Eastern Tiger Swallowtail Butterfly
- March 1, 2024
- 0 comment
The Eastern Tiger Swallowtail Butterfly, a captivating native of North America, is a true marvel of nature. With its striking appearance and graceful flight, this butterfly holds a special place in the hearts of nature enthusiasts and casual observers alike. Sporting vibrant yellow wings adorned with bold black stripes, the Eastern Tiger Swallowtail exudes elegance and charm.
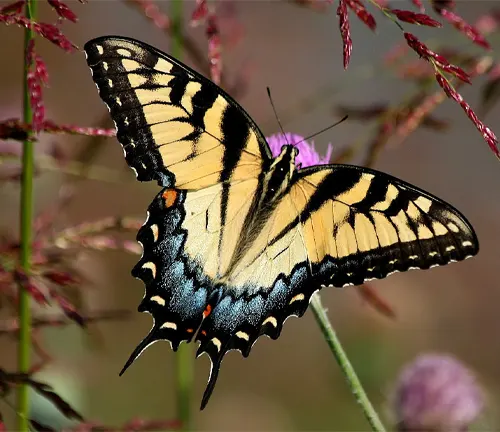

Found across a range of habitats, from forests to urban gardens, these butterflies play crucial roles as pollinators and indicators of ecosystem health. Their life cycle, from egg to larva to pupa and finally to adult, is a testament to the wonders of metamorphosis, captivating audiences with each stage of transformation. Despite facing threats from habitat loss and environmental changes, efforts to conserve these beautiful butterflies are underway, ensuring that future generations can continue to marvel at their beauty and significance in the natural world.
| Specification | Description |
|---|---|
| Scientific Name | Papilio glaucus |
| Common Name | Eastern Tiger Swallowtail Butterfly |
| Appearance | Large butterfly with vibrant yellow wings and black stripes |
| Size | Wingspan ranging from 3.5 to 6 inches (8.9 to 15.2 cm) |
| Gender Dimorphism | Males have yellow wings with black stripes; females have two color forms: yellow and black, and black and blue |
| Habitat | Varied habitats including forests, meadows, gardens, and urban areas |
| Geographic Distribution | Eastern North America, from southern Canada to Florida and westward to the Great Plains |
| Diet | Nectar from flowering plants; caterpillars feed on leaves of host plants such as cherry, ash, and willow |
| Predators | Birds, spiders, certain insects |
| Defense Mechanisms | Camouflage, mimicry, rapid flight; caterpillars possess osmeteria emitting foul-smelling compounds |
| Life Cycle | Egg, larva (caterpillar), pupa (chrysalis), adult |
| Reproduction | Mating rituals; females lay eggs on host plants |
| Migration Patterns | Limited localized movements; dispersal in search of suitable habitats and food sources |
| Conservation Status | Relatively common; threats from habitat loss, pesticide use, and climate change |
| Cultural Significance | Symbolizes transformation, beauty, and freedom |
| Importance in Education | Educational tool for teaching about biodiversity, ecology, and conservation |
A Marvel of Nature
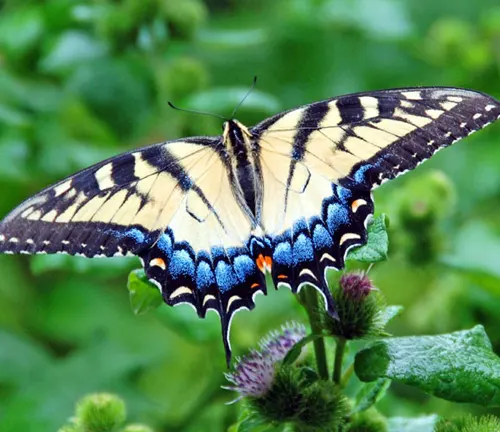

The Eastern Tiger Swallowtail Butterfly, scientifically known as Papilio glaucus, is a stunning species native to North America. Renowned for its vibrant appearance and graceful flight, this butterfly holds a significant place in both natural ecosystems and human culture. In this article, we delve into the fascinating world of the Eastern Tiger Swallowtail, exploring its characteristics, habitat, behavior, and more.
Physical Characteristics
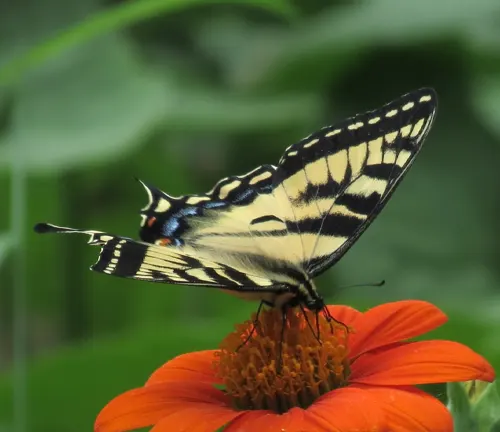
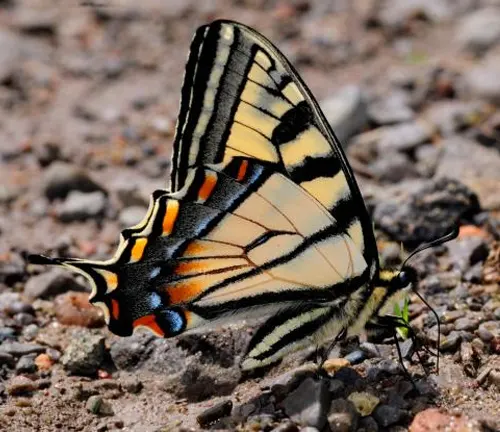


The physical characteristics of the Eastern Tiger Swallowtail Butterfly are distinctive and captivating. These butterflies are known for their large size, with wingspans ranging from 3.5 to 6 inches (8.9 to 15.2 cm). Their wings are adorned with vibrant yellow coloring and bold black stripes, resembling the majestic patterns of a tiger’s coat.
One notable feature of the Eastern Tiger Swallowtail is its gender dimorphism. Male butterflies typically display bright yellow wings with prominent black tiger-like stripes, while females exhibit two distinct color forms. One form features yellow wings with black stripes, similar to males, while the other showcases black wings with blue iridescence, creating a striking contrast.
Habitat and Distribution
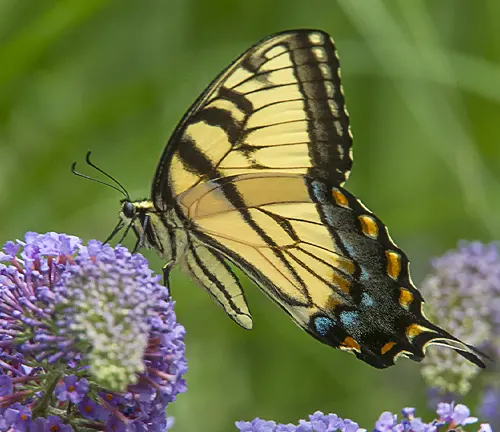

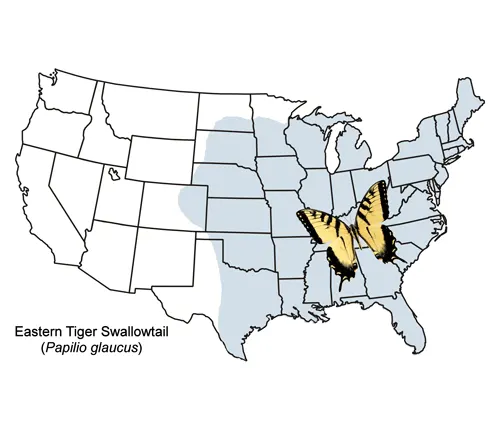
The Eastern Tiger Swallowtail Butterfly is a versatile species that can be found inhabiting a diverse range of environments across eastern North America. These butterflies are known to thrive in various habitats, including forests, meadows, gardens, and even urban areas. Their adaptability allows them to flourish in both natural and human-altered landscapes.
In terms of distribution, the Eastern Tiger Swallowtail is widespread throughout eastern North America, ranging from southern Canada to Florida and extending westward to the Great Plains. Within this geographic range, they can be spotted in abundance, particularly in regions with suitable habitat and ample food sources.
Eastern Tiger Swallowtails are commonly seen fluttering among flowering plants, where they feed on nectar and engage in important pollination activities. Their presence in gardens and parks adds to their accessibility, making them a familiar sight to many people across their range.
Despite their adaptability and wide distribution, Eastern Tiger Swallowtails may exhibit preferences for certain habitats and plant species. They are often attracted to areas with abundant nectar-rich flowers, such as milkweed, thistle, and verbena. Additionally, host plants for their caterpillars, including cherry, ash, and willow, are essential for supporting their populations.
Life Cycle
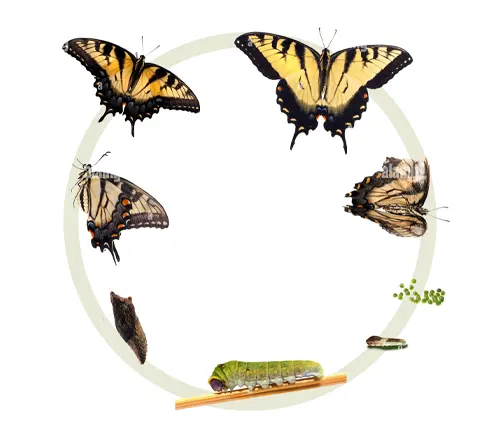

The life cycle of the Eastern Tiger Swallowtail Butterfly is a fascinating journey marked by four distinct stages: egg, larva (caterpillar), pupa (chrysalis), and adult. This metamorphic process, known as complete metamorphosis, showcases the butterfly’s remarkable ability to undergo dramatic transformations as it progresses through each stage.
It all begins with the female Eastern Tiger Swallowtail laying tiny, oval-shaped eggs on the leaves of host plants such as cherry, ash, and willow. These eggs are carefully deposited, typically on the undersides of leaves, providing protection from predators and the elements.
Once the eggs hatch, tiny larvae emerge, known as caterpillars. These caterpillars are voracious feeders, consuming leaves of their host plants to fuel their growth and development. As they grow, they undergo several molts, shedding their old exoskeletons to accommodate their increasing size.
After a period of feeding and growth, the caterpillar enters the next stage of its life cycle: the pupa or chrysalis stage. During this transformative phase, the caterpillar undergoes a remarkable process of metamorphosis, undergoing significant changes in its body structure and physiology. Inside the chrysalis, the caterpillar’s body is broken down and reorganized, ultimately giving rise to the adult butterfly.
Diet and Feeding Habits
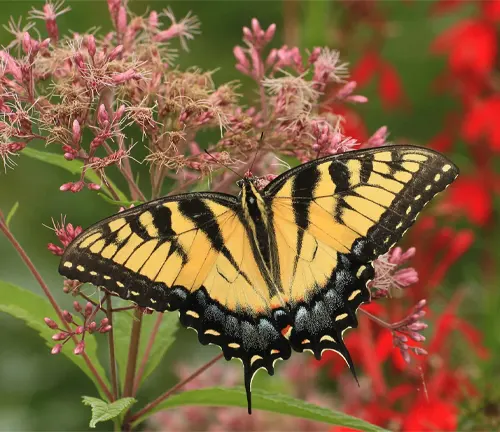
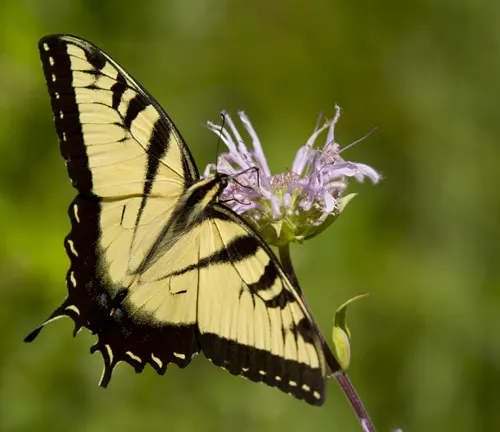


The Eastern Tiger Swallowtail Butterfly has specific dietary preferences and feeding habits that play crucial roles in its survival and development. As adults, these butterflies primarily feed on nectar extracted from a wide variety of flowering plants. They possess a long, straw-like proboscis that they use to sip nectar from the flowers.
Eastern Tiger Swallowtails are known to be attracted to a diverse range of flowering plants, including but not limited to milkweed, thistle, verbena, and butterfly bush. These plants provide essential sources of energy in the form of sugar-rich nectar, which fuels the butterfly’s flight and sustains its daily activities.
In addition to nectar, Eastern Tiger Swallowtail caterpillars have specific dietary requirements during their larval stage. They feed exclusively on the leaves of certain host plants, which provide the nutrients necessary for their growth and development. Common host plants for Eastern Tiger Swallowtail caterpillars include cherry, ash, willow, and tulip trees.
The feeding habits of Eastern Tiger Swallowtail caterpillars are characterized by their voracious appetite and rapid consumption of plant material. Despite their small size, these caterpillars can consume significant quantities of leaves, often defoliating their host plants in the process. This feeding behavior is essential for their survival and growth, allowing them to progress through the various stages of their life cycle.
Predators and Defense Mechanisms
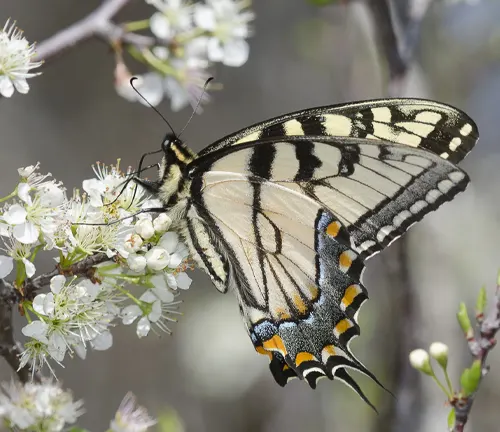
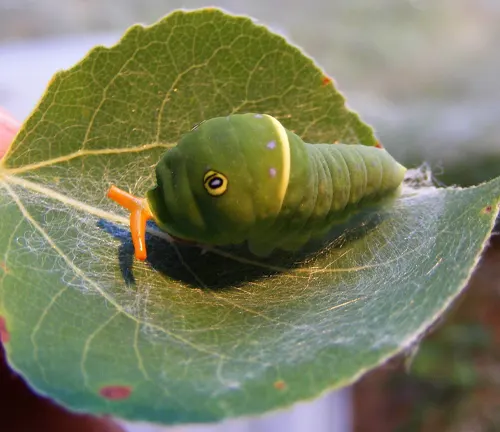


Despite their vibrant appearance, Eastern Tiger Swallowtails face threats from various predators, including birds, spiders, and certain insects. To evade predation, these butterflies employ several defense mechanisms, including camouflage, mimicry, and rapid flight. Additionally, caterpillars possess deterrents such as osmeteria, which emit foul-smelling compounds to deter predators.
Mating and Reproduction
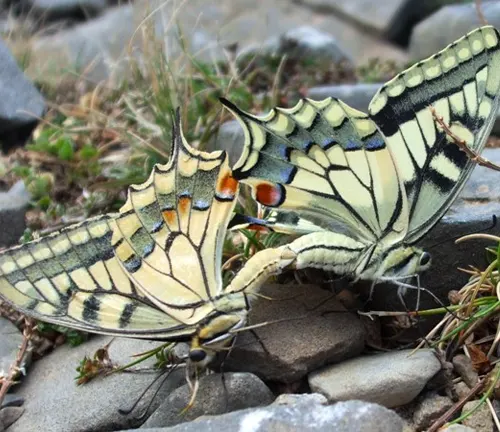
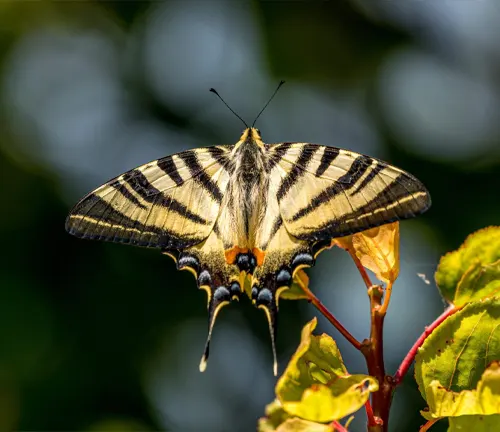


Mating and reproduction are pivotal aspects of the Eastern Tiger Swallowtail Butterfly’s life cycle, crucial for the continuation of the species. The process begins with courtship rituals, typically initiated by male butterflies to attract potential mates. Male Eastern Tiger Swallowtails engage in elaborate aerial displays, fluttering their wings and emitting pheromones to signal their readiness to mate.
Once a suitable mate is found, the male and female Eastern Tiger Swallowtails come together in a delicate mating ritual. During this ritual, the male gently grasps the female’s abdomen with his specialized claspers, ensuring successful copulation. The mating pair may remain connected for several hours, during which the male transfers sperm to the female’s reproductive organs.
After mating, the female Eastern Tiger Swallowtail seeks out appropriate host plants on which to deposit her eggs. Using her specialized ovipositor, she carefully lays small, oval-shaped eggs on the undersides of leaves, often selecting plants that will provide suitable food for her offspring upon hatching.
The eggs hatch into tiny larvae, known as caterpillars, which begin feeding on the leaves of the host plants almost immediately. The caterpillars undergo several molts as they grow, consuming large quantities of plant material to fuel their development.
Migration Patterns
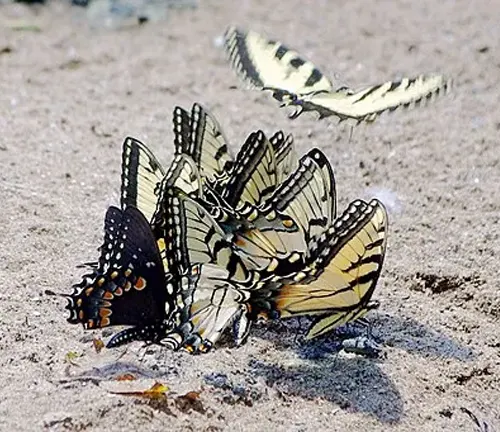

Migration patterns among Eastern Tiger Swallowtail Butterflies vary depending on factors such as geographical location and environmental conditions. Unlike some other butterfly species, Eastern Tiger Swallowtails are not known for long-distance migrations. Instead, their movement patterns are typically localized, with individuals dispersing within their range in search of suitable habitats and resources.
In regions with milder climates, Eastern Tiger Swallowtails may exhibit limited seasonal movements, seeking out areas with abundant food sources and optimal breeding conditions. These movements may involve short-distance flights between neighboring habitats, allowing the butterflies to exploit seasonal variations in temperature and resource availability.
Conservation Status
The Eastern Tiger Swallowtail Butterfly (Papilio glaucus) is generally considered to have a relatively stable population and is not currently classified as a species of conservation concern. However, like many butterfly species, it faces various threats that could potentially impact its long-term survival.
One of the primary threats to the Eastern Tiger Swallowtail is habitat loss and degradation. As human development continues to encroach upon natural habitats, the availability of suitable breeding and foraging areas for these butterflies diminishes. Deforestation, urbanization, and agricultural expansion all contribute to habitat fragmentation and loss of critical host plants and nectar sources.
Human Interaction
Human interaction with the Eastern Tiger Swallowtail Butterfly (Papilio glaucus) encompasses various activities and impacts that can influence the species’ well-being and conservation status. While humans can have both positive and negative effects on butterfly populations, understanding and managing these interactions are crucial for ensuring the continued survival of the species.
Positive human interactions with Eastern Tiger Swallowtails include:
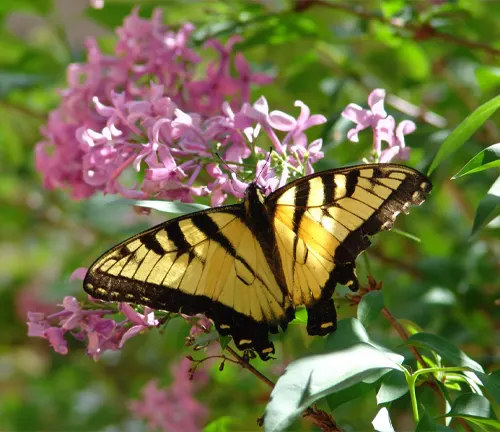


- Butterfly Gardening: Many people cultivate gardens specifically designed to attract butterflies, including the Eastern Tiger Swallowtail. Planting native nectar plants and host plants provides essential food and habitat resources for butterflies, contributing to their conservation.
- Citizen Science: Citizen science projects engage the public in monitoring butterfly populations and contributing valuable data on their distribution, abundance, and behavior. This collective effort helps researchers better understand butterfly ecology and inform conservation strategies.
- Educational Outreach: Outreach programs and educational initiatives raise awareness about the importance of butterflies and their role in ecosystems. By teaching people about the life cycle, behavior, and conservation needs of Eastern Tiger Swallowtails, we can foster appreciation and stewardship for these species.
Cultural Significance
The Eastern Tiger Swallowtail Butterfly holds significant cultural importance across various traditions and beliefs, serving as a symbol of transformation, beauty, and freedom. Throughout history, butterflies, including the Eastern Tiger Swallowtail, have captured the imagination of people around the world, inspiring art, literature, and folklore.
In many cultures, butterflies are associated with metamorphosis and rebirth. The transformation from caterpillar to butterfly symbolizes the journey of personal growth and spiritual enlightenment. The Eastern Tiger Swallowtail’s emergence from its chrysalis represents a powerful metaphor for overcoming adversity and embracing change.
Different Species
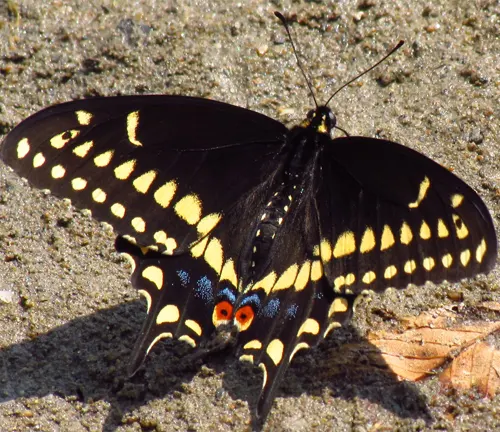
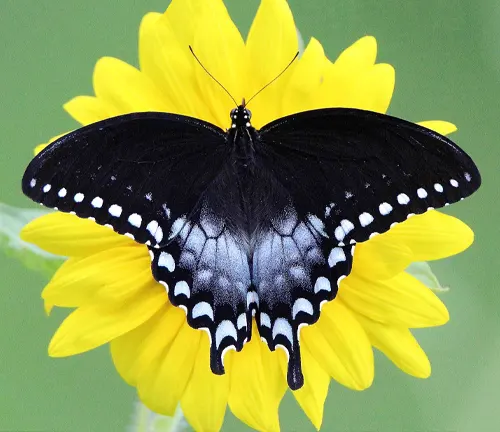
Black Swallowtail
(Papilio polyxenes)
Also known as the American Swallowtail or Parsnip Swallowtail, this butterfly is native to North America. It features black wings with striking yellow spots and markings.
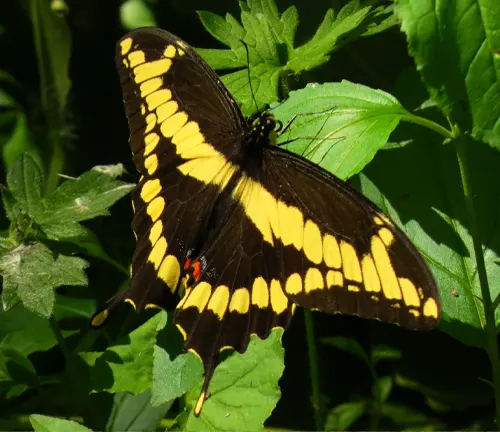


Giant Swallowtail
(Papilio cresphontes)
One of the largest swallowtail butterflies in North America, the Giant Swallowtail boasts wings with a distinctive yellow and black pattern, resembling that of the Eastern Tiger Swallowtail.
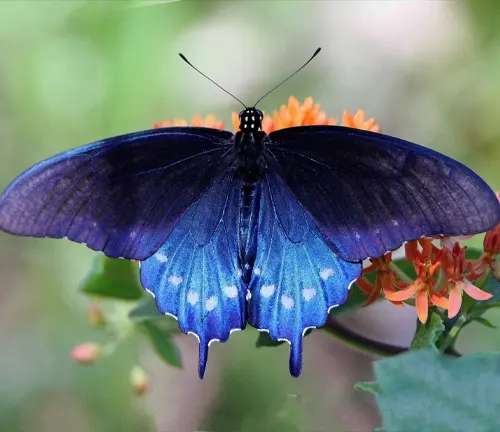
Pipevine Swallowtail
(Battus philenor)
Found primarily in North and Central America, the Pipevine Swallowtail showcases iridescent blue or blue-green wings, making it visually distinct from the Eastern Tiger Swallowtail.
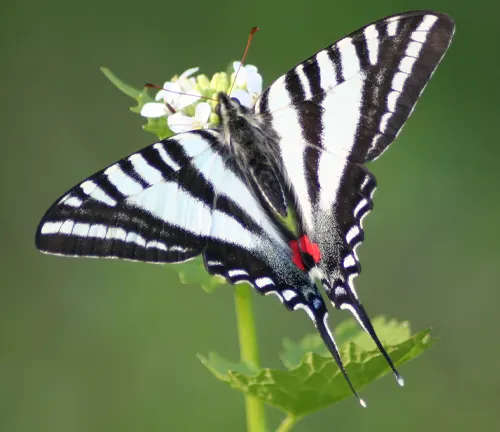


Zebra Swallowtail
(Protographium marcellus)
Native to the eastern United States, the Zebra Swallowtail is characterized by its black and white striped wings, reminiscent of a zebra’s pattern.
Palamedes Swallowtail
(Papilio palamedes)
Indigenous to the southeastern United States, the Palamedes Swallowtail features wings with a combination of dark brown and yellow markings, resembling those of the Eastern Tiger Swallowtail.
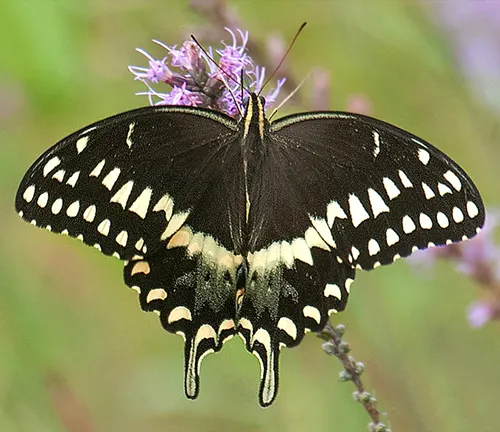
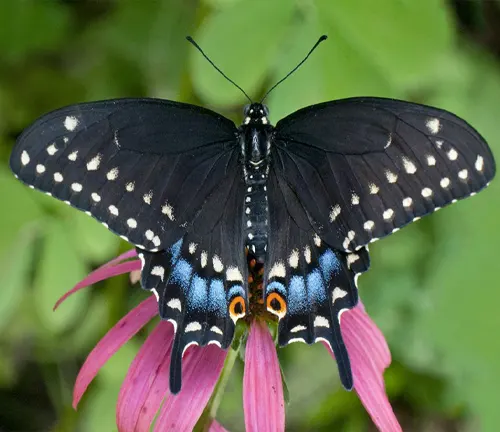


Eastern Black Swallowtail
(Papilio polyxenes asterius)
A subspecies of the Black Swallowtail, the Eastern Black Swallowtail is found in the eastern United States and Canada, featuring similar black wings with yellow markings.
Spicebush Swallowtail
(Papilio troilus)
Named for its preference for spicebush plants, this species is native to North America. It exhibits dark brown wings with orange spots and a distinctive blue iridescence on the hind wings.

Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
- Are Eastern Tiger Swallowtails harmful to plants?
This question addresses concerns about potential damage to plants by Eastern Tiger Swallowtails, particularly regarding their caterpillars’ feeding habits. - Can Eastern Tiger Swallowtails be kept as pets?
Some individuals may inquire about the possibility of keeping Eastern Tiger Swallowtails as pets, seeking information on their suitability for captivity. - How long do Eastern Tiger Swallowtails live?
This question seeks information on the average lifespan of Eastern Tiger Swallowtail butterflies, including the duration of each life stage from egg to adult. - What plants attract Eastern Tiger Swallowtails?
Gardeners and butterfly enthusiasts often seek recommendations for plants that attract Eastern Tiger Swallowtails, promoting biodiversity and habitat conservation. - What are the predators of Eastern Tiger Swallowtails?
This question addresses the natural enemies of Eastern Tiger Swallowtails, including birds, spiders, and other insects, and explores their impact on butterfly populations. - Do Eastern Tiger Swallowtails migrate?
Inquiries about the migratory behaviors of Eastern Tiger Swallowtails may arise, prompting discussions on their movement patterns and seasonal distributions. - How can I attract Eastern Tiger Swallowtails to my garden?
Gardeners interested in attracting Eastern Tiger Swallowtails may seek advice on creating butterfly-friendly habitats and selecting suitable nectar and host plants. - What are the differences between male and female Eastern Tiger Swallowtails?
This question explores the physical and behavioral differences between male and female Eastern Tiger Swallowtails, including variations in wing coloration and mating behaviors. - Are Eastern Tiger Swallowtails endangered?
Concerns about the conservation status of Eastern Tiger Swallowtails may prompt inquiries regarding their population trends, threats, and conservation efforts. - What is the significance of Eastern Tiger Swallowtails in folklore and culture?
This question delves into the symbolic and cultural significance of Eastern Tiger Swallowtails in various traditions and beliefs, exploring their roles in mythology and symbolism.














Leave your comment