Goliath Beetle
- April 8, 2024
- 0 comment
The Goliath beetle, known scientifically as Goliathus spp., is a magnificent insect renowned for its impressive size and striking appearance. Belonging to the Scarabaeidae family, these beetles are among the largest in the world, with some species reaching lengths of up to 4.5 inches (11 centimeters) and weights exceeding 3.5 ounces (100 grams). Their exoskeletons display a dazzling array of colors and patterns, ranging from earthy browns and blacks to vibrant greens, yellows, and oranges. Found primarily in the tropical rainforests of Africa, particularly in regions like Central and West Africa, Goliath beetles inhabit dense forests where they can find abundant food sources and suitable breeding grounds.
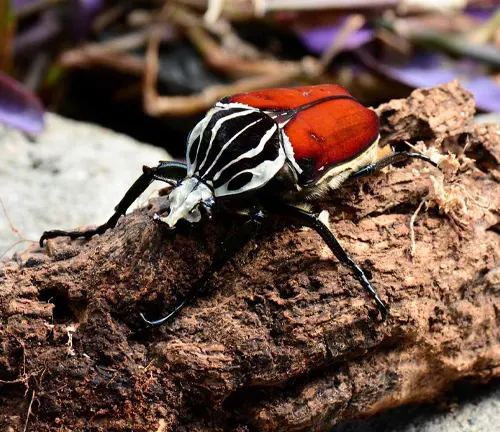

These beetles undergo complete metamorphosis, progressing through egg, larval, pupal, and adult stages. As adults, they primarily feed on fruits, tree sap, and other plant materials. Goliath beetles play a crucial role in their ecosystems as scavengers and decomposers, contributing to the breakdown of organic matter and nutrient cycling in forest environments. Despite their cultural significance and ecological importance, Goliath beetles face threats from habitat loss, deforestation, and climate change, underscoring the need for conservation efforts to ensure their survival for future generations to appreciate and admire.
| Specification | Description |
|---|---|
| Family | Scarabaeidae |
| Scientific Name | Goliathus spp. |
| Size | Up to 4.5 inches (11 centimeters) in length |
| Weight | Over 3.5 ounces (100 grams) |
| Color | Varied, ranging from black, brown, and white to vibrant greens, yellows, and oranges |
| Habitat | Tropical rainforests of Africa, particularly Central and West Africa |
| Diet | Fruits, tree sap, and other plant materials |
| Lifecycle | Complete metamorphosis, progressing through egg, larval, pupal, and adult stages |
| Role in Ecosystem | Scavengers and decomposers, contributing to the breakdown of organic matter and nutrient cycling |
| Conservation Status | Some species are considered vulnerable or endangered due to habitat loss and other threats |
Goliath Beetle
Goliath beetles, scientifically known as Goliathus spp., are among the largest and most impressive insects on the planet. These magnificent creatures belong to the family Scarabaeidae, which includes some of the largest beetles in the world. Goliath beetles are named after the biblical giant Goliath, owing to their impressive size and stature.
Physical Characteristics
Size and Appearance
Goliath beetles are renowned for their impressive size, making them one of the largest beetles in the world. They can reach lengths of up to 4.5 inches (11 centimeters) and weights exceeding 3.5 ounces (100 grams). Their bodies are robust and well-built, with a distinctively elongated shape. Additionally, male Goliath beetles often possess prominent horns on their thorax, which they use in combat and mating displays. Overall, their sheer size and formidable appearance make them a sight to behold in the insect world.
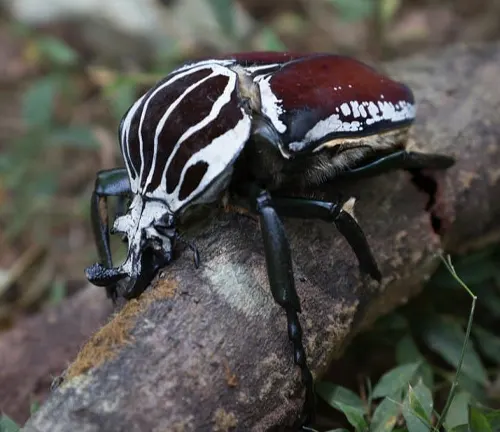

Coloration and Patterns
Goliath beetles showcase a dazzling array of colors and patterns on their exoskeletons. Their coloration can vary widely, ranging from shades of black, brown, and white to vibrant hues of green, yellow, and orange. These colors are often arranged in intricate patterns and designs, enhancing the beetle’s visual appeal. The patterns may include spots, stripes, or mottled markings, which serve both aesthetic and functional purposes. Moreover, the specific coloration and patterns can vary between different species and even among individuals within the same species, adding to the diversity and beauty of these remarkable insects.
Habitat and Distribution
Native Regions
Goliath beetles are primarily found in the tropical rainforests of Africa, particularly in regions such as Central and West Africa. These lush and biodiverse environments provide the ideal conditions for their survival, including ample food sources and suitable breeding grounds. Within their native range, Goliath beetles may inhabit various countries, including Cameroon, Nigeria, Ghana, Democratic Republic of the Congo, and Tanzania. Their distribution within these regions may vary depending on factors such as habitat availability, climate, and ecological dynamics.
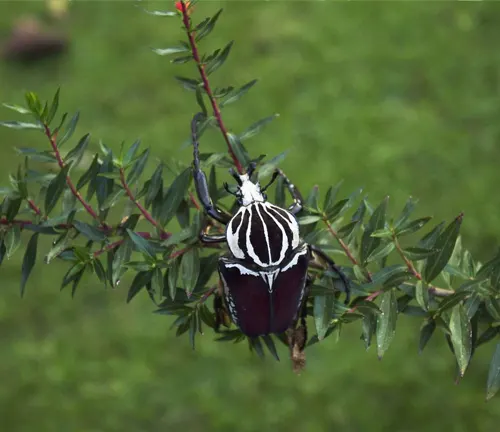
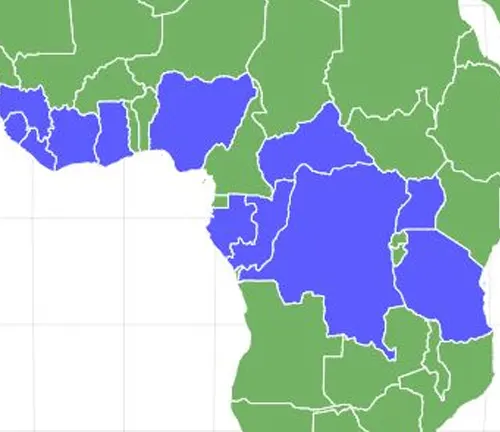

Preferred Habitats
Within their native regions, Goliath beetles prefer dense and humid forests with abundant vegetation. They are commonly found in both primary and secondary forests, where they can find a diverse range of food sources and shelter. Goliath beetles inhabit different microhabitats within the forest ecosystem, including forest floors, canopy levels, and transitional zones between forest and open areas. They may also occur in agricultural areas or disturbed habitats, although their abundance and distribution are typically higher in undisturbed forest environments. These beetles rely on specific environmental conditions, such as high humidity and access to decaying organic matter, for their survival and reproduction.
Lifecycle and Behavior
Life Stages
Goliath beetles undergo complete metamorphosis, progressing through four distinct life stages: egg, larva, pupa, and adult. The life cycle begins when a female lays eggs in decaying organic matter, such as rotting wood or leaf litter, providing a suitable environment for the larvae to develop. After a period of incubation, the eggs hatch into larvae, which are voracious feeders. During the larval stage, Goliath beetle larvae consume large quantities of decaying plant matter and organic debris, growing rapidly as they prepare for pupation. Once fully grown, the larvae enter the pupal stage, where they undergo a transformation into adults. After emerging from the pupal casing, the newly formed adult beetles are ready to mate and continue the life cycle.
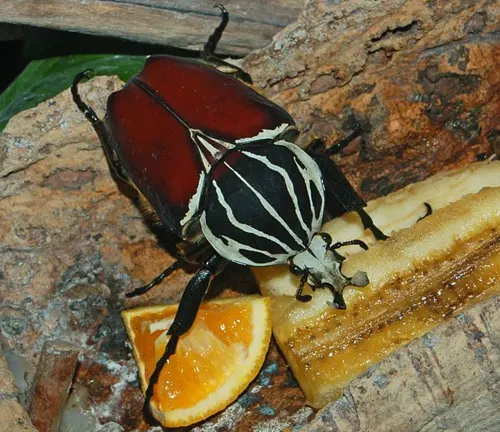
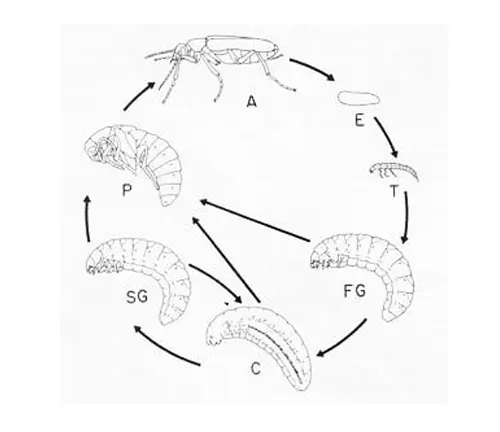

Feeding Habits
As adults, Goliath beetles primarily feed on fruits, tree sap, and other plant materials. Their diet may also include nectar, pollen, and other sugary substances found in their natural habitat. Goliath beetles use their powerful mandibles to chew through tough outer layers of fruits and wood, enabling them to access the nutrient-rich tissues inside. Additionally, they may consume sap from wounded trees or feed on ripe fruits that have fallen to the forest floor. While feeding preferences may vary between species and individuals, Goliath beetles play an important role in the ecosystem as pollinators and seed dispersers, contributing to the maintenance of forest biodiversity.
Mating and Reproduction
During the mating season, male Goliath beetles engage in elaborate mating rituals to attract females. These rituals often involve displays of strength and dominance, with males competing for the attention of receptive females. Once mating is successful, females lay eggs in decaying organic matter, providing a suitable environment for larval development.
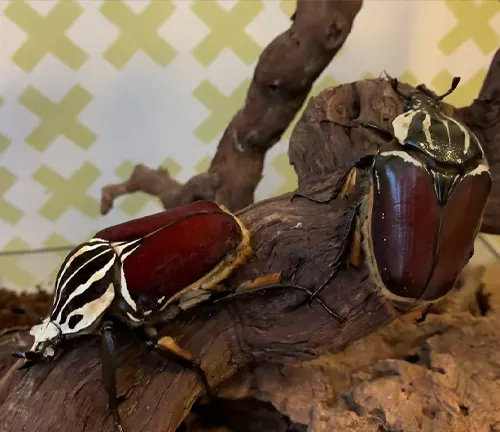

Importance in Ecosystem
Mating in Goliath beetles is a fascinating process that involves intricate behaviors and displays. During the mating season, typically triggered by environmental cues such as temperature and humidity, male Goliath beetles actively seek out receptive females. To attract potential mates, males often engage in elaborate displays of strength and dominance, which may include raising and fluttering their wings, emitting pheromones, and producing audible sounds. These displays serve to advertise the male’s fitness and genetic quality to nearby females.
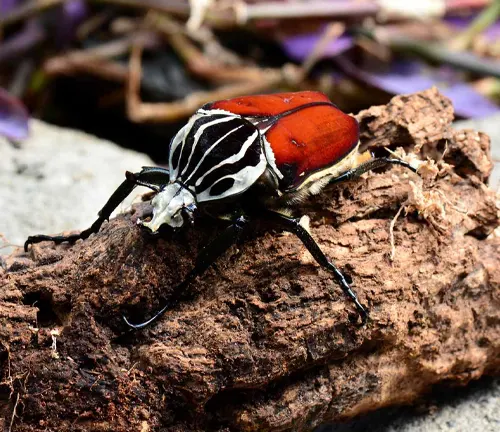

Once a female has been courted successfully, mating occurs through direct physical contact between the male and female beetles. In some species, males may engage in combat with rival males to establish dominance and secure mating opportunities. After mating, the female Goliath beetle lays her eggs in a suitable substrate, such as decaying organic matter or soil, where they are protected from predators and environmental stressors.
Cultural Significance
Goliath beetles hold significant cultural importance in many African societies, where they are revered for their strength, resilience, and beauty. These majestic insects feature prominently in folklore, traditional ceremonies, and art, symbolizing various themes such as power, protection, and transformation. In some cultures, Goliath beetles are associated with spiritual beliefs and rituals, with certain tribes attributing mystical qualities to these iconic insects. Additionally, Goliath beetles are sometimes used in decorative crafts and jewelry, reflecting their cultural significance and aesthetic appeal. Overall, Goliath beetles play an integral role in African culture, serving as symbols of nature’s magnificence and the interconnectedness of all living beings.
Conservation Status
Despite their cultural significance and ecological importance, Goliath beetles face numerous threats to their survival, resulting in varying conservation statuses for different species. Habitat loss and degradation due to deforestation, agricultural expansion, and urban development pose significant challenges to Goliath beetle populations, particularly in their native tropical rainforest habitats. Additionally, climate change and environmental disturbances further exacerbate the threats faced by these beetles and their ecosystems.
Threats and Challenges
The primary threats to Goliath beetles include habitat destruction caused by deforestation, agricultural expansion, and urban development. Fragmentation of forest habitats further exacerbates the challenges faced by these beetles, limiting their ability to find suitable breeding sites and food sources.
Human Interaction and Impact
Human activities such as logging, mining, and agriculture have a significant impact on Goliath beetle populations and their habitats. Deforestation not only destroys crucial habitat but also disrupts ecological processes essential for the survival of these beetles and other forest organisms.
Keeping Goliath Beetles as Pets
In some regions, enthusiasts and collectors keep Goliath beetles as pets, fascinated by their impressive size and unique beauty. However, responsible ownership is essential to ensure the welfare of these beetles and minimize the impact on wild populations.
Interesting Facts and Records
- Goliath beetles are among the heaviest insects in the world, with some individuals weighing as much as a small bird.
- Male Goliath beetles possess distinctive horns on their thorax, which they use in combat and mating displays.
- These beetles have a relatively short lifespan, with adults typically living for only a few months to a year depending on species and environmental conditions.
Research and Study
Scientists and researchers continue to study Goliath beetles to better understand their biology, behavior, and ecological roles. Conservation efforts aim to protect these iconic insects and their habitats for future generations to appreciate and enjoy.
Goliath Beetle in Popular Culture
Goliath beetles have captured the imagination of people worldwide and have appeared in various forms of popular culture, including literature, film, and art. Their impressive size and striking appearance make them popular subjects for documentaries and educational programs.
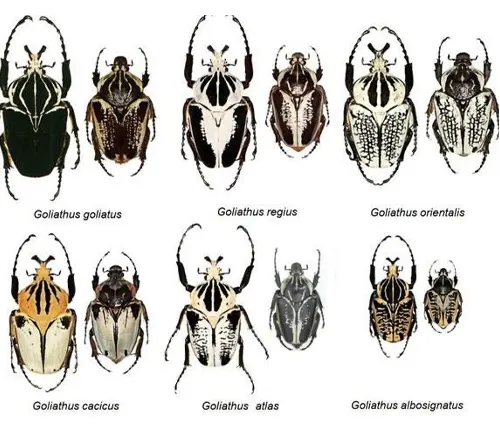
Different Species
Goliathus goliatus
Also known as the Giant African Goliath beetle, this species is one of the largest beetles in the world, native to various countries in West Africa.
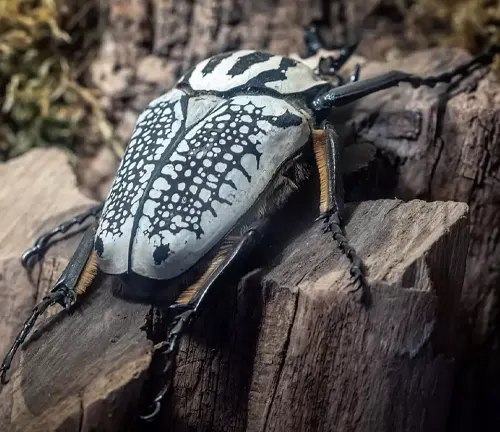
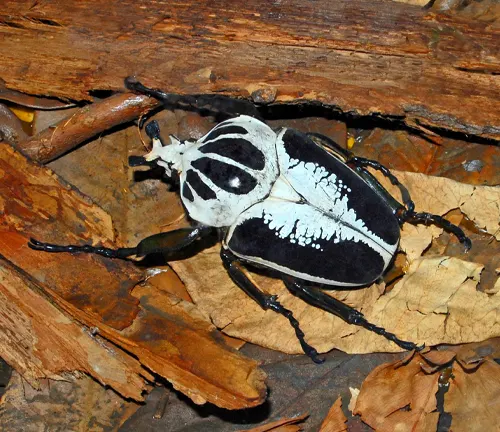


Goliathus regius
Commonly referred to as the Royal Goliath beetle, this species is characterized by its striking coloration, featuring vibrant hues of green, yellow, and black. It is found in Central and West Africa.
Goliathus orientalis
Native to East Africa, particularly countries like Tanzania and Kenya, this species of Goliath beetle is known for its impressive size and distinctive horned appearance.
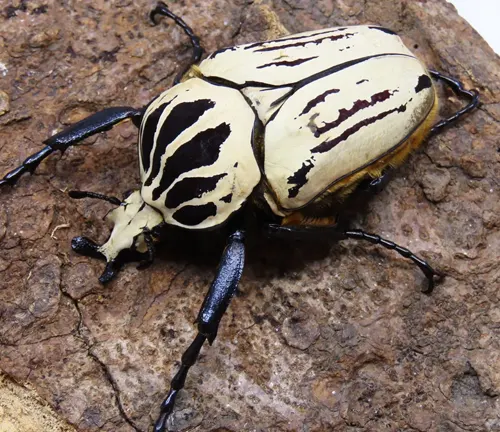
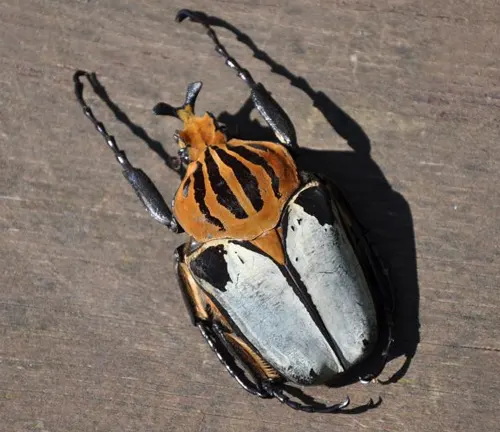


Goliathus cacicus
Found in regions of West Africa, including countries like Nigeria and Cameroon, this species is distinguished by its robust build and intricate patterns on its exoskeleton.
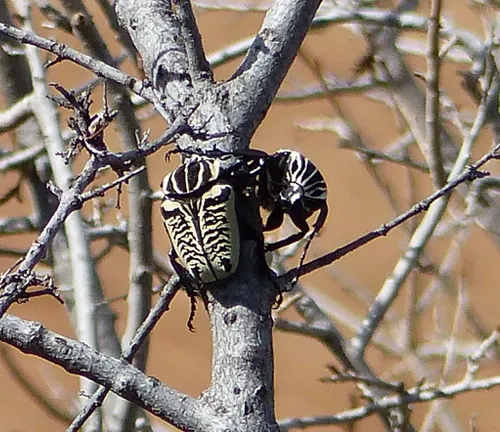
Goliathus albosignatus
Endemic to regions of Central Africa, such as the Democratic Republic of the Congo, this species of Goliath beetle displays a combination of white and black markings on its exoskeleton.

Frequently Asked Question (FAQs)
- What is a Goliath beetle?
A Goliath beetle is a large insect belonging to the Scarabaeidae family, known for its impressive size and striking appearance. - Where are Goliath beetles found?
Goliath beetles are primarily found in the tropical rainforests of Africa, particularly in regions like Central and West Africa. - How big can Goliath beetles get?
Goliath beetles can reach lengths of up to 4.5 inches (11 centimeters) and weights exceeding 3.5 ounces (100 grams), making them one of the largest beetles in the world. - What do Goliath beetles eat?
Goliath beetles primarily feed on fruits, tree sap, and other plant materials, using their powerful mandibles to chew through tough outer layers. - How do Goliath beetles reproduce?
Goliath beetles undergo complete metamorphosis, with females laying eggs in decaying organic matter. Larvae hatch from the eggs and feed voraciously before pupating and emerging as adults. - Do Goliath beetles have any predators?
Goliath beetles may face predation from birds, small mammals, and other insects, particularly during vulnerable life stages such as larvae. - Are Goliath beetles endangered?
- Some species of Goliath beetles are considered vulnerable or endangered due to habitat loss, deforestation, and other threats to their survival.
- Can Goliath beetles fly?
While Goliath beetles have wings, they are not strong fliers and typically rely on climbing and gliding to navigate their environment. - How long do Goliath beetles live in captivity?
In captivity, Goliath beetles can live for several months to a year or more, depending on species and environmental conditions. - What is the cultural significance of Goliath beetles?
Goliath beetles hold symbolic significance in many African cultures, often representing themes such as strength, resilience, and transformation. - Are Goliath beetles commonly kept as pets?
While not as common as some other insect species, Goliath beetles are kept as pets by enthusiasts who appreciate their size and unique beauty.














Leave your comment