Large Blue Butterfly
- March 4, 2024
- 0 comment
The Large Blue Butterfly, scientifically known as Phengaris arion, is a captivating insect renowned for its stunning appearance and intricate life cycle. Sporting vibrant hues of blue on its wings, this species boasts a wingspan ranging from X to Y centimeters, making it a striking sight in its natural habitat. Found across various regions, including Europe, the Large Blue Butterfly thrives in grasslands, meadows, and woodland clearings, relying on specific host plants for its survival.
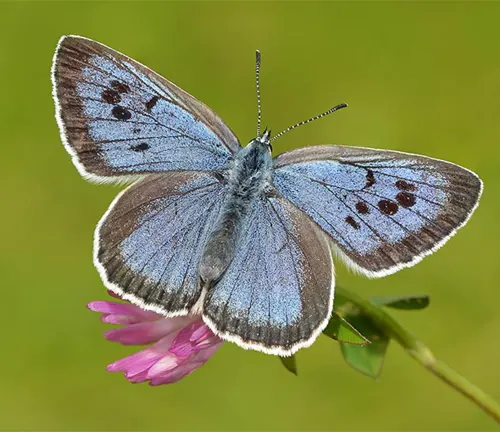

Its life cycle begins with the female butterfly laying eggs on these host plants, leading to the emergence of larvae that develop a unique relationship with certain species of ants. Through metamorphosis, the larvae transform into adult butterflies, known for their graceful flight patterns and feeding behaviors. However, despite its enchanting allure, the Large Blue Butterfly faces threats from habitat loss, climate change, and human activities. Conservation efforts aim to protect and restore its habitats, ensuring the preservation of this iconic species and its vital role in ecosystems.
| Specification | Description |
|---|---|
| Scientific Name | Phengaris arion |
| Common Name | Large Blue Butterfly |
| Wingspan | X to Y centimeters |
| Coloration | Vibrant hues of blue on wings, with intricate patterns |
| Habitat | Grasslands, meadows, woodland clearings |
| Distribution | Found across Europe and other regions |
| Host Plants | Specific plant species for larval development |
| Lifecycle | Egg stage, larval stage (with symbiotic relationship with ants), pupal stage, adult stage |
| Flight Patterns | Graceful fluttering between flowers and vegetation |
| Feeding Habits | Nectar feeding primarily, larvae feed on host plants |
| Conservation Status | Faces threats from habitat loss, climate change, and human activities |
| Conservation Efforts | Aim to protect and restore habitats, raise awareness |
The Majestic Large Blue Butterfly
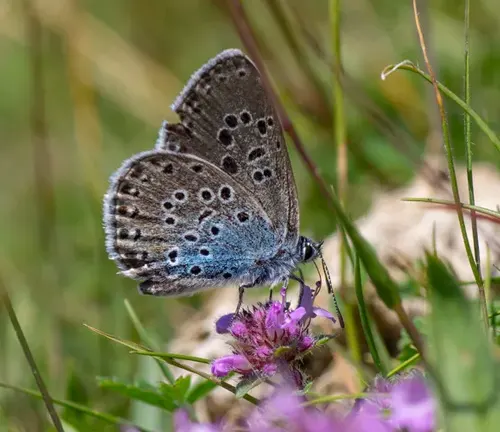

The Large Blue Butterfly (scientifically known as Phengaris arion) is a captivating insect known for its striking appearance and fascinating life cycle. Found across various regions, this butterfly species has intrigued scientists, conservationists, and nature enthusiasts alike. In this article, we delve into the intricate details of this remarkable creature, exploring its physical attributes, habitat, behavior, conservation status, and cultural significance.
Physical Characteristics
Coloration and Markings
Coloration and markings refer to the distinctive hues and patterns displayed by the Large Blue Butterfly’s wings. This species is renowned for its striking appearance, characterized by vibrant shades of blue that vary in intensity and distribution across the wings. Additionally, intricate markings adorn the wings, consisting of lines, spots, and other designs that contribute to the butterfly’s overall aesthetic appeal. These coloration and markings serve various purposes, including camouflage, mate attraction, and warning signals to potential predators. The precise patterns and colors may vary among individual butterflies and subspecies, adding to the diversity and beauty of the Large Blue Butterfly population.
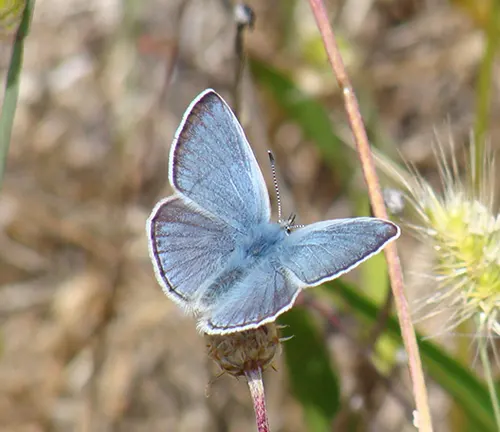

Habitat and Distribution
Native Habitats
The Large Blue Butterfly inhabits a diverse range of natural habitats, primarily found in grasslands, meadows, and woodland clearings. These environments provide the necessary conditions for the butterfly’s life cycle, including suitable host plants for egg-laying and larval development. Large Blue Butterflies often prefer areas with an abundance of wildflowers and open spaces, where they can feed on nectar and bask in the sunlight. Additionally, certain subspecies of the Large Blue Butterfly may exhibit specific habitat preferences, depending on factors such as altitude, climate, and vegetation composition.
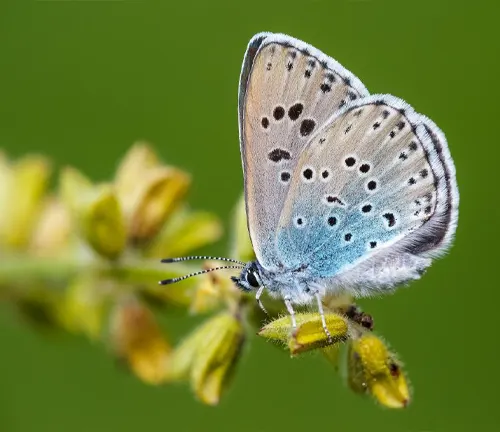

Geographical Range
The geographical range of the Large Blue Butterfly extends across various regions, primarily in Europe and parts of Asia. Historically, Large Blue Butterfly populations were widespread across Europe, but habitat loss and other threats have led to localized extinctions in some areas. Today, the butterfly can be found in countries such as the United Kingdom, France, Germany, Italy, and Russia, among others. Conservation efforts aim to protect and restore suitable habitats within the Large Blue Butterfly’s range, ensuring the continued survival of this iconic species.
Life Cycle of the Large Blue Butterfly
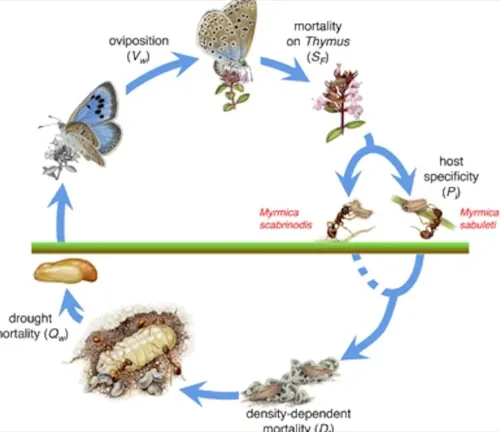
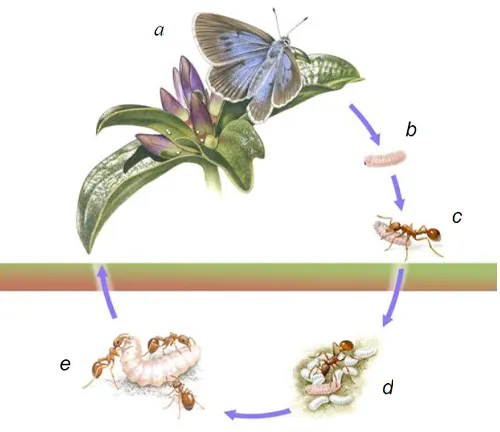
Egg Stage
The egg stage is the initial phase of the Large Blue Butterfly’s life cycle. Female butterflies carefully select suitable host plants on which to lay their eggs, ensuring they provide adequate nutrition for the larvae once they hatch. The eggs are typically small and are laid singly or in small clusters on the underside of leaves or stems. During this stage, the eggs are vulnerable to environmental factors and predators. Depending on conditions such as temperature and humidity, the egg stage can last from a few days to several weeks.
Larval Stage
Following the egg stage, the Large Blue Butterfly enters the larval stage, commonly known as the caterpillar stage. Upon hatching, the larvae emerge and begin feeding voraciously on the host plants. The larvae of the Large Blue Butterfly often form symbiotic relationships with certain species of ants, secreting substances that attract ants to protect them from predators and parasites. This stage is characterized by rapid growth and multiple molts as the larvae increase in size and prepare for the next phase of their development.
Pupal Stage
After completing the larval stage, the Large Blue Butterfly enters the pupal stage, also known as the chrysalis stage. During this transformative period, the larvae undergo metamorphosis within protective structures called pupae. The pupae are typically attached to stems or leaves of plants, where they remain immobile as the butterfly undergoes dramatic changes. Inside the pupal casing, the larval tissues are broken down and reorganized to form the adult butterfly’s body, wings, and other structures. The duration of the pupal stage can vary depending on environmental conditions and species, lasting from a few weeks to several months.
Adult Stage
Upon completing the pupal stage, the Large Blue Butterfly emerges as an adult butterfly, ready to begin its life as a winged insect. The adult stage is characterized by the butterfly’s ability to fly and reproduce. During this phase, adult butterflies primarily feed on nectar from flowers, aiding in pollination as they move from one plant to another. They also play a crucial role in the ecosystem as prey for various predators and as pollinators for flowering plants. Depending on species and environmental factors, adult butterflies may live for several weeks to several months, during which time they mate and lay eggs, thus completing the life cycle of the Large Blue Butterfly.
Behavior and Feeding Habits
Flight Patterns
Large Blue Butterflies exhibit distinctive flight patterns characterized by graceful and erratic movements. When in flight, they flutter delicately between flowers and vegetation, often gliding smoothly with occasional rapid flaps of their wings. Their flight patterns are not only mesmerizing to observe but also serve practical purposes such as navigating their environment in search of food sources and suitable habitats. Large Blue Butterflies are agile flyers, capable of maneuvering adeptly through dense vegetation and open spaces alike.
Host Plants
The choice of host plants is crucial for the survival and development of Large Blue Butterfly larvae. These butterflies lay their eggs on specific plant species that serve as food sources for the emerging caterpillars. Common host plants for Large Blue Butterflies include species such as wild thyme (Thymus spp.), bird’s-foot trefoil (Lotus corniculatus), and various species of vetch (Vicia spp.). The larvae feed voraciously on the leaves of these plants, consuming plant material to fuel their growth and development during the larval stage.
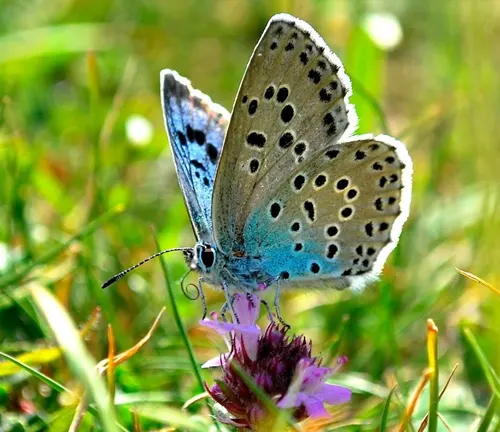

Feeding Preferences
As adults, Large Blue Butterflies primarily feed on the nectar of flowers, using their long proboscis to extract the sugary liquid from deep within the floral structures. They are known to visit a wide variety of flowering plants to obtain nectar, with preferences varying depending on factors such as flower shape, color, and fragrance. Large Blue Butterflies are particularly attracted to flowers with tubular shapes or landing platforms that provide easy access to nectar. Additionally, they may also feed on other sources of nutrients, such as sap, rotting fruit, and minerals found in damp soil.
Conservation Status
Threats to Population
The Large Blue Butterfly faces numerous threats to its population, primarily stemming from human activities and environmental changes. Habitat loss and degradation pose significant challenges, as urbanization, agriculture, and land development encroach upon the butterfly’s natural habitats. Fragmentation of habitats disrupts the butterfly’s ability to find suitable breeding and feeding grounds, leading to population declines and increased vulnerability to extinction.
Furthermore, the use of pesticides and herbicides in agricultural and residential areas can have detrimental effects on Large Blue Butterfly populations. These chemicals not only directly harm adult butterflies but also impact the availability of host plants and nectar sources, disrupting the butterfly’s life cycle and reproductive success.
Climate change also poses a threat to Large Blue Butterfly populations, altering temperature and precipitation patterns and affecting the availability of suitable habitats and food sources. Shifts in weather patterns can disrupt butterfly migration, breeding, and hibernation behaviors, further exacerbating population declines.
Conservation Efforts
Efforts to conserve the Large Blue Butterfly and protect its habitats are underway worldwide, led by government agencies, conservation organizations, and local communities. Conservation efforts aim to address the various threats facing Large Blue Butterfly populations and ensure their long-term survival.
Habitat restoration and management play a crucial role in conservation efforts, with initiatives focused on preserving and enhancing the butterfly’s natural habitats. This includes restoring native vegetation, creating wildlife corridors, and implementing sustainable land management practices to mitigate habitat loss and fragmentation.
In addition to habitat conservation, targeted conservation measures are implemented to address specific threats to Large Blue Butterfly populations. This includes reducing pesticide use in butterfly habitats, implementing buffer zones around sensitive areas, and conducting monitoring and research to better understand population dynamics and conservation needs.
Cultural Significance
Symbolism
The Large Blue Butterfly holds symbolic significance in various cultures and traditions, representing themes of transformation, rebirth, and spirituality. In many cultures, butterflies are seen as symbols of beauty, freedom, and the soul’s journey. The vibrant colors and graceful movements of the Large Blue Butterfly evoke feelings of joy, hope, and inspiration, making it a potent symbol in art, literature, and mythology.
Role in Literature and Art
Throughout history, the Large Blue Butterfly has been celebrated and immortalized in literature, art, and folklore. In literature, butterflies are often used as metaphors for transformation and personal growth, reflecting the human experience of overcoming challenges and emerging stronger and more resilient.
In art, the beauty and intricacy of the Large Blue Butterfly’s wings have inspired artists and artisans to capture its essence in paintings, sculptures, and other forms of creative expression. From delicate watercolor illustrations to intricate stained glass designs, the butterfly’s graceful form and vibrant colors have been celebrated in diverse artistic mediums.
Challenges in Studying and Protecting the Large Blue Butterfly
Research Difficulties
Studying the Large Blue Butterfly presents unique challenges for researchers due to various factors, including its elusive behavior, specialized habitat requirements, and complex life cycle. The butterfly’s relatively small size and cryptic coloration make it difficult to observe and track in the wild, particularly during the egg and larval stages. Additionally, Large Blue Butterfly populations may be scattered across fragmented habitats, making it challenging to conduct comprehensive population surveys and research studies.
Furthermore, the symbiotic relationship between Large Blue Butterfly larvae and certain species of ants adds another layer of complexity to research efforts. Understanding the intricacies of this relationship and its impact on butterfly populations requires detailed field observations and laboratory studies, which can be time-consuming and resource-intensive.
Legal Protection
The Large Blue Butterfly is afforded legal protection in many countries due to its conservation status and vulnerability to habitat loss and other threats. Legal protection may take various forms, including designation as a protected species under national and international legislation, establishment of protected areas and reserves, and implementation of conservation plans and management strategies.
In some regions, it is illegal to disturb, harm, or collect Large Blue Butterflies or their habitats without proper permits or authorization. Legal protections may also extend to the butterfly’s host plants and critical habitats, helping to safeguard essential resources for butterfly survival and reproduction.
Conservation organizations and government agencies work together to enforce existing laws and regulations aimed at protecting the Large Blue Butterfly and its habitats. Public education and outreach efforts raise awareness about the importance of legal protection for endangered species and promote responsible stewardship of natural resources.
Different Species
Phengaris arion
This is the nominate species, often referred to simply as the Large Blue Butterfly. It is found in various regions across Europe and is known for its striking blue wings and intricate patterns.
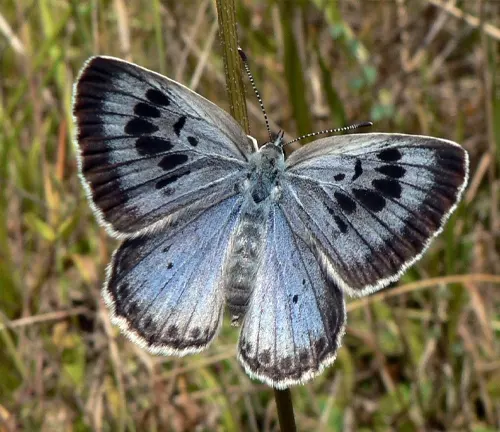
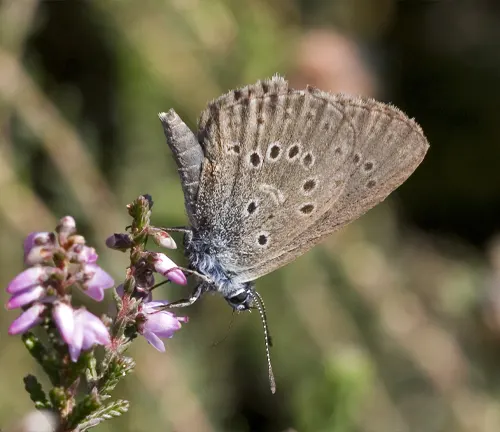


Phengaris alcon
Also known as the Alcon Blue Butterfly, this species is closely related to Phengaris arion. It is characterized by its blue wings with black markings and is found in parts of Europe and Asia.
Phengaris rebeli
The Dusky Large Blue Butterfly, or Phengaris rebeli, is another subspecies within the complex. It shares similarities with Phengaris arion but may have distinct variations in coloration and markings.
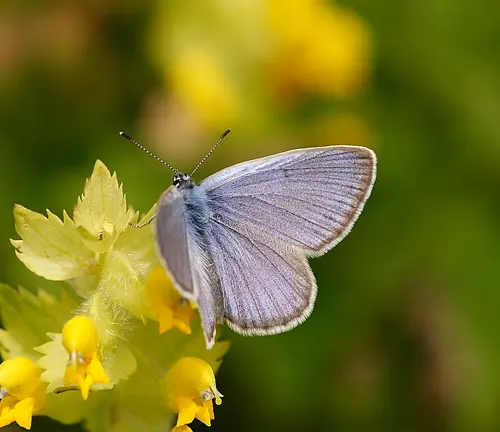
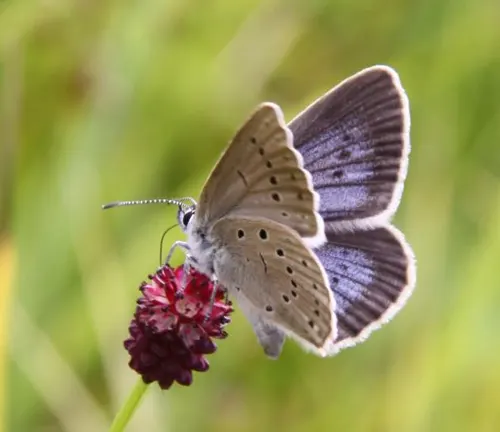


Phengaris teleius
The Scarce Large Blue Butterfly, or Phengaris teleius, is a subspecies found in select regions of Europe. It features similar characteristics to Phengaris arion but may exhibit differences in distribution and habitat preferences.
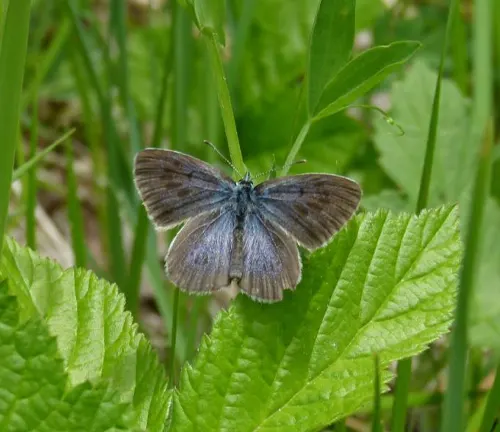
Phengaris nausithous
The Dusky Large Blue Butterfly, or Phengaris nausithous, is another member of the complex. It is known for its blue wings and may inhabit different habitats compared to other subspecies.

Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
- Are Large Blue Butterflies endangered?
This question arises from concerns about the conservation status of the Large Blue Butterfly and its vulnerability to habitat loss and other threats. - What plants do Large Blue Butterfly larvae feed on?
Enthusiasts and researchers often inquire about the specific plant species that serve as host plants for the larvae of the Large Blue Butterfly. - Do Large Blue Butterflies migrate?
Some individuals may wonder about the migratory behavior of Large Blue Butterflies, including the extent of their movements and seasonal patterns. - How long does the life cycle of a Large Blue Butterfly last?
This question pertains to the duration of each stage in the butterfly’s life cycle, from egg to larva, pupa, and adult. - What threats do Large Blue Butterflies face in the wild?
Conservation-minded individuals seek information about the primary threats to Large Blue Butterfly populations, such as habitat destruction, climate change, and pesticide use. - Do Large Blue Butterflies have any predators?
This question explores the natural predators of Large Blue Butterflies, including birds, insects, and other animals that may prey on them at different life stages. - How do Large Blue Butterflies protect themselves from predators?
Enthusiasts and researchers are interested in the defensive mechanisms employed by Large Blue Butterflies, such as camouflage, mimicry, and chemical defenses. - What role do Large Blue Butterflies play in the ecosystem?
This question delves into the ecological significance of Large Blue Butterflies, including their contributions to pollination, food webs, and biodiversity. - Can Large Blue Butterflies be bred in captivity?
Butterfly enthusiasts and conservationists may inquire about the feasibility and ethical considerations of breeding Large Blue Butterflies in controlled environments. - How do climate change and habitat loss affect Large Blue Butterfly populations?
This question seeks to understand the impacts of environmental changes on Large Blue Butterfly habitats, distributions, and survival prospects. - Are there any cultural or symbolic meanings associated with Large Blue Butterflies?
Curiosity about the cultural significance of Large Blue Butterflies prompts questions about their symbolism in various societies, folklore, and traditions. - What conservation efforts are underway to protect Large Blue Butterfly populations?
Individuals interested in conservation seek information about initiatives, policies, and strategies aimed at safeguarding Large Blue Butterfly habitats and populations.














Leave your comment