Red Fox
- January 11, 2024
- 0 comment
The red fox, scientifically known as Vulpes vulpes, is a captivating and adaptable creature that holds a special place in the natural world. Renowned for its striking reddish fur, the red fox belongs to the Canidae family and can be found across the Northern Hemisphere in diverse habitats. Beyond its aesthetic appeal, this small to medium-sized carnivore plays a crucial role in ecosystem balance as a keystone species. Its opportunistic omnivorous diet and clever hunting techniques showcase its versatility in adapting to various environments.
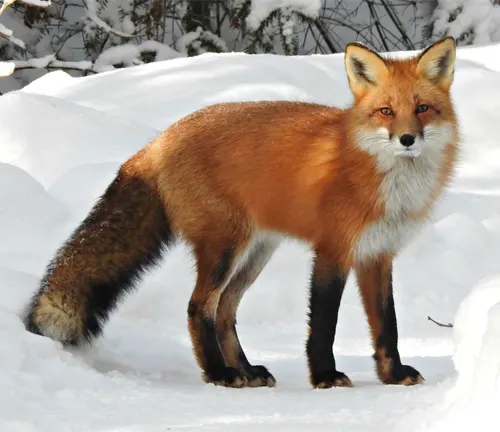

The red fox’s physical characteristics, from its bushy tail to its keen senses, contribute to its survival in the wild. Despite being primarily solitary, the species engages in family-oriented behavior during the crucial phases of mating, gestation, and rearing of cubs. The red fox has also left its mark in human history, symbolizing cunning and resilience in various cultures. However, it faces contemporary challenges, including human-wildlife conflict and environmental changes. Conservation efforts and wildlife reserves play vital roles in securing the red fox’s future. As we explore its fascinating biology, behavior, and cultural significance, we gain a deeper understanding of this remarkable species and the importance of preserving it for future generations.
| Aspect | Details |
|---|---|
| Scientific Name | Vulpes vulpes |
| Family | Canidae |
| Size | Small to medium-sized |
| Weight | Varies, but typically between 7 to 15 pounds (3 to 7 kg) |
| Fur Coloration | Mainly red, but variations include silver and cross foxes |
| Physical Features | Bushy tail, keen senses |
| Habitat | Diverse, spanning the Northern Hemisphere in various climates and landscapes |
| Diet | Opportunistic omnivore |
| Hunting Techniques | Agile and stealthy, combining predation and scavenging tactics |
| Reproduction | Mating season varies; gestation period approximately 53 days; cubs raised by parents |
| Social Structure | Primarily solitary, with family-oriented behavior during reproductive phases |
| Adaptations | Camouflaged fur, predominantly nocturnal behavior |
| Interactions with Humans | Historically significant in various cultures; faces challenges in urbanized areas |
| Conservation Status | Faces threats from human-wildlife conflict, habitat loss, and climate change |
| Conservation Efforts | Various initiatives and wildlife reserves contribute to the protection |
| Cultural Symbolism | Represents cunning and resilience; featured in art, literature, and folklore |
A Closer Look into Nature’s Cunning Creature
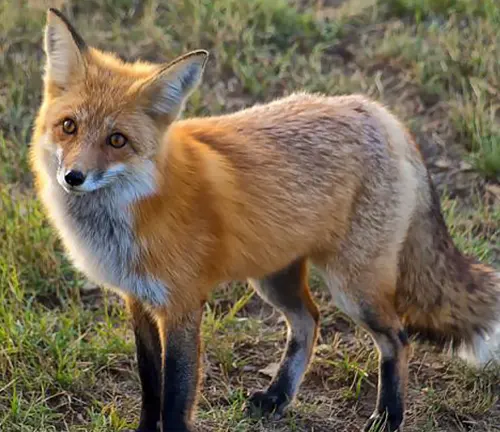

Nature has bestowed upon us a fascinating array of wildlife, and among the myriad species, the red fox stands out as an intriguing and versatile creature. This article aims to explore the various facets of the red fox, from its physical characteristics to its cultural significance, shedding light on its importance in our ecosystems.
The red fox, scientifically known as Vulpes vulpes, is a small to medium-sized carnivore belonging to the Canidae family. Renowned for its distinctive reddish fur, the red fox is found in diverse habitats across the Northern Hemisphere.
As a keystone species, the red fox plays a vital role in controlling prey populations, contributing to the balance of ecosystems. Understanding its significance is crucial for appreciating the delicate web of life in which it participates.
Physical Characteristics
Fur Coloration
The iconic red fur of the red fox is not universal; variations in color, including silver and cross foxes, add to its allure. This section delves into the genetics behind fur coloration and its adaptability.

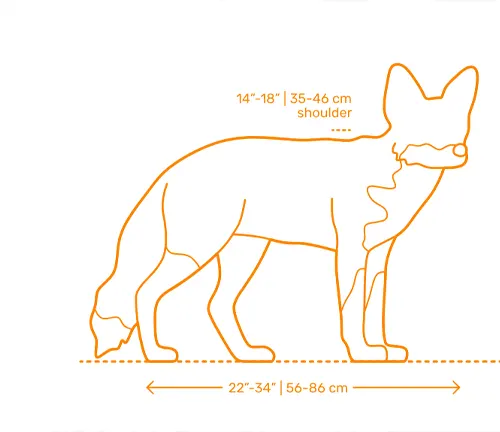
Size and Weight
Exploring the dimensions of the red fox provides insight into its agility and adaptability, traits that contribute to its survival in diverse environments.
Notable Features
From its bushy tail to its keen senses, the red fox possesses distinct features that aid in its daily activities. Understanding these features enhances our appreciation for their evolutionary adaptations.
Habitat and Distribution
Geographic Range
The red fox’s habitat spans a wide geographic range, encompassing various climates and landscapes. Exploring its distribution offers a glimpse into its ability to thrive in different environments.
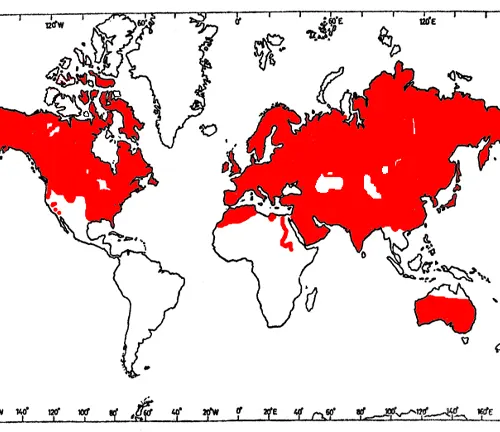
Preferred Habitats
While adaptable, red foxes exhibit preferences for specific habitats. Unraveling these preferences provides valuable insights into their behavior and survival strategies.
Diet and Hunting Behavior
Primary Diet
Examining the red fox’s dietary habits reveals its role as an opportunistic omnivore. Understanding its diet is crucial for comprehending its impact on local ecosystems.
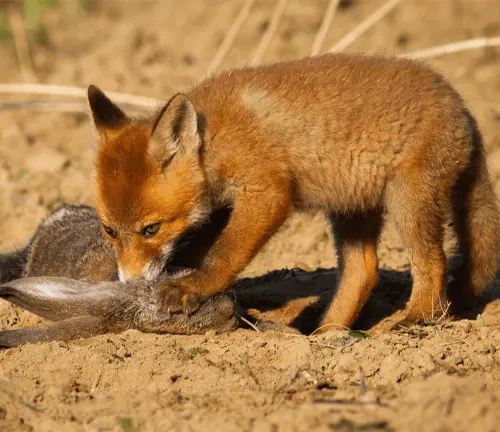

Hunting Techniques
The red fox employs a range of hunting techniques, combining stealth and agility. Analyzing these strategies sheds light on its role as both predator and scavenger.

Reproduction
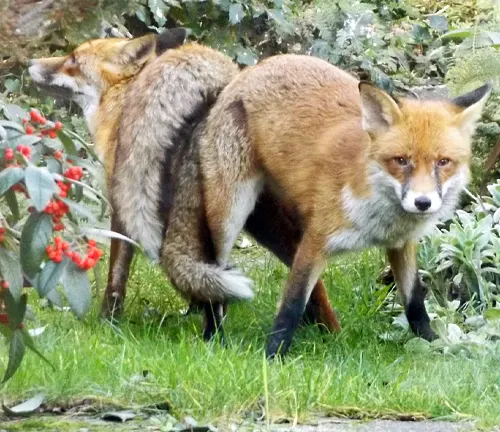

Mating Season
The red fox’s mating season is a crucial period in its life cycle. Exploring the intricacies of courtship and mating rituals unveils the species’ reproductive strategies.
Gestation Period
Understanding the gestation period and the challenges faced by vixens during this time provides a glimpse into the hardships faced by red fox mothers.
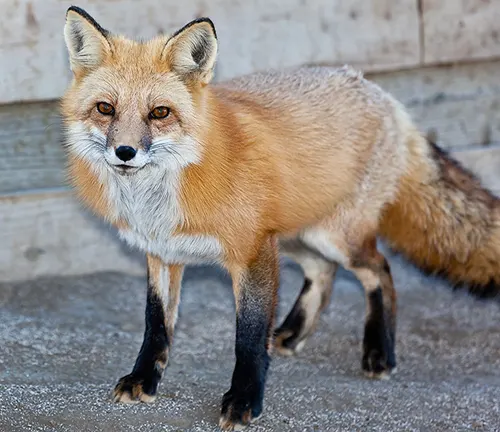
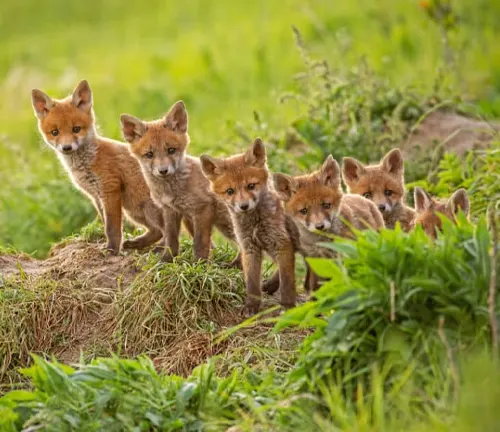


Rearing of Cubs
The nurturing behavior of red fox parents and the development of cubs offer a captivating insight into family dynamics within the species.
Social Structure
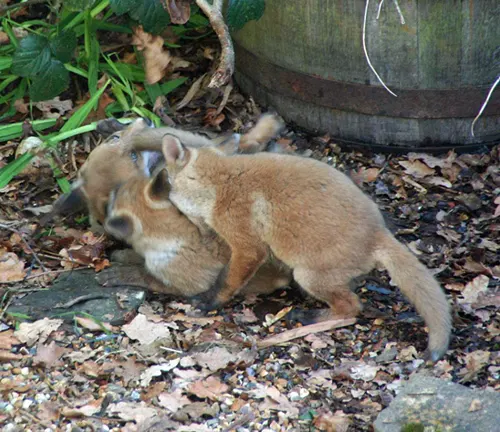
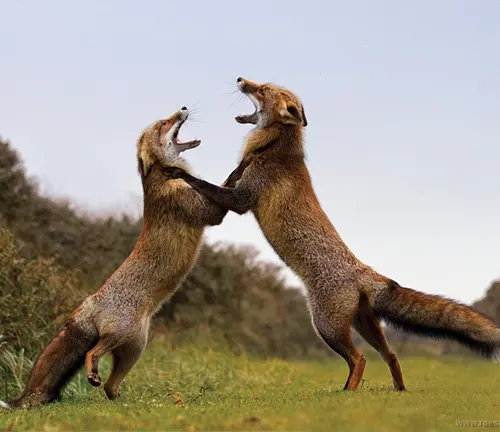


Solitary Nature
Despite its family-oriented approach during reproduction, the red fox is primarily a solitary creature. Examining its social structure unveils the reasons behind this behavior.
Communication Methods
Communication is vital for the red fox’s survival. Delving into its vocalizations and body language unravels the intricate web of signals it uses to navigate its surroundings.
Adaptations to Environment
Camouflage
The red fox’s coat serves not only for warmth but also as a form of camouflage. Exploring the adaptive nature of its fur coloration highlights its role in survival.
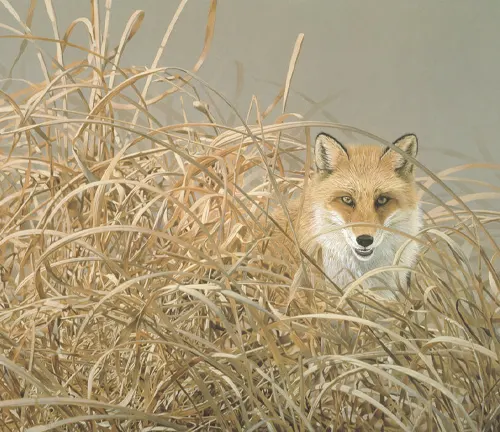

Nocturnal Behavior
Being predominantly nocturnal, the red fox has evolved to thrive in low-light conditions. Understanding its nocturnal behavior enhances our comprehension of its lifestyle.
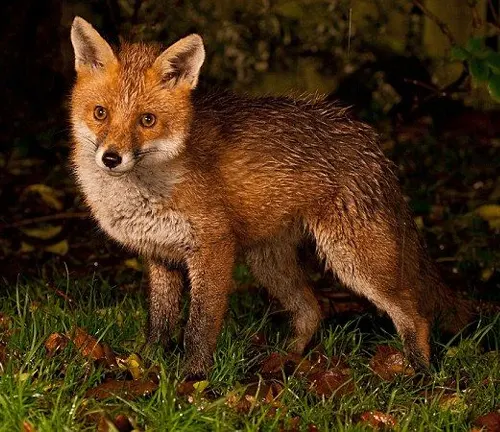

Interactions with Humans
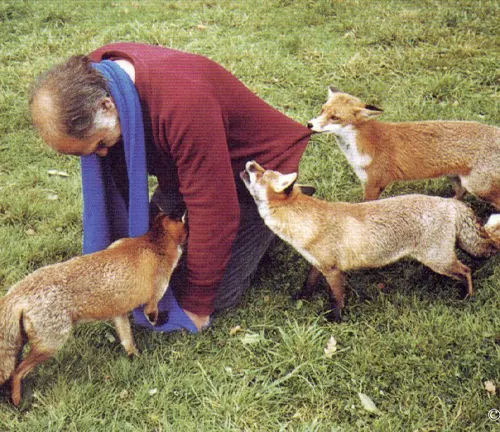

Historical Significance
Throughout history, the red fox has held cultural and symbolic significance in various societies. Examining its historical interactions with humans provides a cultural context.
Current Conservation Status
As human-wildlife interactions intensify, the red fox faces challenges. Assessing its current conservation status sheds light on the efforts required to ensure its survival.
Folklore and Cultural Significance
Myths and Legends
The red fox features prominently in myths and legends worldwide. Unraveling these stories provides a glimpse into the symbolic meanings attributed to the species.
Symbolism in Different Cultures
Across cultures, the red fox holds diverse symbolic meanings. Analyzing its role in different belief systems adds depth to its cultural significance.
Challenges and Threats
Human-Wildlife Conflict
As urbanization expands, the red fox encounters increasing challenges. Delving into the complexities of human-wildlife conflict highlights the need for sustainable coexistence.
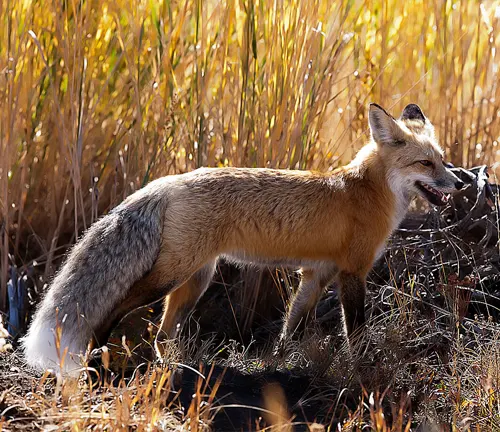

Environmental Changes
Climate change and habitat loss pose significant threats to the red fox. Examining these challenges underscores the urgency of conservation efforts.
Conservation Efforts
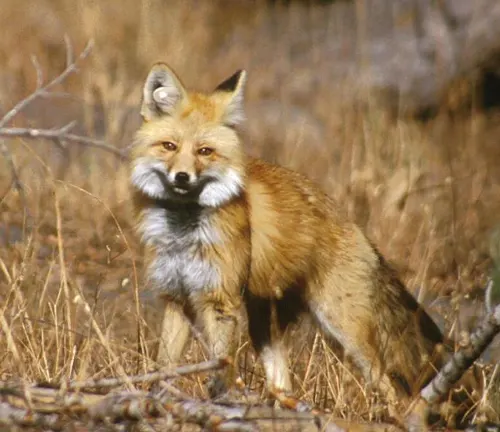

Initiatives and Programs
Numerous conservation initiatives aim to protect the red fox and its habitats. Exploring these programs provides hope for the species’ future.
Role of Wildlife Reserves
Wildlife reserves play a crucial role in safeguarding the red fox. Understanding the importance of these reserves enhances our appreciation for conservation efforts.
Red Fox as a Symbol
Representations in Art and Literature
The red fox’s beauty and cunning have inspired artists and writers. Examining its representations in art and literature offers a cultural perspective.
Symbolic Meanings
From trickster symbolism to spiritual significance, the red fox carries diverse symbolic meanings. Unraveling these meanings adds depth to our understanding of its cultural role.
Different Species
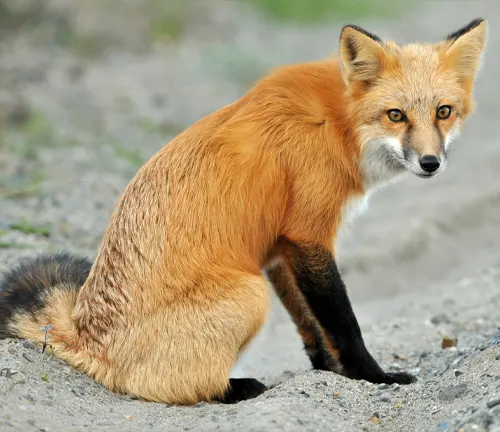
Red Fox (Standard)
The classic red fox is characterized by its reddish-brown fur, white underbelly, and bushy tail with a white tip.

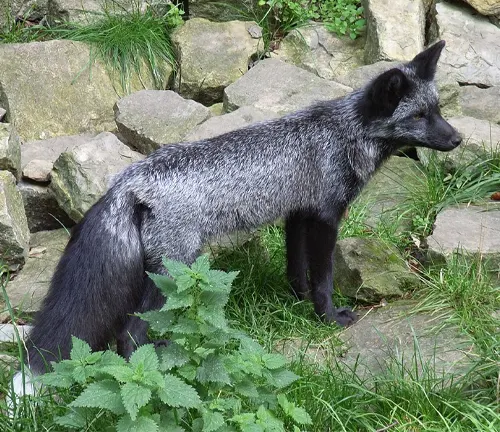
Silver Fox
This variation features silver-gray to black fur, with a dark stripe running down the back. The tail is often tipped in black.

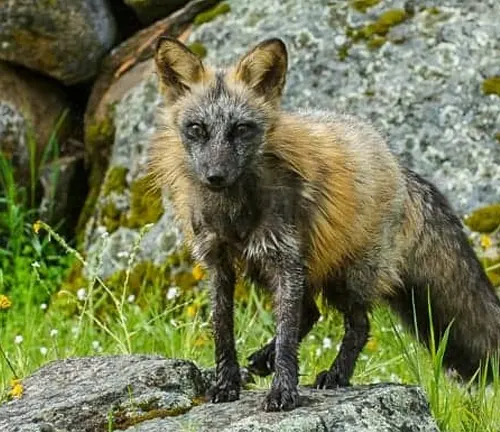
Cross Fox
Cross foxes exhibit a mix of red and silver coloring, with a dark line running down the back and across the shoulders, forming a cross-like pattern.

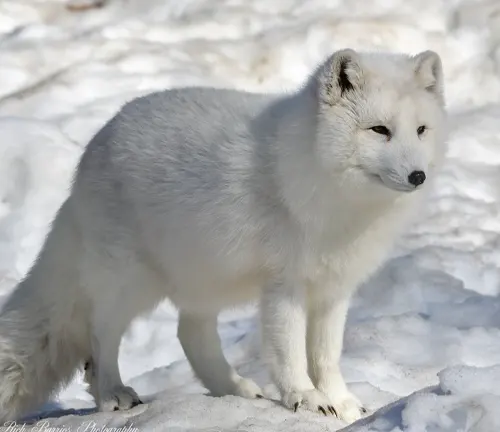
While not a color variation of the red fox, the Arctic fox (Vulpes lagopus) is a distinct species adapted to cold climates, featuring a thick white fur coat in winter and a brownish-gray coat in summer.

Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
- Are red foxes dangerous to humans?
Red foxes are generally not dangerous to humans. They are shy and tend to avoid direct contact. - What is the average lifespan of a red fox in the wild?
In the wild, red foxes typically live for about 3 to 4 years, although some individuals can live longer. - Do red foxes hibernate during winter?
Red foxes do not hibernate. They are active year-round, adapting their behavior to seasonal changes. - How many cubs does a red fox typically have?
A red fox litter usually consists of 4 to 6 cubs, although the number can vary. - What is the primary diet of red foxes?
Red foxes are opportunistic omnivores, feeding on a variety of prey including small mammals, birds, fruits, and insects. - Can red foxes climb trees?
Red foxes are not known for climbing trees. They are more adept at digging and jumping. - Do red foxes mate for life?
Red foxes are not monogamous and may have different mates in different breeding seasons. - Are red foxes more active during the day or night?
Red foxes are primarily crepuscular (active during dawn and dusk) but can be nocturnal or diurnal depending on factors like human activity and food availability. - Do red foxes have natural predators?
Red foxes may face predation from larger carnivores such as wolves, coyotes, and birds of prey. - Can red foxes be kept as pets?
Keeping red foxes as pets is generally not recommended. They have specific needs and may not thrive in a domestic environment. - How far do red foxes roam in search of food?
Red foxes can cover extensive distances while foraging, and their home ranges may vary from a few square miles to tens of square miles. - Do red foxes vocalize?
Yes, red foxes communicate using a variety of vocalizations, including barks, screams, and howls, especially during the mating season. - How do red foxes adapt to urban environments?
Red foxes are known for their adaptability, and in urban areas, they may find food in garbage bins and establish dens in quiet spaces. - What are the conservation challenges faced by red foxes?
Red foxes face threats from habitat loss, disease, and human-wildlife conflict. Conservation efforts are crucial to ensure their survival. - Do red foxes migrate seasonally?
Red foxes typically do not migrate seasonally. They may change their home ranges based on food availability and other factors.














Leave your comment