Baskettail Dragonfly
- April 4, 2024
- 0 comment
The Baskettail Dragonfly, a mesmerizing creature of the skies, embodies grace and agility as it glides effortlessly over freshwater habitats around the world. With its slender body, intricate wings, and striking colors, this insect captivates the imagination of all who encounter it. Found near ponds, lakes, rivers, and streams, the Baskettail Dragonfly plays a crucial role in maintaining the delicate balance of ecosystems. As a voracious predator, it preys upon small insects, including mosquitoes, helping to control their populations and reduce nuisance.
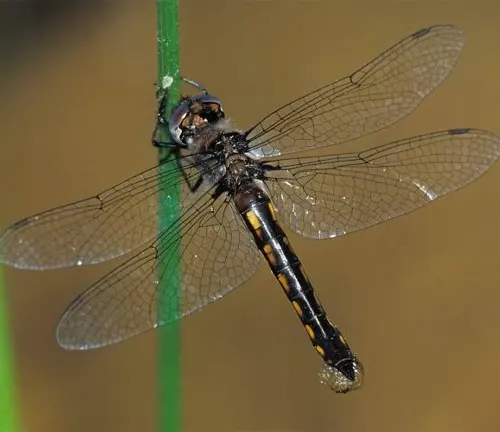

Throughout its life cycle, from egg to nymph to adult, the Baskettail Dragonfly showcases remarkable adaptability and resilience. Despite facing threats from habitat loss and environmental degradation, conservation efforts are underway to safeguard its existence and ensure future generations can marvel at its beauty. The Baskettail Dragonfly serves as a symbol of the interconnectedness of all living beings and the importance of preserving biodiversity in our natural world.
| Attribute | Description |
|---|---|
| Family | Corduliidae |
| Genus | Epitheca |
| Habitat | Freshwater habitats such as ponds, lakes, rivers, and streams |
| Distribution | Found worldwide in various regions |
| Body Structure | Slender body with transparent wings |
| Coloration | Varied, including shades of brown, blue, and green |
| Feeding Habits | Predatory, feeding on small insects like mosquitoes, flies, and gnats |
| Behavior | Agile flyers capable of swift movements in the air |
| Life Cycle | Egg, nymph, and adult stages, undergoes metamorphosis |
| Predators | Birds, fish, and larger insects |
| Defense Mechanisms | Agility and camouflage to evade capture |
| Importance in Ecosystem | Controls insect populations, serves as an indicator of environmental health |
| Threats | Habitat loss, pollution, and climate change |
| Conservation Status | Not currently endangered but faces threats |
| Human Interaction | Vulnerable to impacts from urbanization, agriculture, and pollution |
| Cultural Significance | Revered in various cultures for their beauty and symbolism |
| Observing Tips | Visit freshwater habitats during warm and sunny weather, approach slowly and quietly |
Baskettail Dragonfly: A Fascinating Insect of the Skies
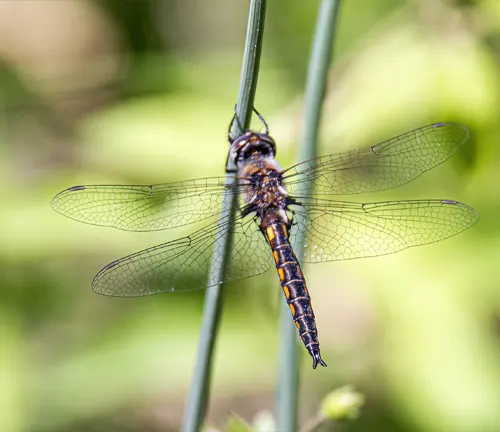

Dragonflies are among the most captivating creatures found in nature, and one particular species that stands out is the Baskettail Dragonfly. This article delves into the intriguing world of the Baskettail Dragonfly, exploring its taxonomy, habitat, behavior, ecological significance, and more.
Taxonomy and Classification
The Baskettail Dragonfly belongs to the family Corduliidae, which is a diverse group of dragonflies commonly found in freshwater habitats. Within the family Corduliidae, the Baskettail Dragonfly is classified under the genus Epitheca. This genus comprises several species, each exhibiting unique characteristics and distribution patterns. Taxonomists categorize these species based on various morphological features, including body size, coloration, wing venation, and genitalia structure. Despite the variations among species, Baskettail Dragonflies share common traits such as slender bodies, transparent wings, and agile flight behavior.
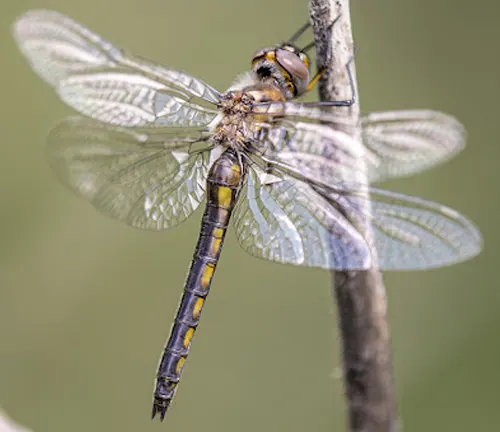

Taxonomic studies help scientists understand the evolutionary relationships and biodiversity within the family Corduliidae, shedding light on the ecological roles and conservation needs of Baskettail Dragonflies in freshwater ecosystems.
Physical Characteristics
The Baskettail Dragonfly boasts a distinctive appearance characterized by its slender body, elongated abdomen, and intricate wings. Typically, these dragonflies measure between two to three inches in length, although sizes may vary slightly among different species. One of the most striking features of the Baskettail Dragonfly is its large, compound eyes, which provide exceptional visual acuity for hunting prey and navigating its surroundings.
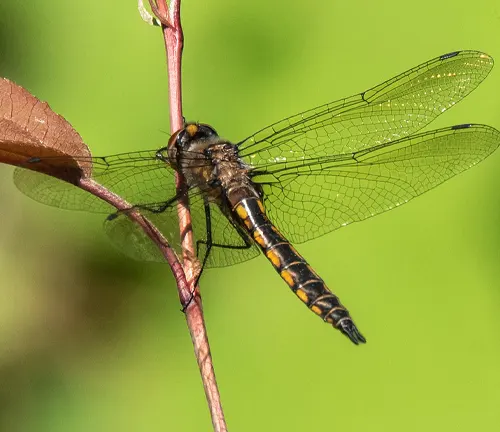

The coloration of Baskettail Dragonflies varies widely, ranging from muted shades of brown and gray to vibrant hues of blue, green, and yellow. Some species may display intricate patterns or markings on their bodies and wings, adding to their aesthetic appeal. Additionally, Baskettail Dragonflies possess transparent wings with delicate veining, allowing for efficient flight and maneuverability.
Another notable physical characteristic of the Baskettail Dragonfly is its thorax, which houses powerful flight muscles essential for aerial locomotion. The abdomen of these dragonflies is elongated and segmented, tapering towards the end and often adorned with markings or color patterns.
Habitat and Distribution
Baskettail Dragonflies are predominantly found in freshwater habitats, making them a common sight near ponds, lakes, rivers, streams, and marshes. They have a wide distribution range, spanning various regions across the globe. These dragonflies exhibit adaptability to different environmental conditions, thriving in both natural and human-altered landscapes.
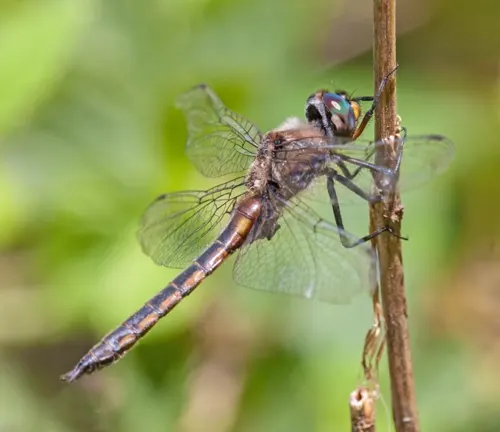

Within their preferred freshwater habitats, Baskettail Dragonflies tend to gravitate towards areas with ample vegetation, as it provides shelter, breeding sites, and hunting grounds. They are often observed perched on aquatic plants or flying low over the water’s surface, hunting for prey and engaging in territorial behaviors.
The distribution of Baskettail Dragonflies can vary depending on factors such as climate, habitat availability, and seasonal changes. Some species may exhibit preferences for specific types of freshwater environments, while others are more generalist in their habitat selection.
Behavior and Life Cycle
Baskettail Dragonflies display fascinating behaviors and undergo a remarkable life cycle, transitioning through several stages from egg to adult.
As agile flyers, Baskettail Dragonflies exhibit precise and swift movements in the air, allowing them to efficiently hunt for prey and navigate through their surroundings. They are often observed performing aerial acrobatics, darting and diving as they pursue flying insects or defend their territories.
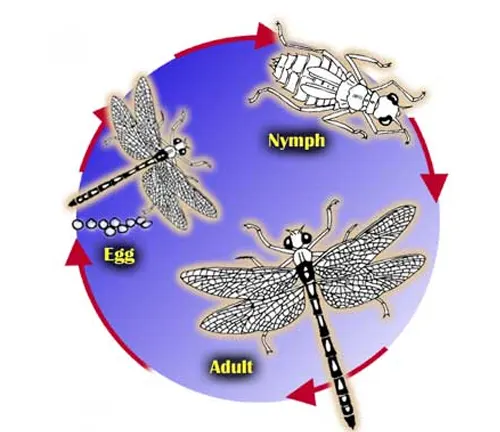
The life cycle of Baskettail Dragonflies begins with egg-laying by adult females in freshwater habitats. Once hatched, the larvae, known as nymphs, undergo a period of growth and development in the water. Nymphs are voracious predators, feeding on small aquatic organisms and molting several times as they grow.
After completing their nymphal stage, Baskettail Dragonflies emerge from the water as winged adults. The transition from nymph to adult is marked by a final molt, during which the dragonfly sheds its exoskeleton and undergoes physical changes to its body structure, including the development of wings and reproductive organs.
As adults, Baskettail Dragonflies engage in mating behaviors, with males often performing elaborate courtship displays to attract females. Once mating occurs, females lay eggs in freshwater habitats, completing the life cycle and ensuring the continuation of the species.
Diet and Feeding Habits
Baskettail Dragonflies are formidable predators with voracious appetites, primarily feeding on a wide variety of small insects found in their freshwater habitats. Their diet typically consists of mosquitoes, flies, gnats, mayflies, and other flying insects that are abundant near water bodies.
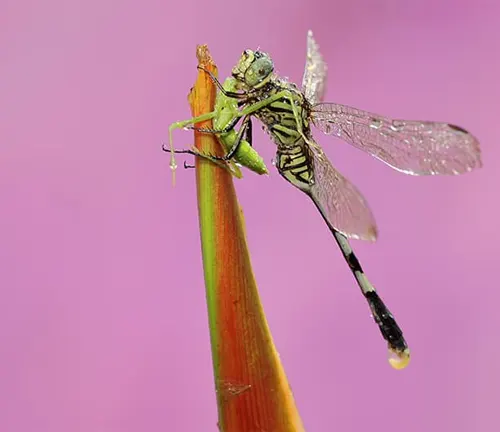

These dragonflies employ a sit-and-wait hunting strategy, perching on vegetation or other objects near the water’s edge and patiently waiting for prey to come within striking distance. Once a suitable target is detected, Baskettail Dragonflies launch themselves into the air with remarkable speed and agility, seizing their prey mid-flight using their specialized legs.
Their keen eyesight, coupled with acute sensory organs, allows them to track and intercept prey with precision, making them highly efficient hunters. Baskettail Dragonflies are capable of capturing multiple insects in rapid succession, consuming them on the wing or returning to a perch to consume their catch.
Predators and Defense Mechanisms
Baskettail Dragonflies, despite their agile flight and predatory prowess, face threats from various predators in their natural habitats. Common predators include birds such as swallows and kingfishers, fish such as bass and trout, and larger insects like damselflies and other dragonfly species. To evade capture, Baskettail Dragonflies employ several defense mechanisms, including:
- Agility: Baskettail Dragonflies are incredibly agile flyers, capable of swift and unpredictable movements in the air. This agility allows them to evade predators by quickly changing direction or darting out of harm’s way.
- Camouflage: Some species of Baskettail Dragonflies exhibit coloration and patterns that help them blend into their surroundings, making them less visible to predators. This camouflage provides them with additional protection from detection and attack.
- Speed: Baskettail Dragonflies are adept at flying at high speeds, allowing them to outmaneuver pursuing predators and escape potential threats.
- Territorial Behavior: Adult Baskettail Dragonflies may defend their territory from intruders, engaging in aggressive behaviors such as aerial displays or physical combat to deter potential predators.
Importance in Ecosystem
Baskettail Dragonflies play a significant role in freshwater ecosystems, contributing to ecological balance and biodiversity in several ways:
- Predator Control: As voracious predators themselves, Baskettail Dragonflies help regulate populations of small insects such as mosquitoes, flies, and gnats, thereby reducing the abundance of potential pests in their habitats.
- Indicator Species: The presence of Baskettail Dragonflies is often indicative of clean and healthy freshwater habitats. Monitoring their populations can provide valuable insights into the overall health and quality of aquatic ecosystems.
- Prey Base: Baskettail Dragonflies serve as a food source for various predators, including birds, fish, and larger insects, forming an essential component of the food web in freshwater environments.
- Pollination: While primarily carnivorous, Baskettail Dragonflies may inadvertently contribute to pollination by transferring pollen grains between plants as they move from one feeding site to another.
Threats and Conservation Status
While Baskettail Dragonflies are not currently listed as endangered, they face threats from habitat loss, pollution, and climate change. Conservation efforts are essential to safeguard their populations and habitats.
Human Interaction and Impact
Human activities such as urbanization, agriculture, and pollution can adversely affect Baskettail Dragonflies and their habitats. Responsible stewardship and conservation practices are necessary to mitigate these impacts.
Interesting Facts about Baskettail Dragonflies
- Baskettail Dragonflies are known for their remarkable aerial acrobatics.
- Some species of Baskettail Dragonflies migrate over long distances.
- These insects have been revered in various cultures for their beauty and symbolism.
Common Myths and Misconceptions
Despite their harmless nature, Baskettail Dragonflies have often been associated with myths and superstitions in different cultures. These misconceptions often stem from their unique appearance and behavior.
Baskettail Dragonflies in Culture and Art
Throughout history, Baskettail Dragonflies have inspired artists, poets, and storytellers with their ethereal beauty and graceful movements. They are often depicted in paintings, literature, and folklore.
Tips for Observing Baskettail Dragonflies
- Visit freshwater habitats such as ponds, lakes, and streams during warm and sunny weather.
- Approach slowly and quietly to avoid startling the dragonflies.
- Bring binoculars or a camera to observe their intricate details up close.
Different Species
Common Baskettail
(Epitheca cynosura)
Found across North America, this species is known for its distinctive markings and widespread distribution.
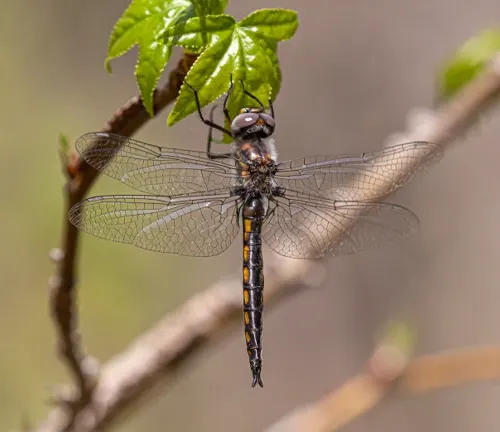
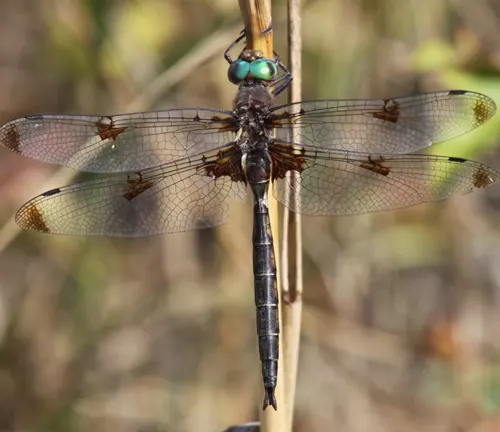


Prince Baskettail
(Epitheca princeps)
Native to eastern North America, the Prince Baskettail is recognized by its large size and prominent green eyes.
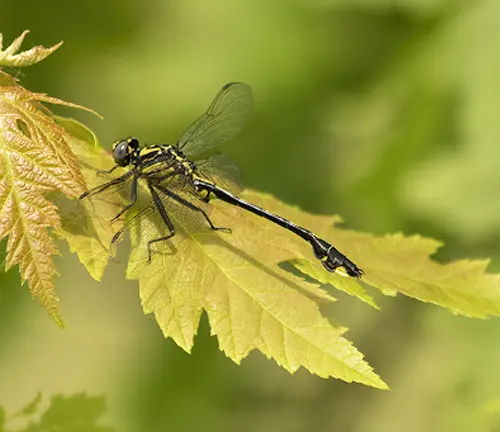
Cobra Clubtail
(Epitheca verax)
This species is primarily found in the eastern United States, characterized by its elongated abdomen and unique clubbed tail.
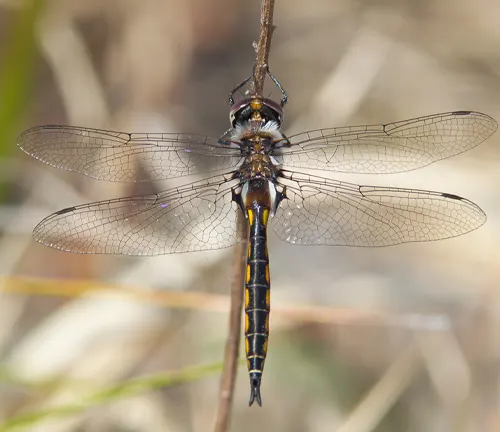


Slender Baskettail
(Epitheca costalis)
Native to eastern North America, the Slender Baskettail is identified by its slender body and pale coloration.
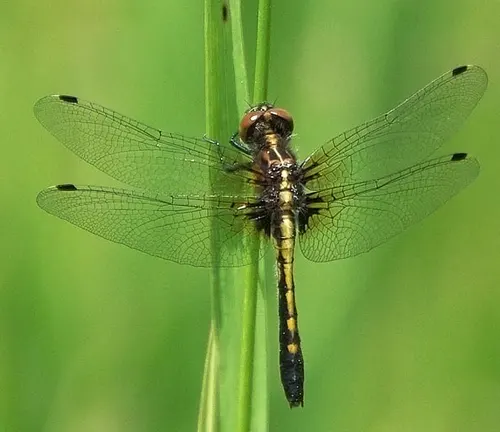
Dot-tailed Whiteface
(Leucorrhinia intacta)
While not technically a Baskettail Dragonfly, the Dot-tailed Whiteface is often grouped with Baskettails due to similarities in appearance and habitat preference.

Frequently Asked Question (FAQs)
- What is a Baskettail Dragonfly?
A Baskettail Dragonfly is a species of dragonfly known for its slender body, transparent wings, and varied coloration. - Where can I find Baskettail Dragonflies?
Baskettail Dragonflies inhabit freshwater habitats such as ponds, lakes, rivers, and streams around the world. - Do Baskettail Dragonflies bite humans?
No, Baskettail Dragonflies do not bite humans as they are harmless insects. - How do Baskettail Dragonflies reproduce?
Baskettail Dragonflies undergo a life cycle that includes egg-laying in water, nymphal development, and emergence as adults. - Are Baskettail Dragonflies endangered?
While some species may face threats, Baskettail Dragonflies are not generally considered endangered. - What do Baskettail Dragonflies eat?
Baskettail Dragonflies are predatory insects that feed on small insects such as mosquitoes, flies, and gnats. - How can I attract Baskettail Dragonflies to my garden?
Creating a suitable habitat with freshwater sources and ample vegetation can attract Baskettail Dragonflies to your garden. - What are the predators of Baskettail Dragonflies?
Predators of Baskettail Dragonflies include birds, fish, and larger insects that prey on them in their natural habitats. - Can Baskettail Dragonflies be found in urban areas?
Yes, Baskettail Dragonflies can adapt to urban environments if suitable freshwater habitats are available. - Do Baskettail Dragonflies have any cultural significance?
Yes, Baskettail Dragonflies are revered in various cultures for their beauty and symbolism, often appearing in art, literature, and folklore. - How do Baskettail Dragonflies defend themselves?
Baskettail Dragonflies employ defensive tactics such as agility and camouflage to evade predators. - What is the lifespan of a Baskettail Dragonfly?
The lifespan of Baskettail Dragonflies varies among species but typically ranges from a few months to a few years.














Leave your comment