Indian Red Scorpion
- March 27, 2024
- 0 comment
The Indian Red Scorpion, scientifically known as Hottentotta tamulus, is a species of scorpion found predominantly in the Indian subcontinent. Renowned for its striking reddish-brown coloration, this arachnid typically measures between 2.5 and 4 inches in length. Despite its small size, the Indian Red Scorpion possesses a venomous sting that contains potent neurotoxins, making it one of the deadliest scorpions in the world. Its habitat ranges from semi-arid regions to urban areas, where it preys on insects, spiders, and small vertebrates during the night.
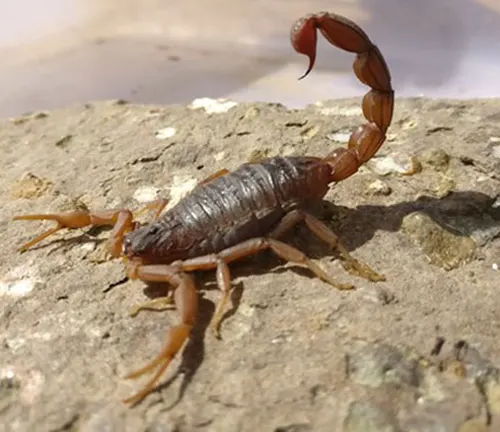

While playing a crucial role in controlling pest populations, encounters with humans can lead to severe medical emergencies, as its venom can cause respiratory distress, convulsions, and even death if left untreated. Conservation efforts aim to protect its natural habitat and raise awareness about its importance in the ecosystem. Understanding its behavior and venom composition is crucial for developing effective treatment strategies and ensuring safe coexistence with this formidable creature.
Indian Red Scorpion Characteristics
| Characteristic | Description |
|---|---|
| Scientific Name | Hottentotta tamulus |
| Size | Typically 2.5 to 4 inches in length |
| Coloration | Reddish-brown |
| Venom | Highly potent neurotoxin |
| Habitat | Semi-arid regions, including forests and urban areas |
| Diet | Insects, spiders, small vertebrates |
| Nocturnal Activity | Hunts during the night |
| Behavior | Aggressive when provoked |
| Importance | Plays a crucial role in controlling pest populations |
| Medical Significance | Venom can cause severe symptoms in humans, including respiratory distress and convulsions |
| Conservation Status | Faces threats from habitat loss and human encroachment |
| Research Focus | Understanding behavior, venom composition, and medical implications |
| Interesting Facts | Fluoresces under ultraviolet light, known for distinctive mating rituals, capable of delivering lethal stings |
Physical Characteristics
Size and Coloration
The Indian Red Scorpion, typically measures between 2 to 3 inches in length. While it may not boast the imposing stature of larger predators, its compact size belies its lethal capabilities. What truly captures the attention, however, is its vivid crimson hue. Adorned in shades ranging from burnt orange to deep red, the Indian Red Scorpion stands out as a beacon of danger amidst the diverse flora and fauna of its habitat.
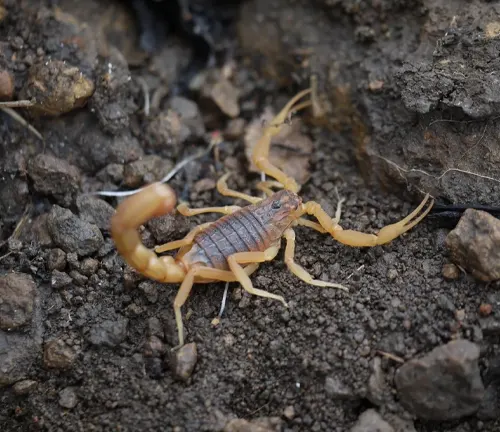
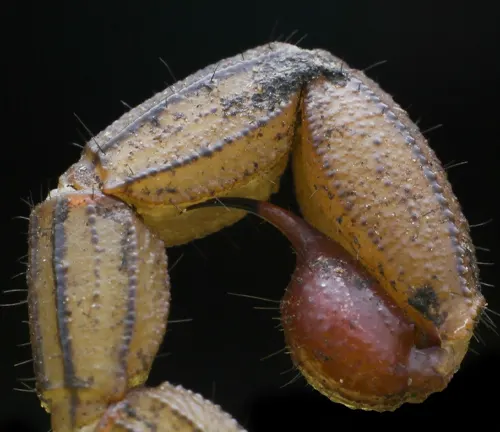


Venomous Stinger
Beneath its innocuous appearance lies a potent weapon – the venomous stinger. Positioned at the end of its tail, this formidable appendage serves as both a means of defense and a tool for subduing prey. The venom injected by the Indian Red Scorpion is a complex cocktail of neurotoxins, enzymes, and peptides, meticulously crafted to incapacitate its victims swiftly and efficiently.
Habitat and Distribution
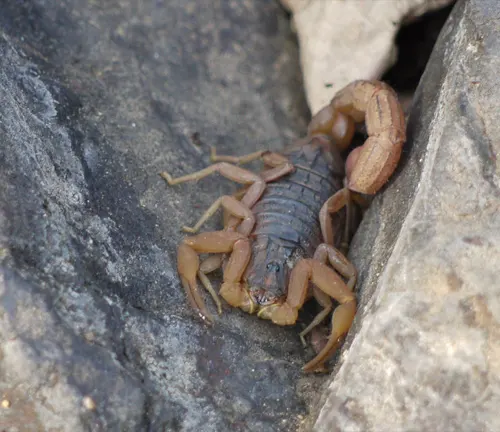

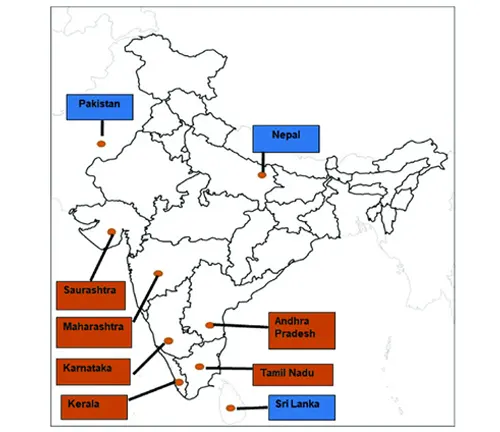
Habitat and Distribution: Nestled within the varied landscapes of the Indian subcontinent, the Indian Red Scorpion finds its niche in habitats characterized by warmth, moisture, and abundant prey. From arid deserts to lush forests, this resilient arachnid adapts to a diverse array of environments, each offering unique challenges and opportunities for survival.
The Indian Red Scorpion’s preferred habitats include dry and sandy regions, where it seeks refuge in burrows or crevices to escape the scorching sun. These arid landscapes provide ample opportunities for hunting, as the scorpion preys upon insects, spiders, and even small vertebrates that venture too close. Despite its affinity for dry climates, the Indian Red Scorpion can also be found in more humid environments, such as tropical forests and coastal areas, where it thrives amidst the dense vegetation and abundant prey populations.
In terms of distribution, the Indian Red Scorpion boasts a widespread presence across the Indian subcontinent, spanning regions from the foothills of the Himalayas to the southern tip of the peninsula. Its range encompasses countries such as India, Nepal, Sri Lanka, and Bangladesh, where it establishes colonies in both rural and urban settings. Within these territories, the Indian Red Scorpion exhibits a remarkable ability to adapt to human-altered landscapes, often taking up residence in agricultural fields, gardens, and even urban dwellings.
Behavior and Diet
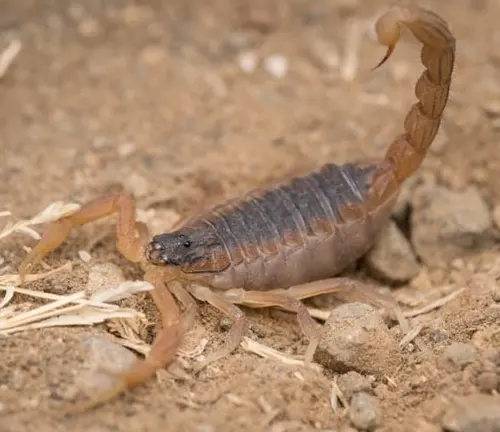
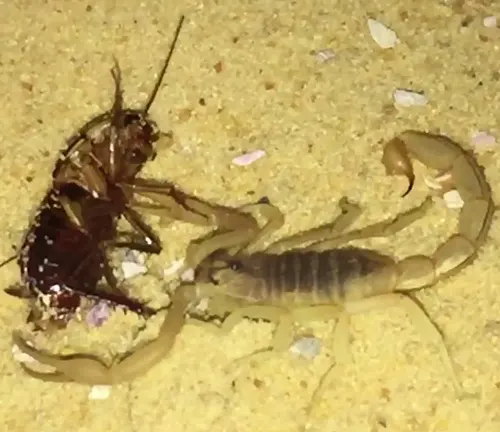


Beneath the veil of its crimson exoskeleton lies a creature of remarkable complexity – the Indian Red Scorpion. Beyond its formidable appearance, this arachnid exhibits a repertoire of behaviors and dietary preferences that contribute to its survival in the harsh environments of the Indian subcontinent.
The Indian Red Scorpion is a nocturnal predator, preferring to emerge under the cover of darkness to hunt for prey. Armed with its keen sense of smell and vibration-sensitive hairs, it prowls the sandy terrain in search of unsuspecting victims. In urban environments, it may also seek shelter in dark, secluded spaces such as basements, attics, or abandoned structures, where it can remain hidden from potential predators and disturbances.
As an opportunistic feeder, the Indian Red Scorpion preys upon a wide range of invertebrates, including insects, spiders, centipedes, and even small vertebrates such as lizards and rodents. Using its powerful pincers and venomous stinger, it subdues and immobilizes its prey before delivering a lethal dose of venom. This potent combination of hunting tactics ensures the Indian Red Scorpion’s success as a formidable predator in its ecosystem.
Importance and Impact
The Indian Red Scorpion, with its vibrant crimson hue and potent venom, holds a significant place in the ecosystems of the Indian subcontinent. Despite its small size, this arachnid plays a crucial role in regulating insect populations and contributing to the balance of its habitat. However, its presence also carries implications for human health and well-being, underscoring the need for a nuanced understanding of its venom toxicity and effective treatment for stings.
Medical Significance
Venom Toxicity
One of the most striking features of the Indian Red Scorpion is its venomous sting, which contains a complex cocktail of neurotoxins, enzymes, and peptides. Upon envenomation, the venom targets the nervous system, causing a cascade of symptoms ranging from localized pain and swelling to systemic effects such as muscle spasms, respiratory distress, and cardiovascular collapse. In severe cases, particularly in vulnerable populations such as children and the elderly, envenomation can be life-threatening, highlighting the importance of recognizing and promptly treating scorpion stings.
Treatment for Stings
The management of Indian Red Scorpion stings hinges on a combination of supportive care and administration of antivenom. Upon encountering a scorpion sting victim, it is crucial to assess the severity of symptoms and provide immediate first aid measures, including cleaning the wound, applying ice packs to reduce swelling, and immobilizing the affected limb to minimize the spread of venom. In cases of moderate to severe envenomation, the administration of specific antivenom remains the cornerstone of treatment, neutralizing the effects of the scorpion venom and alleviating symptoms.
Conservation Status
The Indian Red Scorpion, despite its formidable reputation, faces threats to its survival due to habitat loss, pesticide use, and human encroachment. While it currently lacks a formal conservation status, efforts to protect its natural habitat and mitigate human-wildlife conflicts are essential for ensuring its long-term viability in the wild.
Interesting Facts
- Despite their small size, Indian Red Scorpions are capable of delivering a lethal sting to humans.
- They are known for their distinctive mating rituals, which involve intricate dances and displays.
- Indian Red Scorpions fluoresce under ultraviolet light, making them easier to detect in the dark.
Prevention and Safety Measures
To minimize encounters with the Indian Red Scorpion and reduce the risk of stings, individuals living in areas where the species is present should take proactive measures such as sealing cracks and crevices in homes, using insect screens on windows and doors, and exercising caution when handling outdoor debris or reaching into dark, secluded spaces.
Research and Study
Ongoing research into the biology, behavior, and venom composition of the Indian Red Scorpion is essential for deepening our understanding of this enigmatic species. By studying its ecological role, venom toxicity, and interactions with other organisms, researchers can inform conservation strategies, develop effective antivenoms, and enhance public awareness of scorpion safety.
Mythology and Folklore
The Indian Red Scorpion holds a prominent place in the mythology and folklore of the Indian subcontinent, where it is often depicted as a symbol of danger, cunning, and mystique. Tales of encounters with the scorpion abound in local folklore, serving as cautionary tales or sources of inspiration for storytelling traditions passed down through generations.
Comparisons with Other Scorpions
In comparison to other scorpion species worldwide, the Indian Red Scorpion stands out for its vibrant coloration, potent venom, and widespread distribution across the Indian subcontinent. While it shares certain characteristics with other scorpions, such as nocturnal behavior and predatory habits, its unique adaptations and ecological niche distinguish it as a species of significant interest to researchers and enthusiasts alike.
Future Implications
Looking ahead, the conservation and management of the Indian Red Scorpion hold implications not only for the species itself but also for broader ecological dynamics and human well-being. By prioritizing habitat conservation, promoting coexistence with wildlife, and advancing scientific research and public education initiatives, we can foster a future where humans and scorpions can thrive in harmony.
Different Species
Hottentotta tamulus
This is the most well-known species commonly referred to as the Indian Red Scorpion. It is found primarily in the Indian subcontinent and is notorious for its potent venom.
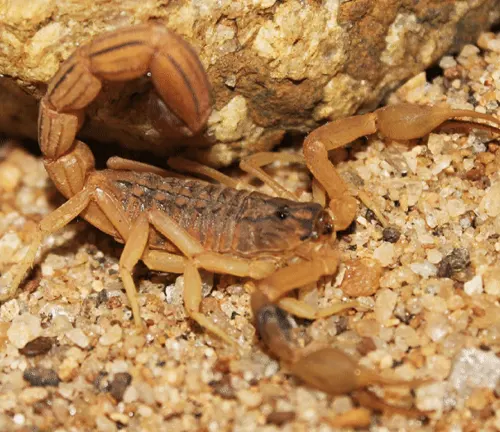
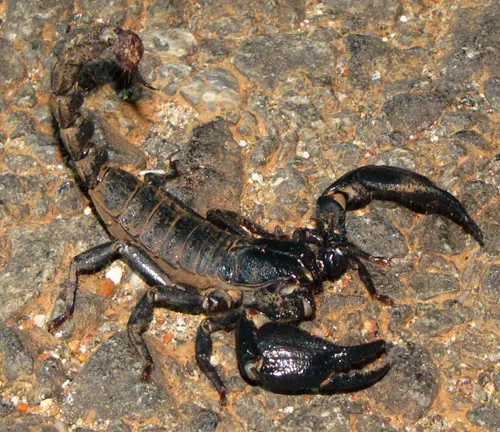


Heterometrus bengalensis
Also known as the Indian Black Scorpion, this species is closely related to the Indian Red Scorpion. It is found in various regions of India and is known for its dark coloration.
Isometrus maculatus
While not as prominently red as the other species, the Isometrus maculatus, commonly known as the Lesser brown Scorpion, still possesses a reddish-brown coloration. It is found in parts of India and Sri Lanka.

Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
- Are Indian Red Scorpions deadly?
Yes, Indian Red Scorpions possess venom that can be lethal to humans, especially if left untreated. - What should I do if I encounter an Indian Red Scorpion?
It’s crucial to remain calm and slowly retreat from the area. Seek medical attention immediately if stung. - Can Indian Red Scorpions be kept as pets?
While some enthusiasts keep them in captivity, their venomous nature makes them risky pets and requires specialized care. - How can I identify an Indian Red Scorpion?
Look for their reddish-brown coloration and distinctive thin pincers, along with their venomous stinger. - What measures can be taken to prevent encounters with Indian Red Scorpions?
Seal cracks and crevices in buildings, wear protective clothing when working outdoors, and avoid leaving food sources accessible to insects, which may attract scorpions. - What are the symptoms of an Indian Red Scorpion sting?
Symptoms may include intense pain, swelling, sweating, difficulty breathing, and convulsions. - Is antivenom available for Indian Red Scorpion stings?
Yes, specific antivenoms are available for treating severe envenomation caused by Indian Red Scorpion stings. - Where are Indian Red Scorpions commonly found?
They are primarily found in semi-arid regions of the Indian subcontinent, including parts of India, Nepal, and Sri Lanka. - Do Indian Red Scorpions have any predators?
While they are apex predators in their habitat, Indian Red Scorpions may face predation from larger animals such as birds, reptiles, and mammals. - How long do Indian Red Scorpions live?
The lifespan of Indian Red Scorpions varies but typically ranges from three to five years in the wild. - Can Indian Red Scorpions climb walls or surfaces?
Yes, Indian Red Scorpions are adept climbers and can scale walls and other vertical surfaces using their specialized claws. - Do Indian Red Scorpions have any natural enemies?
While they have few natural enemies, certain species of birds, mammals, and other predators may feed on Indian Red Scorpions, helping to regulate their population.














Leave your comment