Petaltail Dragonfly
- April 5, 2024
- 0 comment
The Petaltail Dragonfly, scientifically known as Tachopteryx thoreyi, is a mesmerizing insect species renowned for its unique physical characteristics and graceful behavior. With its elongated body and paddle-shaped hind wings resembling delicate petals, this dragonfly captivates observers with its ethereal beauty. Found in wooded areas near streams, ponds, and marshes, the Petaltail Dragonfly thrives in habitats with clean water and abundant vegetation. Its territorial nature adds to its mystique, as it fiercely defends its hunting grounds from other dragonflies and predators. Throughout its complex lifecycle, from egg to larva to adult, the Petaltail Dragonfly plays a crucial role in maintaining ecosystem balance by preying on smaller insects.
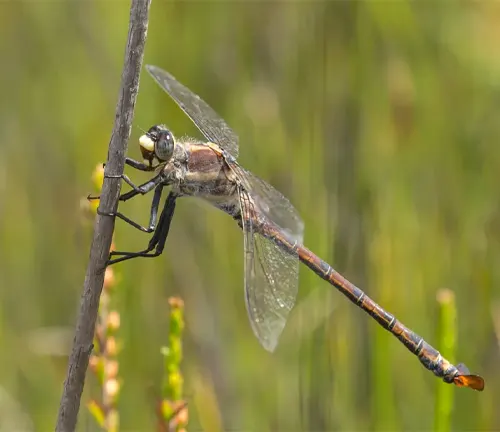

Despite facing threats such as habitat loss and pollution, conservation efforts are underway to preserve this enchanting insect and its habitats. The Petaltail Dragonfly stands as a symbol of resilience and natural beauty, reminding us of the intricate interconnectedness of all living beings in the natural world.
| Specifications | Details |
|---|---|
| Scientific Name | Tachopteryx thoreyi |
| Common Name | Petaltail Dragonfly |
| Family | Petaluridae |
| Body Length | Approximately 2 to 3 inches (5 to 7.5 centimeters) |
| Wingspan | Around 3 to 4 inches (7.5 to 10 centimeters) |
| Body Shape | Elongated and slender |
| Wing Shape | Paddle-shaped hind wings resembling petals |
| Coloration | Varied, often featuring intricate patterns |
| Habitat | Wooded areas near streams, ponds, and marshes |
| Distribution | Global, with varying species found in different regions |
| Behavior | Territorial, agile flyers, skilled hunters |
| Lifecycle | Egg, larva, nymph, adult |
| Diet | Small insects such as mosquitoes, flies, and midges |
| Importance | Plays a crucial role in controlling insect populations |
| Threats | Habitat loss, pollution, climate change |
| Conservation Status | Varied, some species may face threats |
| Conservation Efforts | Habitat restoration, research, public awareness campaigns |
| Symbolism | Represents resilience, natural beauty, ecosystem balance |
Petaltail Dragonfly: The Enigmatic Jewel of Nature
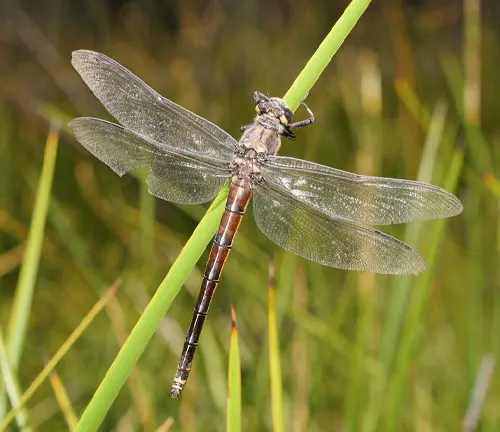

The Petaltail Dragonfly, scientifically known as Tachopteryx thoreyi, is a remarkable insect species renowned for its distinctive appearance and behavior. Found in various habitats across the globe, these dragonflies captivate enthusiasts and researchers alike with their elegant flight and unique features.
Physical Characteristics of Petaltail Dragonfly
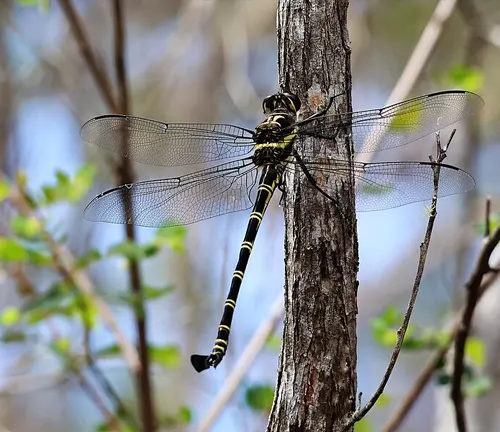
The Petaltail Dragonfly, known scientifically as Tachopteryx thoreyi, boasts several distinctive physical characteristics that set it apart from other dragonfly species. Here are some notable features:
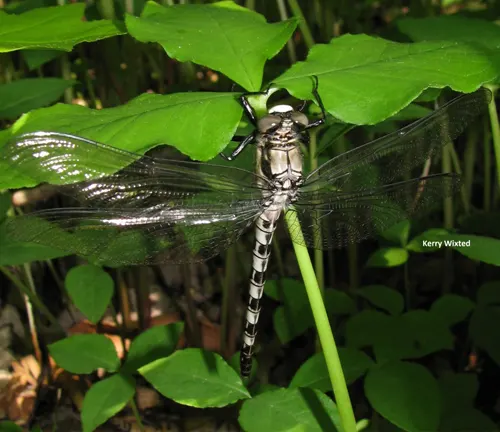
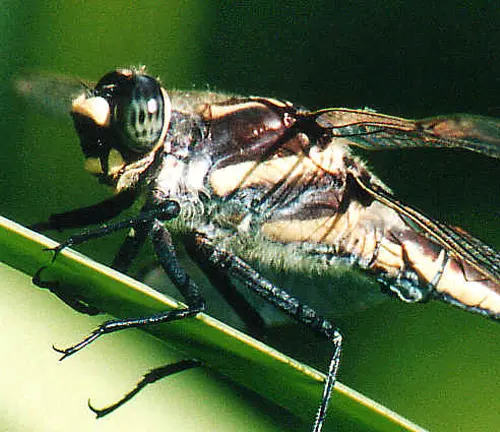


- Body Shape: Petaltail Dragonflies have an elongated and slender body, which contributes to their graceful appearance and streamlined flight.
- Wing Shape: One of the most striking features of the Petaltail Dragonfly is its unique wing shape. The hind wings are paddle-shaped, resembling delicate petals, hence the name “petaltail.”
- Size: These dragonflies typically measure approximately 2 to 3 inches (5 to 7.5 centimeters) in length, with a wingspan of around 3 to 4 inches (7.5 to 10 centimeters), though sizes may vary slightly among different species and individuals.
- Coloration: Petaltail Dragonflies display a range of colors and patterns on their bodies and wings. They often feature intricate designs and markings, which can vary depending on species and environmental factors.
- Eyes: Like other dragonflies, Petaltail Dragonflies have large compound eyes that provide excellent vision for hunting prey and navigating their surroundings.
- Abdomen: The abdomen of Petaltail Dragonflies is elongated and segmented, with each segment adorned with unique patterns and colors.
- Legs: Petaltail Dragonflies have six long and slender legs, which they use for perching, walking, and capturing prey.
- Flight: These dragonflies are known for their agile and swift flight, capable of darting and hovering with precision as they hunt for smaller insects.
Habitat and Distribution

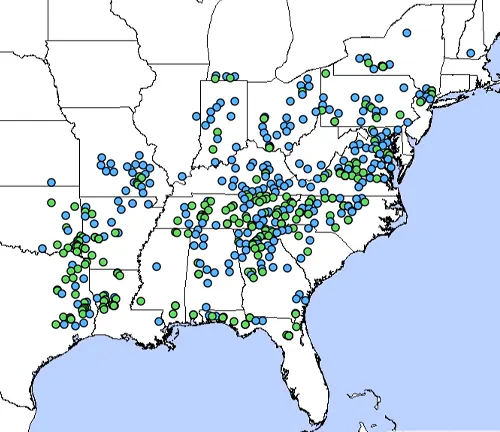
Petaltail Dragonflies are distributed across various regions worldwide, although specific species may have more localized ranges. They are commonly found in North America, Europe, Asia, Africa, and Australia, showcasing their adaptability to diverse environments. Within these regions, their distribution may vary based on factors such as climate, habitat availability, and geographical features.
In North America, for example, species like Tachopteryx thoreyi, also known as the Eastern Least Clubtail, can be found in eastern parts of the continent, ranging from Canada to the United States. Similarly, in Australia, species like Tachopteryx rufibasis, known as the Australian Petaltail, are native to the region, thriving in habitats across the continent.
Behavior and Lifecycle
The behavior and lifecycle of the Petaltail Dragonfly offer intriguing insights into the fascinating world of these insects. Here’s a closer look at their behavior patterns and developmental stages:
Behavior
Petaltail Dragonflies exhibit various behaviors that contribute to their survival and reproduction. One notable behavior is their territorial nature, where they fiercely defend their hunting grounds from other dragonflies and potential predators. This territorial behavior helps ensure access to essential resources such as food and suitable breeding sites.
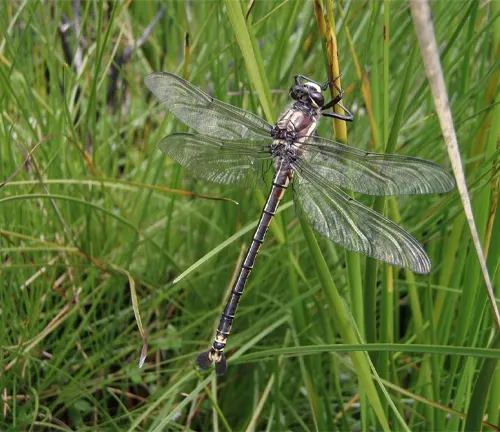

In addition to territoriality, Petaltail Dragonflies are skilled hunters, using their keen eyesight and agile flight to capture smaller insects in mid-air. They employ various hunting techniques, including aerial pursuits and ambush tactics, to catch prey efficiently. Petaltail Dragonflies are also known for their graceful flight patterns, often darting and hovering with precision as they navigate their surroundings.
Lifecycle
The lifecycle of Petaltail Dragonflies consists of several distinct stages, starting from egg deposition to adulthood. The lifecycle typically unfolds as follows:
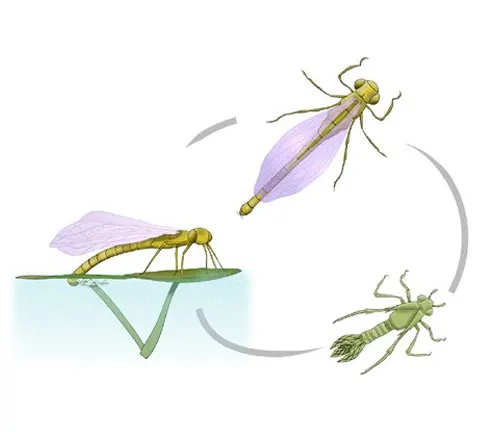
- Egg Stage: Female Petaltail Dragonflies lay their eggs in aquatic environments, often attaching them to submerged vegetation or debris. The eggs hatch into aquatic larvae, known as nymphs, within a few weeks.
- Nymph Stage: Nymphs spend the majority of their development underwater, where they feed on small aquatic organisms and molt several times as they grow. This stage can last anywhere from a few months to several years, depending on species and environmental conditions.
- Emergence: Once nymphs reach maturity, they undergo a process called emergence, where they leave the water and climb onto nearby vegetation or rocks. During emergence, the nymph sheds its aquatic exoskeleton and transforms into an adult dragonfly.
- Adult Stage: The newly emerged adult dragonfly undergoes a brief period of maturation, during which its wings expand and harden. Once fully developed, the adult Petaltail Dragonfly takes to the air, where it will spend the remainder of its lifespan hunting, mating, and contributing to the ecosystem..
Importance of Petaltail Dragonflies
The importance of Petaltail Dragonflies extends beyond their enchanting beauty, as they play a crucial role in maintaining ecosystem balance and health. Here are some key aspects highlighting their significance:
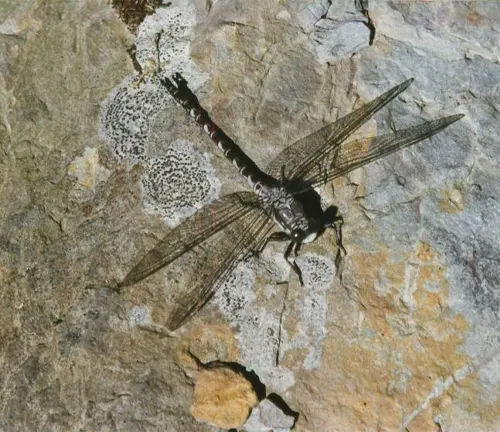
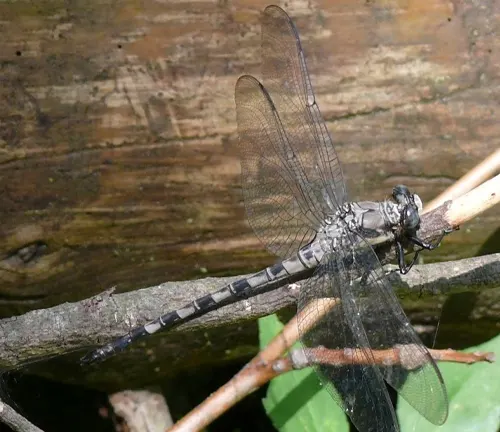


- Predator Control: Petaltail Dragonflies are efficient predators, preying on smaller insects such as mosquitoes, flies, and midges. By regulating insect populations, they help control pest populations and reduce the spread of diseases carried by insects.
- Indicator Species: Petaltail Dragonflies are sensitive to changes in environmental conditions, particularly water quality. As such, their presence or absence in an area can serve as an indicator of ecosystem health. Monitoring populations of Petaltail Dragonflies can provide valuable insights into the overall well-being of aquatic ecosystems.
- Biodiversity Support: As apex predators in their habitats, Petaltail Dragonflies contribute to biodiversity by maintaining the balance of species within ecosystems. By controlling insect populations, they prevent any one species from dominating, thus promoting biodiversity and supporting a healthy ecosystem.
- Nutrient Cycling: As larvae, Petaltail Dragonflies play a role in nutrient cycling within aquatic environments. They consume organic matter and other small organisms, contributing to the breakdown and recycling of nutrients. This process helps maintain nutrient levels in water bodies, supporting the growth of aquatic plants and other organisms.
- Pollination: While primarily predators, adult Petaltail Dragonflies also play a minor role in pollination. As they visit flowers in search of nectar, they may inadvertently transfer pollen from one flower to another, contributing to the reproductive success of flowering plants.
- Aesthetic Value: Petaltail Dragonflies are admired for their elegant flight, vibrant colors, and intricate wing patterns. As such, they hold aesthetic value for nature enthusiasts, photographers, and artists, enriching our appreciation of the natural world.
- Educational and Scientific Value: Studying Petaltail Dragonflies provides valuable insights into insect behavior, ecology, and evolutionary biology. Their diverse habitats, behaviors, and life cycles offer opportunities for scientific research and education, advancing our understanding of ecosystems and biodiversity.
Threats and Conservation Efforts
Despite their resilience, Petaltail Dragonflies face various threats such as habitat loss, pollution, and climate change. Conservation efforts are underway to safeguard their habitats and promote awareness about their significance in ecosystems. Initiatives include habitat restoration, research projects, and public education campaigns aimed at preserving these captivating insects.
Fascinating Facts about Petaltail Dragonflies
- Petaltail Dragonflies are among the oldest insect species, with fossil records dating back millions of years.
- They are adept fliers, capable of swift aerial maneuvers and precise hunting techniques.
- Some species of Petaltail Dragonflies exhibit migratory behavior, traveling long distances in search of suitable breeding grounds.
The Significance of Petaltail Dragonflies in Ecosystems
Petaltail Dragonflies contribute to ecosystem health by controlling insect populations, including mosquitoes and other pests. Their presence indicates the overall health and biodiversity of aquatic environments, making them valuable indicators for conservation efforts.
How to Spot a Petaltail Dragonfly
Observing Petaltail Dragonflies in their natural habitat requires patience and keen observation skills. Look for them near water bodies, particularly in wooded areas with dense vegetation. Their distinctive appearance and flight pattern make them stand out from other dragonfly species.
Tips for Observing Petaltail Dragonflies
- Choose early morning or late afternoon for optimal observation opportunities when dragonflies are most active.
- Wear neutral-colored clothing to avoid startling them, allowing for closer observation.
- Use binoculars or a camera with a telephoto lens for detailed viewing and documentation.
Petaltail Dragonflies in Art and Culture
Throughout history, Petaltail Dragonflies have inspired artists, poets, and storytellers across cultures. Their graceful flight and ethereal beauty have been depicted in various art forms, symbolizing themes of transformation, resilience, and natural beauty.
Petaltail Dragonflies as Symbols
In different cultures, Petaltail Dragonflies hold symbolic significance, representing concepts such as adaptability, agility, and renewal. They are often associated with themes of change and metamorphosis, reflecting their lifecycle and transformative journey from larvae to adult dragonflies.
Conservation Organizations and Initiatives
Several organizations worldwide are dedicated to the conservation of Petaltail Dragonflies and their habitats. These organizations conduct research, habitat restoration projects, and public outreach efforts to raise awareness about the importance of preserving these enchanting insects.
Different Species
Tachopteryx bambusae
Native to parts of China and Southeast Asia, including Vietnam and Laos, the Bamboo Petaltail is known for its preference for bamboo forests and dense vegetation along streams and rivers.
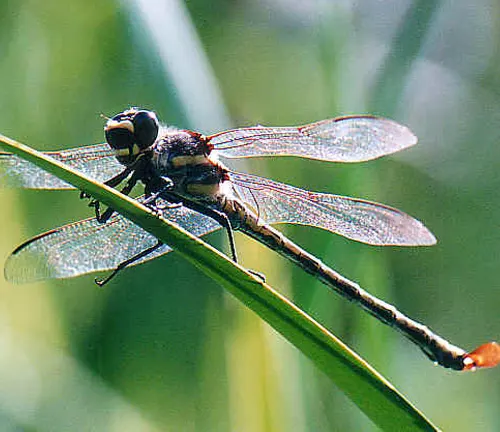

Frequently Asked Question (FAQs)
- Where are Petaltail Dragonflies found?
Petaltail Dragonflies are found in various habitats worldwide, including wooded areas near streams, ponds, marshes, and sometimes even in urban environments. - What is the significance of the name “Petaltail”?
The name “Petaltail” refers to the distinctive paddle-shaped hind wings of these dragonflies, which resemble delicate petals. - How do Petaltail Dragonflies reproduce?
Petaltail Dragonflies undergo a complex reproductive process, starting with the female laying eggs in aquatic environments. Larvae hatch from these eggs and undergo several stages of development before emerging as adult dragonflies. - What predators do Petaltail Dragonflies have?
Petaltail Dragonflies face predation from various creatures, including birds, larger insects, and other dragonfly species. - Do Petaltail Dragonflies have any natural enemies?
While they have predators, Petaltail Dragonflies do not have specific natural enemies. They are well-adapted to their environments and employ various strategies to avoid predation. - How fast can Petaltail Dragonflies fly?
Petaltail Dragonflies are known for their agility and speed in flight, capable of reaching impressive speeds to capture prey and evade predators. - Do Petaltail Dragonflies have any unique behaviors?
Yes, Petaltail Dragonflies exhibit territorial behavior, defending their hunting grounds from other dragonflies and predators. They are also skilled hunters, employing various hunting techniques to catch prey. - What role do Petaltail Dragonflies play in ecosystems?
Petaltail Dragonflies play a crucial role in maintaining ecosystem balance by controlling insect populations, including mosquitoes and other pests. They also serve as indicators of environmental health. - How can I attract Petaltail Dragonflies to my garden?
Creating a habitat with clean water, suitable vegetation, and minimal pesticide use can attract Petaltail Dragonflies to your garden. Providing perches and sheltered areas can also encourage them to visit. - Can Petaltail Dragonflies be harmful to humans?
No, Petaltail Dragonflies are not harmful to humans. In fact, they are beneficial as they help control insect populations, including disease-carrying mosquitoes. - What adaptations do Petaltail Dragonflies have for survival?
Petaltail Dragonflies have various adaptations for survival, including their agile flight, keen vision, and ability to camouflage in their surroundings.














Leave your comment