Hercules Beetle
- April 5, 2024
- 0 comment
The Hercules Beetle, known scientifically as Dynastes hercules, is a captivating insect renowned for its impressive size and strength. Named after the legendary Greek hero Hercules, this beetle inhabits the dense tropical forests of Central and South America. With males reaching lengths of up to 6.7 inches (17 centimeters) and weights exceeding 100 grams, the Hercules Beetle stands as one of the largest beetles in the world. Its exoskeleton displays a stunning array of colors and patterns, ranging from shades of green and brown to vibrant blues and purples. Despite its formidable appearance, the Hercules Beetle is primarily herbivorous, feeding on sap, fruit, and nectar.
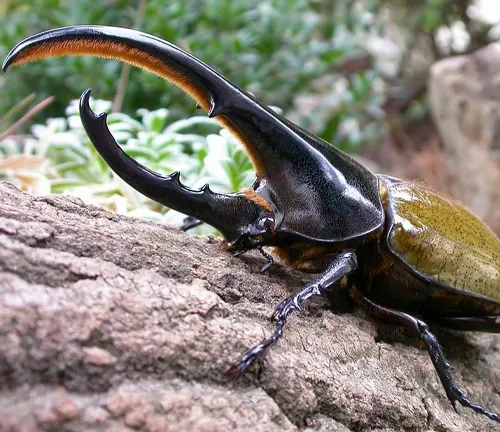

Throughout history, this majestic creature has been revered in various cultures for its symbolism of strength and endurance. While not currently endangered, habitat loss and human activities pose significant threats to its survival. Conservation efforts are underway to protect the habitats of the Hercules Beetle and ensure its continued existence in the wild.
| Specifications | Details |
|---|---|
| Scientific Name | Dynastes hercules |
| Common Name | Hercules Beetle |
| Size | Up to 6.7 inches (17 centimeters) |
| Weight | Exceeds 100 grams |
| Habitat | Tropical forests of Central and South America |
| Diet | Primarily herbivorous, feeding on sap, fruit, and nectar |
| Lifespan | Several months to a year as adults |
| Conservation Status | Not currently endangered, but habitat loss poses threats |
| Predators | Birds, reptiles, mammals |
| Symbolism | Strength, resilience, endurance |
| Threats | Habitat loss, deforestation, human activities |
Exploring the Mighty Hercules Beetle: Nature’s Impressive Giant
The Hercules Beetle (Dynastes hercules) is a remarkable insect that belongs to the family Scarabaeidae, known for its immense strength and impressive size. Named after the legendary Greek hero Hercules, this beetle captures the imagination of entomologists and nature enthusiasts alike.
Physical Characteristics of Hercules Beetle
Size and Weight
The Hercules Beetle (Dynastes hercules) is renowned for its impressive size and weight. Males of this species can reach lengths of up to 6.7 inches (17 centimeters), making them one of the largest beetles in the world. Additionally, their weight can exceed 100 grams, making them true heavyweights in the insect world. These dimensions contribute to their imposing presence and remarkable strength.
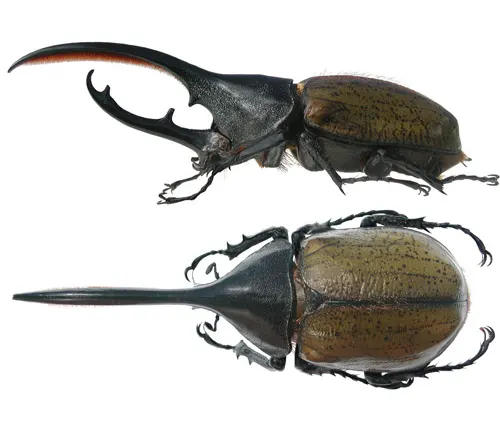
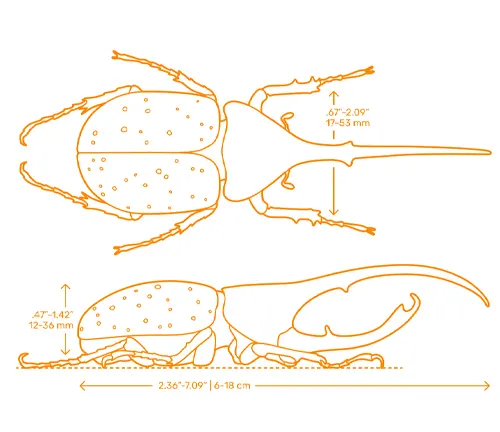

Coloration and Patterns
Hercules Beetles exhibit a fascinating array of colors and patterns on their exoskeletons. Their coloration ranges from various shades of green and brown to vibrant hues of blue and purple. Some species even feature metallic iridescence, adding to their visual appeal. Additionally, Hercules Beetles may display intricate patterns such as stripes, spots, or bands, further enhancing their aesthetic allure. These colors and patterns serve various purposes, including camouflage, mate attraction, and species recognition, making each Hercules Beetle a unique and visually striking specimen in the insect world.
Habitat and Distribution
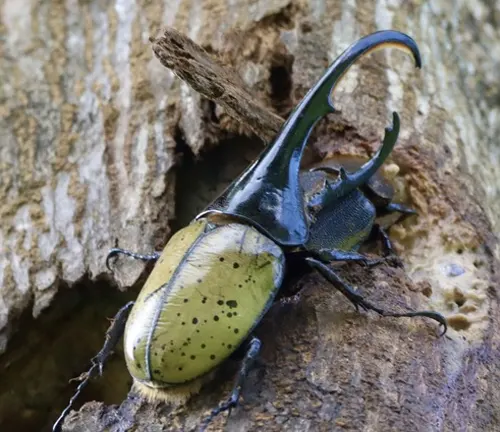

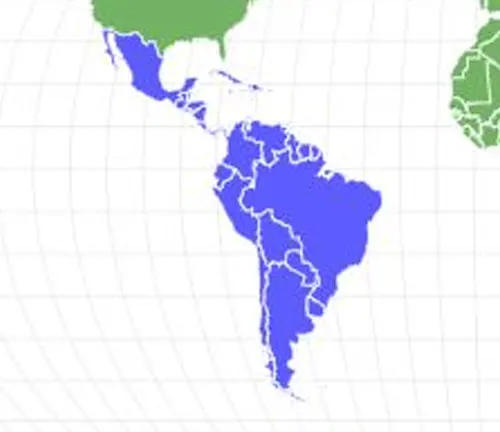
The Hercules Beetle (Dynastes hercules) is primarily found in the tropical forests of Central and South America. These dense jungles and rainforests provide the ideal habitat for the Hercules Beetle, offering ample food sources and suitable breeding grounds. Within these habitats, Hercules Beetles are often found in areas with abundant vegetation and rotting wood, which they use for feeding and reproduction.
In terms of distribution, Hercules Beetles can be found in various countries throughout Central and South America, including but not limited to Brazil, Venezuela, Colombia, Ecuador, Peru, and Bolivia. Their range extends from the lush Amazon rainforest to other tropical regions with suitable environmental conditions. While they prefer lowland forests, Hercules Beetles can also be found at higher elevations in mountainous areas, provided there is sufficient vegetation and humidity to support their needs.
Lifecycle of Hercules Beetle
Egg Stage
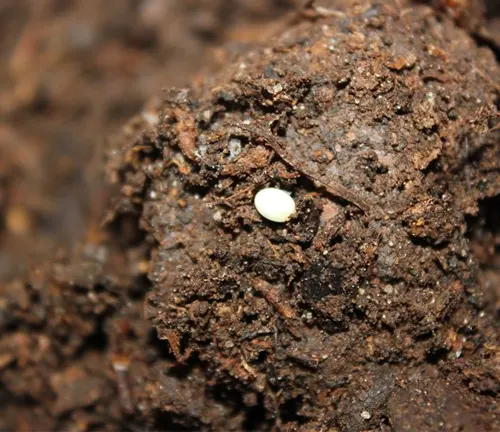
The lifecycle of a Hercules Beetle begins with the egg stage. Female Hercules Beetles typically lay their eggs in decaying wood, where they are protected from predators and provide a suitable environment for the developing larvae. The eggs are small and oval-shaped, and the female beetle carefully selects a suitable location for egg deposition. Once laid, the eggs hatch into larvae, marking the beginning of the next stage of development.
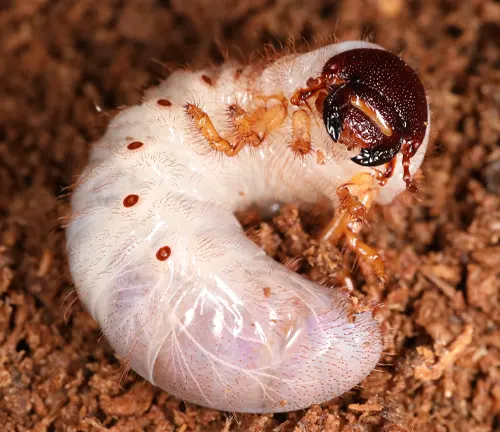


Larval Stage
During the larval stage, Hercules Beetle larvae, commonly known as grubs, emerge from the eggs and begin feeding on the surrounding decaying wood. They possess strong mandibles that allow them to break down tough plant fibers, aiding in their growth and development. The larvae undergo several molts as they grow, gradually increasing in size. This stage is crucial for the larvae to acquire the nutrients needed for their subsequent development into adults.
Pupal Stage
After completing the larval stage, Hercules Beetle larvae enter the pupal stage. During this stage, the larvae undergo metamorphosis, undergoing profound changes in their body structure as they transform into adults. Inside the pupal case, which is often buried in the soil or hidden within decaying wood, the larvae undergo a remarkable transformation process that ultimately leads to the emergence of an adult beetle.
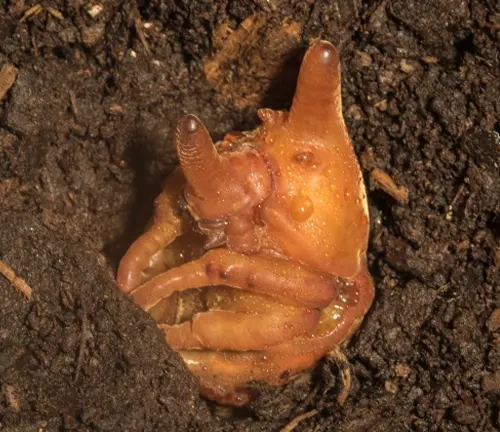
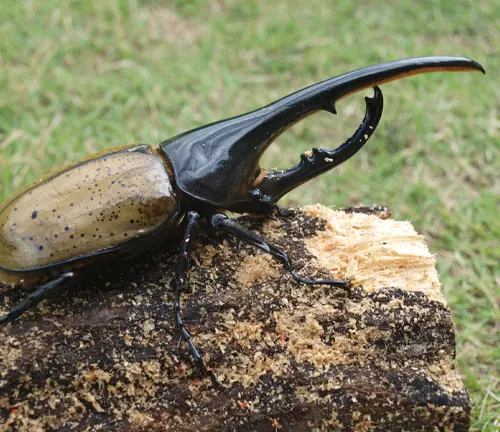


Adult Stage
Once fully developed, the adult Hercules Beetle emerges from its pupal case. At this stage, the beetle is sexually mature and capable of reproducing. Adult Hercules Beetles spend their time foraging for food, seeking out potential mates, and engaging in mating rituals. They play a crucial role in pollination and nutrient recycling within their ecosystem. The adult stage marks the final stage of the Hercules Beetle’s lifecycle, completing the cycle from egg to larva to pupa to adult.
Diet and Feeding Habits
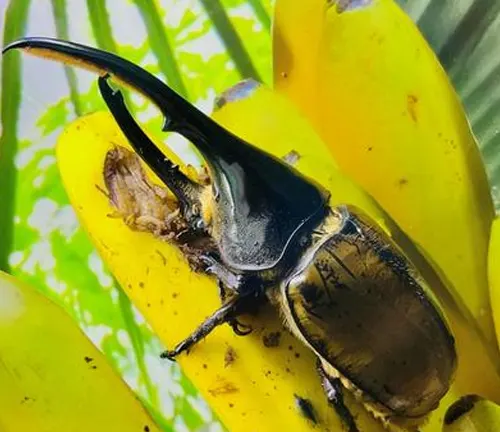
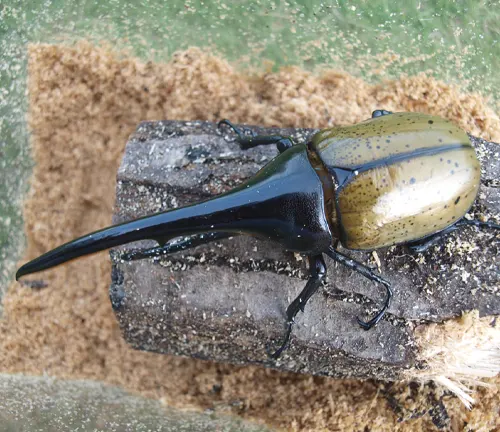


Hercules Beetles are primarily herbivorous insects, meaning they primarily feed on plant matter. Their diet consists mainly of sap, fruit, and nectar obtained from various sources within their habitat. Adult Hercules Beetles use their strong mandibles to access sap from trees, piercing through bark to reach the nutrient-rich fluids within. They also feed on ripe fruits and consume nectar from flowers, playing a crucial role in pollination.
During their larval stage, Hercules Beetle larvae, commonly known as grubs, have a different feeding habit. They are specialized decomposers, feeding on decaying wood and plant matter. Their strong mandibles allow them to break down tough plant fibers, aiding in the decomposition process. This feeding behavior not only helps recycle nutrients within their ecosystem but also contributes to the breakdown of dead organic matter, playing a vital role in nutrient cycling.
Behavior and Adaptations
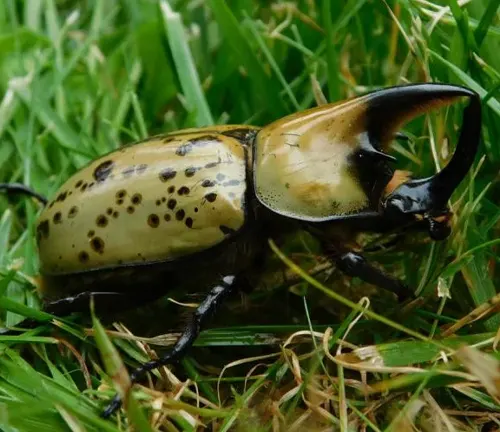
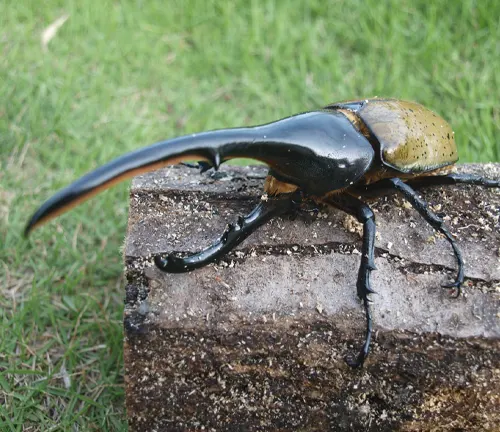


The Hercules Beetle (Dynastes hercules) exhibits fascinating behavior and possesses remarkable adaptations that enable it to thrive in its natural habitat. These beetles are primarily nocturnal, meaning they are most active during the night. During the day, they typically seek shelter in leaf litter, under logs, or within the crevices of trees to avoid predators and regulate their body temperature. At night, they emerge to forage for food and search for potential mates.
One of the most striking adaptations of the Hercules Beetle is its impressive strength, particularly in males. Male Hercules Beetles possess large, horn-like structures on their heads, which they use for combat with rival males and for asserting dominance during mating competitions. These horns are a testament to their formidable strength and play a crucial role in establishing territories and securing mating opportunities.
Defense Mechanisms
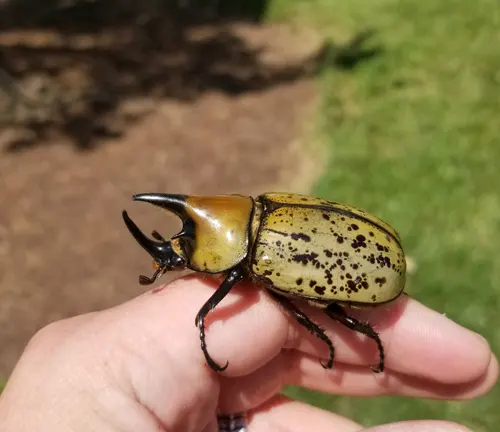

Despite their imposing size and strength, Hercules Beetles also employ various defense mechanisms to protect themselves from predators. One such mechanism is camouflage, where their coloration and patterns help them blend into their surroundings, making them less visible to potential threats.
In addition to camouflage, some Hercules Beetles can emit foul-smelling odors or produce loud hissing sounds when threatened, startling predators and giving the beetle an opportunity to escape. This behavior serves as a warning signal to predators, indicating that the beetle is not an easy target.
Furthermore, the robust exoskeleton of the Hercules Beetle provides physical protection against predators. Their hardened outer shell acts as a shield, reducing the risk of injury from attacks by predators such as birds, reptiles, and mammals.
Importance in Ecosystem
Hercules Beetles play a crucial role in their ecosystem as decomposers. By feeding on decaying organic matter, they help recycle nutrients and contribute to soil fertility.
Mythology and Cultural Significance
Throughout history, Hercules Beetles have been revered in various cultures for their strength and resilience. In ancient mythology, they symbolize power and endurance, often depicted as symbols of strength and protection.
Conservation Status
While Hercules Beetles are not currently considered endangered, habitat loss and deforestation pose significant threats to their survival. Conservation efforts are underway to protect their natural habitats and ensure their long-term viability.
Threats and Challenges
Human activities such as deforestation, urbanization, and illegal trade pose significant challenges to Hercules Beetle populations. Efforts to mitigate these threats are essential for preserving their habitats and preventing further declines in population numbers.
Human Interaction and Conservation Efforts
Scientists and conservationists are working tirelessly to study Hercules Beetles and implement conservation measures to protect their habitats. Initiatives such as habitat restoration, captive breeding programs, and public awareness campaigns are crucial for safeguarding these magnificent creatures.
Fascination with Hercules Beetle
Despite their intimidating appearance, Hercules Beetles continue to fascinate people around the world. Their extraordinary strength and unique adaptations make them a subject of admiration and intrigue among nature enthusiasts and researchers alike.
Different Species
Dynastes hercules
This is the most well-known species of Hercules Beetle, often referred to simply as the Hercules Beetle. It is native to the tropical forests of Central and South America.
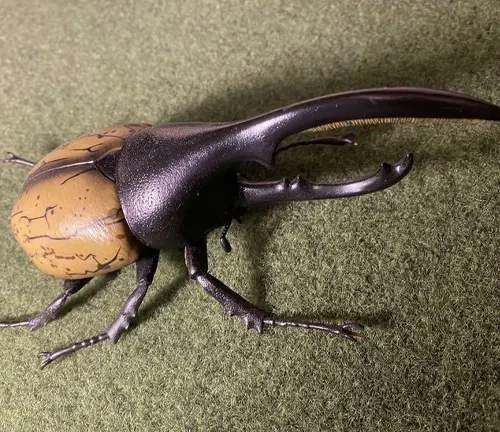
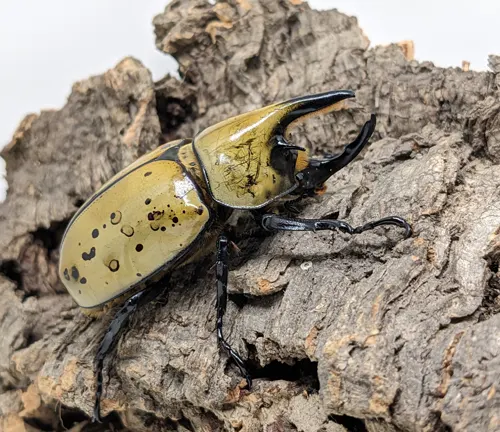


Dynastes tityus
Also known as the Eastern Hercules Beetle, this species is found in the eastern United States, particularly in states such as Florida and Georgia. It is slightly smaller than Dynastes hercules but still possesses impressive size and strength.
Dynastes granti
Found in Mexico and parts of the southwestern United States, including Arizona and New Mexico, Dynastes granti is commonly known as the Western Hercules Beetle. It is similar in appearance to Dynastes tityus but has distinct regional variations.
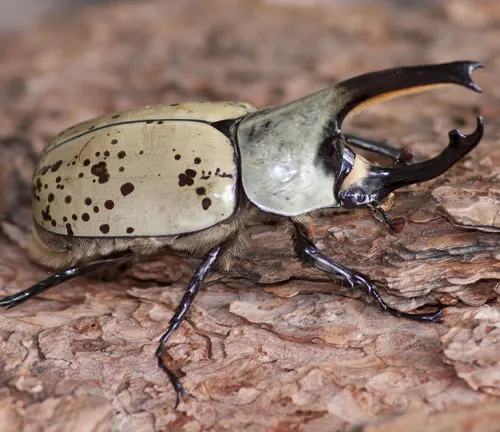
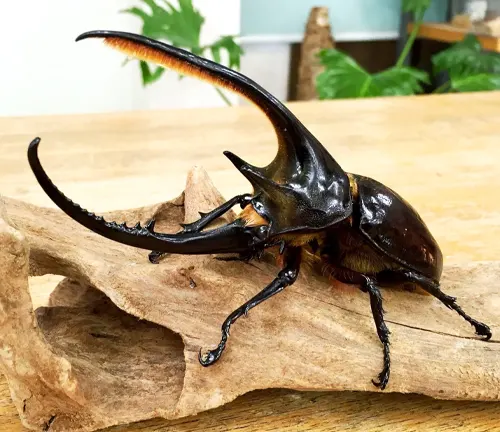


Dynastes neptunus
Native to South America, Dynastes neptunus is often called the Neptune Beetle. It is closely related to Dynastes hercules and shares similar physical characteristics, including large size and colorful exoskeleton.
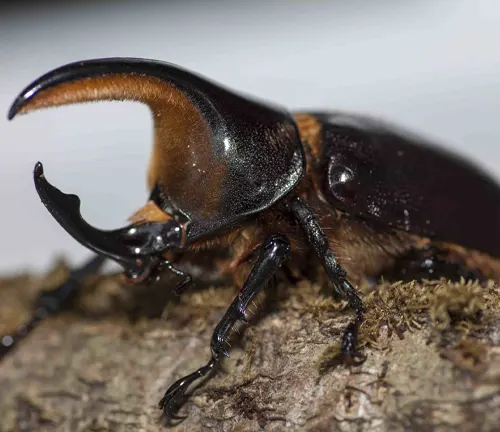
Dynastes satanas
This species, known as the Satanic Hercules Beetle, is found in the Amazon rainforest of South America. It is characterized by its striking black coloration and impressive horn-like structures on its head.

Frequently Asked Question (FAQs)
- Are Hercules Beetles aggressive?
Generally, Hercules Beetles are not aggressive towards humans. They may exhibit defensive behaviors if provoked but are not known to actively seek confrontation. - What do Hercules Beetles eat in the wild?
Hercules Beetles are primarily herbivorous, feeding on sap, fruit, and nectar. During their larval stage, they feed on decaying wood. - How big can Hercules Beetles grow?
Hercules Beetles can reach impressive sizes, with males growing up to 6.7 inches (17 centimeters) in length. - Do female Hercules Beetles have horns like males?
No, female Hercules Beetles typically do not have horns. Only male Hercules Beetles possess the characteristic horns on their heads, which they use for combat and mating displays. - What is the purpose of the horns on Hercules Beetles?
The horns on male Hercules Beetles serve multiple purposes, including combat with rival males for territory and mating rights, as well as attracting females during the breeding season. - How do Hercules Beetles defend themselves from predators?
Hercules Beetles employ various defense mechanisms to protect themselves from predators, including camouflage, hissing sounds, and foul-smelling secretions. - Do Hercules Beetles make good pets?
While some people may keep Hercules Beetles as pets, they require specific care and habitat conditions. It’s essential to research their needs thoroughly before considering them as pets. - Can Hercules Beetles be found outside of their natural habitat?
Hercules Beetles are primarily found in tropical forests, but they may occasionally be found in captivity or as exotic pets in other regions. - How long do Hercules Beetles stay in their pupal stage?
The duration of the pupal stage varies depending on environmental conditions and species, but it typically lasts several weeks to a few months. - Are Hercules Beetles nocturnal or diurnal?
Hercules Beetles are primarily nocturnal, meaning they are most active during the night. However, they may also be active during the early morning or evening hours. - Do Hercules Beetles have any cultural significance?
Yes, Hercules Beetles have been revered in various cultures throughout history for their symbolism of strength, resilience, and endurance. They often appear in mythology and folklore as symbols of power and protection.














Leave your comment