Darners Dragonfly
- April 4, 2024
- 0 comment
The darner dragonfly, a captivating member of the Aeshnidae family, is a creature of both beauty and intrigue. With its elongated body, adorned with large, multifaceted eyes and intricate wing patterns, the darner dragonfly is a symbol of grace and agility in the natural world. Found near freshwater habitats such as ponds, lakes, and streams, these creatures enchant observers with their agile flight and mesmerizing colors. Throughout its life cycle, from egg to nymph to adult, the darner dragonfly plays a vital role in its ecosystem, preying on small insects and contributing to the balance of the food chain.
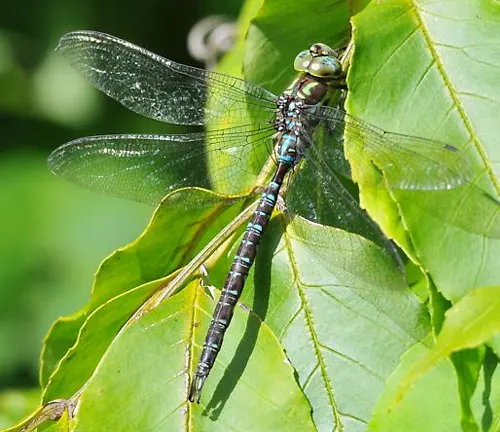

Despite facing threats such as habitat loss and pollution, efforts to conserve these magnificent insects are underway, highlighting their importance in maintaining healthy ecosystems. With their cultural significance and ecological value, darner dragonflies continue to fascinate and inspire admiration among nature enthusiasts worldwide.
| Specifications | Details |
|---|---|
| Family | Aeshnidae |
| Appearance | Elongated body, large multifaceted eyes, intricate wing patterns |
| Habitat | Near freshwater habitats such as ponds, lakes, and streams |
| Behavior | Agile flight, adept at hovering and changing direction swiftly |
| Diet | Predatory, feeding on small insects |
| Lifecycle | Egg stage, nymph stage (spent underwater), adult stage |
| Importance in Ecosystem | Apex predators, help regulate insect populations |
| Threats | Habitat loss, pollution, climate change |
| Conservation Efforts | Habitat restoration, pollution mitigation, public awareness campaigns |
| Cultural Significance | Symbol of grace and agility, themes of renewal and protection |
| Lifespan | Several weeks to a few months (adult stage) |
| Migration | Some species undertake long-distance migrations |
| Predators | Birds, fish, frogs, and other insectivorous animals |
| Fascination | Inspires art, photography, and admiration among nature enthusiasts |
Darners Dragonfly: Nature’s Graceful Flyers
Darners dragonflies, members of the Aeshnidae family, are captivating insects known for their elegance and aerial prowess. These creatures, often spotted near water bodies or in open fields, play significant roles in ecosystems worldwide.
Characteristics of Darners Dragonfly
Physical Appearance
Darner dragonflies boast an elongated body structure, characterized by a sleek and slender form. They possess large, multifaceted eyes that grant them exceptional vision, enabling them to detect prey and navigate their surroundings with precision. One of the most striking features of darner dragonflies is their vibrant coloration, which varies among species but often includes hues of green, blue, brown, and black. Their wings are transparent and membranous, adorned with intricate patterns that add to their aesthetic appeal. Additionally, darner dragonflies are equipped with spiny legs, which they use to grasp onto surfaces and capture prey during flight.
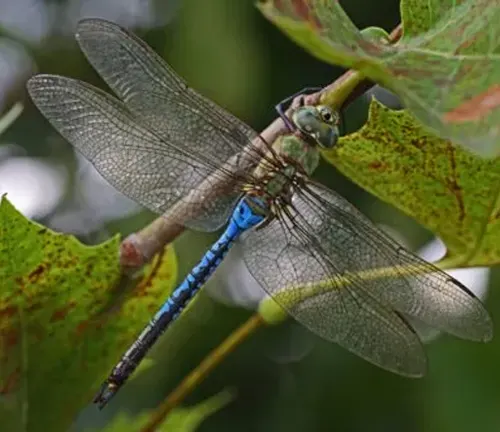


Behavior
Darner dragonflies are renowned for their agile and graceful flight patterns, making them adept aerial hunters. They possess remarkable maneuverability, allowing them to dart and hover with ease as they pursue prey or defend their territory. Their flight capabilities are further enhanced by their ability to change direction swiftly, enabling them to evade predators and navigate complex environments effectively. Darner dragonflies are primarily diurnal, meaning they are active during the daytime, and they are often seen basking in the sunlight or patrolling their territory in search of food. Their behavior also includes courtship rituals, which involve intricate aerial displays and mating rituals designed to ensure successful reproduction. Overall, the behavior of darner dragonflies reflects their adaptability and efficiency as apex predators in their respective ecosystems.
Habitat and Distribution
Where can darners dragonflies be found?
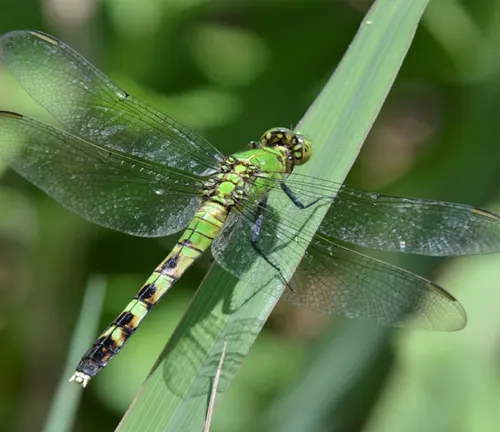
Darner dragonflies are commonly found in a variety of habitats across the globe, with a preference for areas near freshwater sources. These habitats include ponds, lakes, rivers, streams, marshes, and wetlands, where they can find suitable breeding grounds and ample food sources. Additionally, darner dragonflies can be observed in open fields, meadows, and grasslands, particularly in areas with abundant vegetation and access to water. Their presence is often associated with regions that offer a diverse range of habitats, providing them with opportunities for foraging, mating, and resting. Overall, darner dragonflies exhibit a wide distribution and can thrive in diverse environments as long as their basic habitat requirements are met.

Preferred Habitats
Darner dragonflies exhibit a preference for habitats with specific characteristics that cater to their ecological needs. They are commonly found in areas with clean, unpolluted water bodies, as they require suitable aquatic environments for breeding and nymphal development. Vegetated habitats, such as those with emergent aquatic plants or dense foliage along the water’s edge, are particularly attractive to darner dragonflies, providing them with perching sites and shelter from predators. Additionally, habitats with abundant insect populations serve as ideal foraging grounds for adult darner dragonflies, ensuring a steady food supply. Overall, darner dragonflies thrive in habitats that offer a combination of freshwater resources, vegetation, and suitable microhabitats for various life stages, making them a common sight in diverse ecosystems worldwide.
Life Cycle
Egg Stage
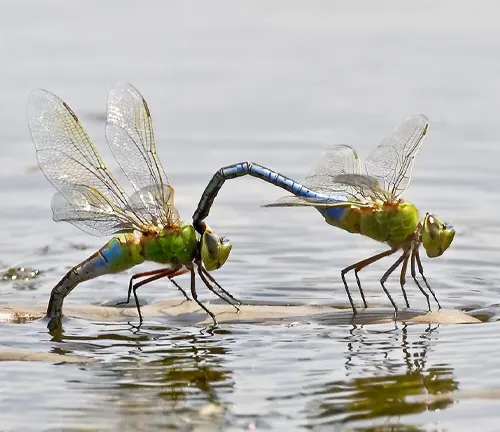
During the egg stage of the darner dragonfly’s life cycle, females lay their eggs in or near water bodies, typically within aquatic vegetation or along the water’s edge. The eggs are deposited either singly or in clusters, depending on the species, and adhere to submerged vegetation or other surfaces. Darner dragonfly eggs are small and elongated, with a protective outer layer that shields them from desiccation and predation. The duration of the egg stage varies among species but typically lasts for several weeks to months, depending on environmental conditions such as temperature and water quality.
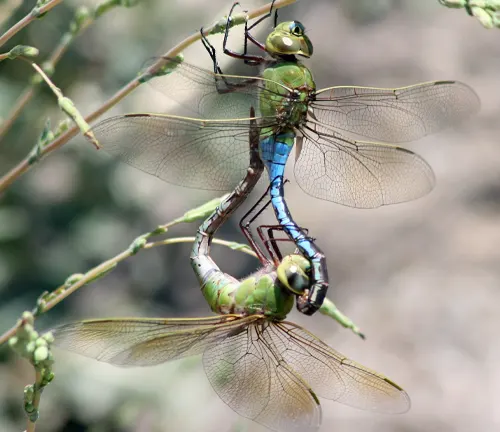

Larval Stage
After hatching from the eggs, darner dragonfly larvae, known as nymphs or naiads, enter the larval stage of their development. Nymphs are aquatic and spend the majority of their lives underwater, where they feed on a variety of small aquatic organisms such as insect larvae, small fish, and tadpoles. They possess elongated bodies with segmented abdomens, gills for respiration, and powerful mandibles for capturing prey. Darner dragonfly nymphs undergo several molts as they grow, shedding their exoskeletons to accommodate their increasing size. The duration of the larval stage can range from several months to several years, depending on factors such as species and environmental conditions.
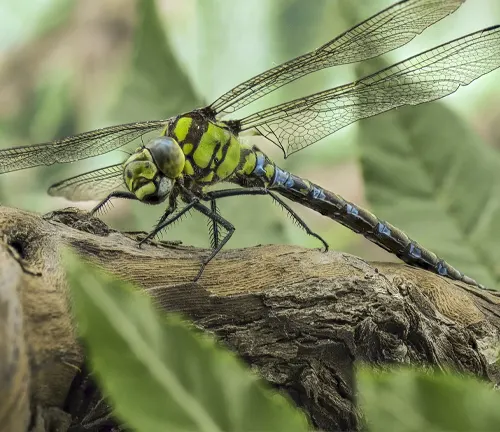

Adult Stage
Upon reaching maturity, darner dragonfly nymphs emerge from the water and undergo metamorphosis to transform into winged adults. The adult stage is relatively short-lived compared to the larval stage, focusing primarily on mating and reproduction. Adult darner dragonflies have elongated bodies with four membranous wings, large multifaceted eyes, and intricate wing patterns. They are powerful fliers and are often seen patrolling their territory in search of mates or hunting for prey. The lifespan of adult darner dragonflies varies among species but typically ranges from several weeks to a few months. During this time, they play a crucial role in ecosystems as apex predators, controlling insect populations and contributing to the balance of the food chain.
Diet and Feeding Habits
What do darners dragonflies eat?
Darner dragonflies are voracious predators and primarily feed on a wide variety of small flying insects. Their diet includes mosquitoes, flies, midges, moths, butterflies, and other insects that are commonly found in their habitat. Adult darner dragonflies are skilled hunters and rely on their exceptional eyesight and aerial agility to locate and capture prey mid-flight. They are opportunistic feeders and will actively pursue flying insects while patrolling their territory or hovering near water bodies.
Hunting Techniques
Darner dragonflies employ several hunting techniques to capture their prey effectively. One of their primary hunting strategies involves aerial pursuit, where they chase down flying insects in flight. Using their keen eyesight to detect movement and their agile flight capabilities to maneuver swiftly, darner dragonflies close in on their prey with precision and speed. Once within striking distance, they use their spiny legs to grasp onto their prey and immobilize it, securing it for consumption.
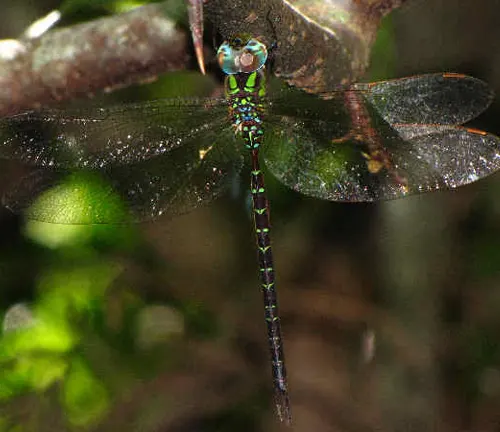

Predators and Defense Mechanisms
Natural Predators
Despite their agility and speed, darner dragonflies face predation from various natural predators. Among the most common predators are birds, including species such as swallows, kingfishers, and larger dragonflies. Birds often snatch darner dragonflies mid-flight, taking advantage of their aerial pursuits to capture them for food. Additionally, fish, amphibians like frogs and toads, and larger predatory insects such as mantises and robber flies are known to prey on darner dragonflies, particularly during their vulnerable larval and adult stages. These natural predators play an essential role in regulating darner dragonfly populations and contributing to the balance of ecosystems.
Adaptive Defenses
To evade predators and ensure their survival, darner dragonflies have developed several adaptive defenses. One of their primary defenses is their remarkable aerial agility, allowing them to perform intricate flight maneuvers to avoid capture. Darner dragonflies are capable of rapid changes in direction, sudden dives, and swift accelerations, making them challenging targets for predators. Additionally, their vibrant coloration and intricate wing patterns serve as a form of camouflage, helping them blend into their surroundings and evade detection by potential threats.
Importance in the Ecosystem
Role in the Food Chain
Darner dragonflies play a crucial role in the food chain as apex predators in their respective ecosystems. As voracious hunters, they prey on a wide variety of small flying insects, including mosquitoes, flies, midges, and other pests. By controlling the populations of these insects, darner dragonflies help regulate the abundance of prey species, preventing outbreaks and maintaining ecological balance. Their predatory activities also contribute to the overall health of ecosystems by reducing competition among insect species and promoting biodiversity. Additionally, darner dragonflies serve as a food source for various predators, including birds, fish, frogs, and other insectivorous animals, further integrating them into the intricate web of the food chain.
Ecological Significance
Darner dragonflies hold significant ecological importance due to their role as indicators of environmental health and ecosystem functionality. Their presence in freshwater habitats serves as a barometer of water quality and habitat suitability, as they require clean water and abundant vegetation for breeding and survival. Declines in darner dragonfly populations may signal environmental degradation, pollution, or habitat loss, prompting conservation efforts to address underlying issues and restore ecosystem balance. Furthermore, darner dragonflies contribute to nutrient cycling and energy transfer within ecosystems through their predation activities, redistributing energy from lower trophic levels to higher trophic levels. Overall, the ecological significance of darner dragonflies underscores the importance of conserving these majestic insects and preserving the habitats upon which they depend.
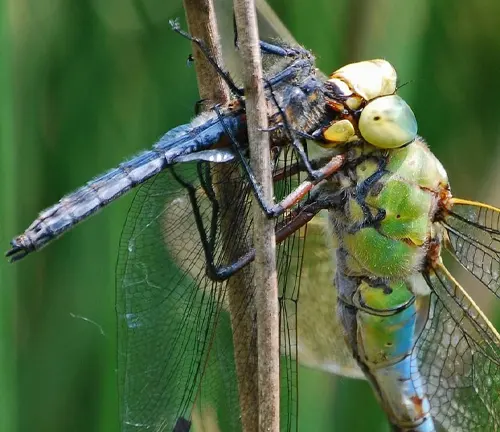

Conservation Status
Threats to Darners Dragonflies
Darner dragonflies face several threats that endanger their populations and habitats. Habitat loss and degradation, resulting from urbanization, agricultural expansion, and infrastructure development, pose significant challenges to darner dragonflies by reducing the availability of suitable breeding sites and foraging grounds. Pollution, including water pollution from agricultural runoff, industrial discharge, and pesticide contamination, can also negatively impact darner dragonflies by impairing water quality and disrupting their reproductive cycles. Climate change exacerbates these threats by altering temperature and precipitation patterns, affecting darner dragonfly populations’ distribution, phenology, and habitat availability.
Additionally, invasive species, such as non-native fish and aquatic plants, compete with darner dragonflies for resources and disrupt ecosystem balance, further compromising their survival. Addressing these threats requires collaborative efforts to mitigate human impacts on darner dragonfly habitats and promote conservation measures to safeguard their populations and habitats for future generations.
Conservation Efforts
Numerous conservation efforts are underway to protect darner dragonflies and their habitats, aiming to mitigate threats and promote their long-term survival. Habitat restoration projects focus on restoring degraded wetlands, riparian zones, and other critical habitats to provide suitable breeding sites and foraging areas for darner dragonflies. Pollution mitigation efforts target reducing water pollution through improved agricultural practices, stormwater management, and wastewater treatment to ensure clean water sources for darner dragonflies and other aquatic organisms. Climate change adaptation strategies involve monitoring darner dragonfly populations and habitats, identifying vulnerable areas, and implementing measures to enhance their resilience to climate impacts.
Additionally, public awareness campaigns and educational programs raise awareness about the importance of darner dragonflies and the need for their conservation, encouraging individuals and communities to take action to protect these invaluable insects and their habitats. By combining scientific research, community engagement, and policy advocacy, conservation efforts aim to safeguard darner dragonflies and ensure their continued presence in the natural world.
rners dragonflies include habitat restoration, pollution mitigation, and public awareness campaigns to promote their protection.
Fascination with Darners Dragonflies
Cultural Significance
Darner dragonflies hold cultural significance in various societies around the world, often symbolizing themes of transformation, agility, and grace. In some cultures, they are associated with spiritual beliefs and are believed to represent the soul’s journey or the cycle of life and death. Darner dragonflies may also feature in folklore and mythology, where they are depicted as messengers, guardians, or symbols of good fortune and prosperity.
Symbolism
In folklore and mythology, darnAcross different cultures, darner dragonflies symbolize different concepts and qualities. In Japanese culture, for example, dragonflies are associated with courage, strength, and happiness, and are often depicted in art and literature as symbols of resilience and perseverance. In Native American traditions, dragonflies symbolize transformation, adaptability, and the ability to navigate life’s changes with grace and agility.ers dragonflies are often associated with themes of renewal, spiritual growth, and protection.
Observing Darners Dragonflies
Tips for Dragonfly Watching
- Choose the Right Time and Place: Visit wetlands, ponds, or other bodies of water during warm, sunny days when dragonflies are most active.
- Be Patient and Observant: Dragonflies may take some time to appear, so be patient and observe their behavior from a distance.
- Wear Neutral Colors: Bright clothing may scare away dragonflies, so opt for neutral colors to blend into the surroundings.
- Move Slowly: Approach dragonflies slowly and avoid sudden movements to avoid startling them.
- Bring Binoculars and Field Guides: Binoculars can help you observe dragonflies from a distance, while field guides can aid in identification.
Equipment Needed
- Binoculars: Essential for observing dragonflies from a distance.
- Field Guide: Helps in identifying different species of dragonflies based on their characteristics.
- Camera: Optional but useful for capturing photographs of dragonflies for documentation or personal enjoyment.
- Insect Net: Optional for catching and studying dragonflies up close, but be sure to release them unharmed afterward.
Interesting Facts
Unique Characteristics
- Elongated Body: Darner dragonflies have a slender, elongated body structure that distinguishes them from other dragonfly species.
- Large Eyes: Their large, multifaceted eyes provide excellent vision and enable them to detect prey and predators with precision.
- Agile Flight: Darner dragonflies are known for their agile flight patterns, allowing them to maneuver with grace and speed in pursuit of prey.
- Vibrant Colors: Many darner dragonfly species exhibit vibrant colors and intricate wing patterns, making them visually striking and appealing to observers.
Lesser-Known Facts
- Some darner dragonfly species undertake long-distance migrations, traveling hundreds or even thousands of miles in search of suitable breeding grounds.
- Darner dragonflies are among the fastest flying insects, capable of reaching speeds up to 30 miles per hour.
- Nymphs of darner dragonflies are aquatic and spend the majority of their lives underwater, where they prey on small aquatic organisms.
- Darner dragonflies have been used as bioindicators of water quality due to their sensitivity to pollution and habitat degradation.
- In some cultures, darner dragonflies are considered symbols of good luck and are believed to bring prosperity and positive energy to those who encounter them.
Different Species
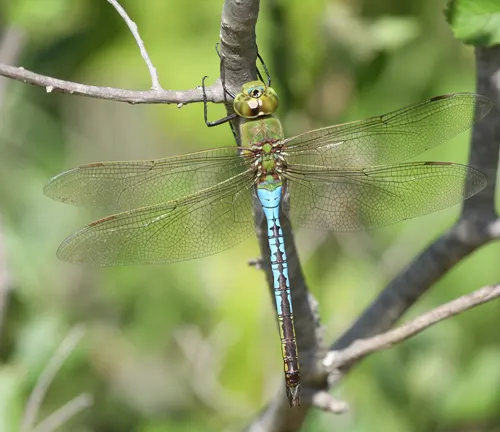
Common Green
Darner (Anax junius)
One of the most widespread species, known for its bright green thorax and blue abdomen. Found across North America.
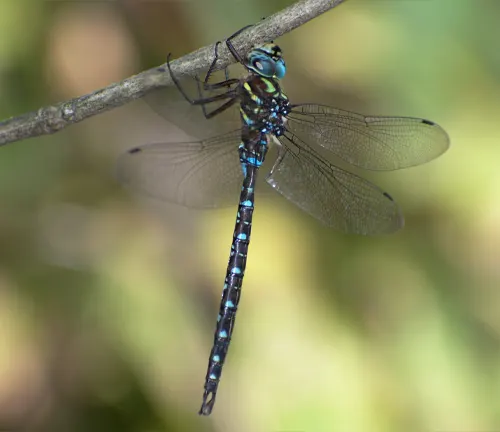


Shadow Darner
(Aeshna umbrosa)
Characterized by its dark coloration and distinct wing venation. Often found near shaded streams and forested areas.
Variable Darner
(Aeshna interrupta)
Exhibits variability in coloration, ranging from green to brown, with distinctive yellow spots on the abdomen. Found in various habitats, including marshes and ponds.
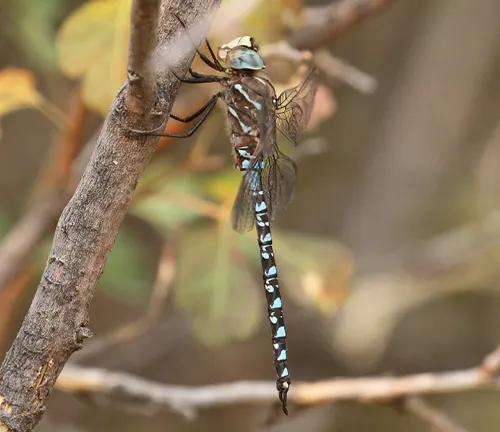
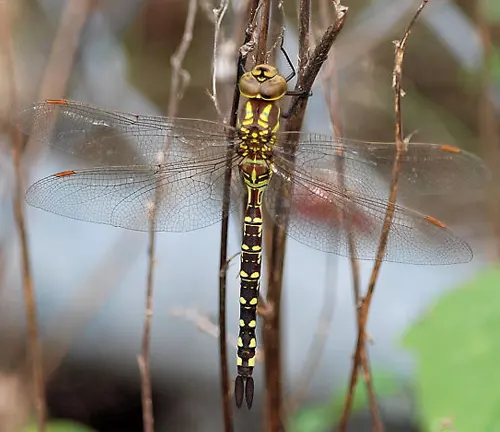


Mosaic Darner
(Aeshna mosaicus)
Recognizable by its mosaic-like abdominal pattern, consisting of blue, black, and yellow markings. Commonly found near slow-moving rivers and wetlands.
Paddle-tailed Darner
(Aeshna palmata)
Named for its paddle-shaped appendages at the end of the abdomen. Prefers habitats with dense vegetation near water bodies.
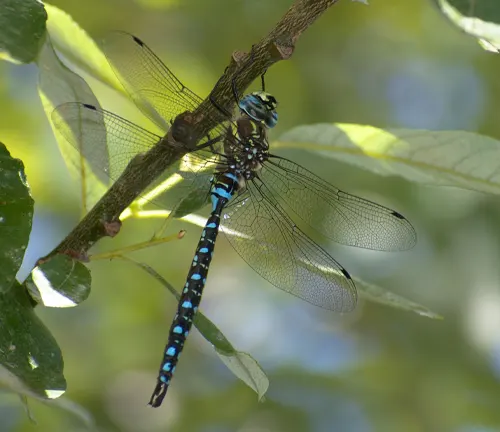
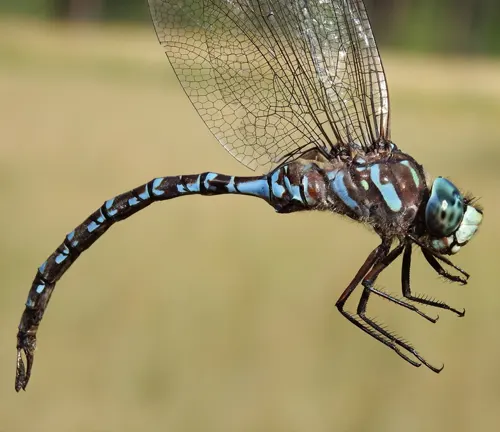


Canada Darner
(Aeshna canadensis)
Native to North America, characterized by its brownish coloration and distinctive yellow stripe on the thorax. Often seen near lakes and ponds.
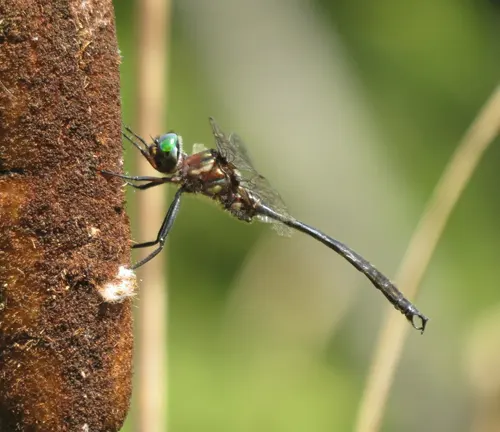
Clamp-tipped Darner
(Aeshna tuberculifera)
Identified by the presence of distinctive claspers at the end of the abdomen. Typically found near ponds and slow-moving streams.

Frequently Asked Question (FAQs)
- What is the difference between a Darner Dragonfly and other dragonfly species?
Darner Dragonflies belong to the Aeshnidae family and are characterized by their elongated bodies and agile flight, distinguishing them from other dragonfly species. - Where can I find Darner Dragonflies in the wild?
Darner Dragonflies are commonly found near freshwater habitats such as ponds, lakes, streams, and wetlands, as well as wooded areas and grasslands. - Are Darner Dragonflies harmful to humans?
Darner Dragonflies are harmless to humans and do not pose a threat. They primarily feed on small insects and play a beneficial role in controlling insect populations. - What is the significance of Darner Dragonflies in ecosystems?
Darner Dragonflies serve as apex predators in their habitats, helping regulate insect populations and contributing to the balance of ecosystems. - How do Darner Dragonflies reproduce?
Darner Dragonflies undergo a complex reproductive process, including courtship behaviors and oviposition (egg-laying) by females in or near water bodies. - What are the main threats to Darner Dragonflies?
Darner Dragonflies face threats such as habitat loss, pollution, climate change, and predation, which can impact their populations and habitats. - Are there any conservation efforts focused on protecting Darner Dragonflies?
Yes, various conservation efforts aim to protect Darner Dragonflies, including habitat restoration, pollution mitigation, and public awareness campaigns. - How can I attract Darner Dragonflies to my garden or backyard?
Creating a diverse habitat with water features, native plants, and ample perching spots can attract Darner Dragonflies and other beneficial insects to your garden. - Can I photograph Darner Dragonflies without disturbing them?
Yes, with patience and a respectful approach, you can capture stunning photographs of Darner Dragonflies in their natural habitats without causing them harm. - Are there any citizen science projects focused on studying Darner Dragonflies?
Yes, several citizen science projects invite enthusiasts to contribute observations and data on Darner Dragonflies, aiding research and conservation efforts. - What role do Darner Dragonflies play in controlling mosquito populations?
Darner Dragonflies are voracious predators of mosquitoes and other small flying insects, helping to reduce mosquito populations naturally.














Leave your comment