siberian Arctic Fox thrives in the harsh Siberian climate. Its adaptations reflect the challenges posed by the Siberian tundra.
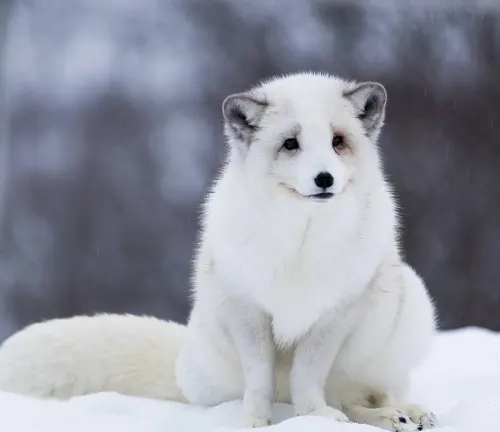

Vulpes lagopus beringensis
(Bering Sea Arctic Fox)
Inhabiting the Bering Sea region, including parts of Alaska and Russia, this subspecies showcases adaptations specific to the coastal and island environments surrounding the Bering Sea.

Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
- Are Arctic Foxes dangerous to humans?
Arctic Foxes are generally not considered dangerous to humans. They are elusive and shy, and interactions with humans are rare. - How does the Arctic Fox survive in such harsh conditions?
The Arctic Fox’s survival is attributed to its thick fur coat, specialized hunting techniques, and behavioral adaptations to cope with extreme cold. - Can Arctic Foxes be kept as pets?
Keeping Arctic Foxes as pets is not recommended. They are wild animals with specific environmental and dietary needs. - What are the main threats to Arctic Fox populations?
Natural predators, habitat loss, and climate change are significant threats to Arctic Fox populations. - How can individuals contribute to Arctic Fox conservation?
Individuals can contribute by supporting conservation organizations, raising awareness, and adopting sustainable practices to mitigate climate change. - Do Arctic Foxes hibernate during the winter?
Arctic Foxes do not hibernate. Instead, they remain active throughout the winter, relying on their fur and fat reserves for insulation. - What is the lifespan of an Arctic Fox in the wild?
In the wild, Arctic Foxes typically live for 3 to 6 years. Various factors, including environmental conditions and food availability, influence their lifespan. - How do Arctic Foxes communicate with each other?
Arctic Foxes communicate using a range of vocalizations, body language, and scent marking. Their social structure involves complex interactions within family groups. - Do Arctic Foxes migrate?
Some Arctic Fox populations are known to migrate in search of food. Migration patterns can vary based on geographical location and seasonal changes. - What is the status of the Arctic Fox population in terms of conservation?
Arctic Foxes are considered a species of least concern globally, but some regional populations, such as those in Scandinavia, face conservation challenges. - How do Arctic Foxes find food in the snow-covered landscape?
Arctic Foxes use their keen sense of hearing to locate prey beneath the snow. They may also rely on scent and memory to find cached food. - Are there any cultural beliefs or superstitions associated with the Arctic Fox?
Various indigenous cultures have traditional stories and beliefs related to the Arctic Fox, often portraying it as a clever and adaptive creature in folklore. - Do Arctic Foxes live in groups or are they solitary animals?
Arctic Foxes exhibit both solitary and social behaviors. While they may form family groups, some individuals may also lead more solitary lives. - How do Arctic Foxes adapt to the changes in daylight during the Arctic’s extreme seasons?
Arctic Foxes undergo changes in their behavior and activity patterns to adapt to the extreme variations in daylight, altering their hunting and resting habits accordingly.














Leave your comment