Mouse Lemur
- January 22, 2024
- 0 comment
The Mouse Lemur, belonging to the Microcebus genus, is a remarkable group of primates native to the biodiverse island of Madagascar. Renowned for their diminutive size, these tiny creatures hold a unique place in the world of wildlife. Mouse lemurs are some of the smallest primates on Earth, with the smallest species, Madame Berthe’s mouse lemur, measuring a mere 9.2 cm (3.6 inches) in length. These pint-sized primates are primarily nocturnal, making them masters of the night with their large, expressive eyes adapted for exceptional night vision.
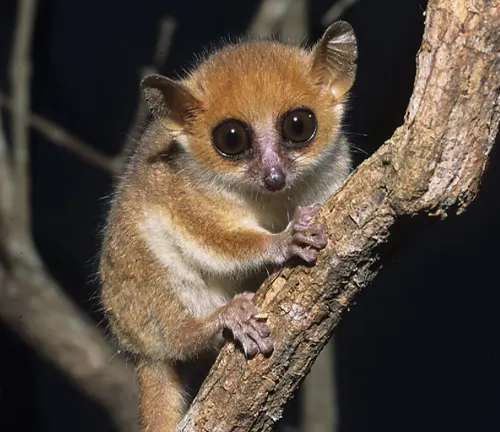

Their habitat spans across various ecosystems in Madagascar, from lush rainforests to dry deciduous forests, where they exhibit incredible adaptability. Mouse lemurs are omnivorous, with a diverse diet that includes fruits, flowers, insects, and even small vertebrates. This adaptability to different food sources allows them to thrive in diverse environments.
Mouse lemurs are known for their solitary nature, although social behavior can vary among species. They establish home ranges, communicate with scent markings, and become more active and vocal during the mating season. Despite their unique characteristics and abilities, mouse lemurs face threats such as habitat loss and the illegal pet trade, making conservation efforts crucial for their survival.
| Characteristic | Description |
|---|---|
| Scientific Name | Microcebus |
| Average Length | Around 9.2 cm (3.6 inches) |
| Native Habitat | Madagascar |
| Nocturnal | Yes (Primarily active at night) |
| Eye Adaptation | Excellent night vision |
| Diet | Omnivorous (Fruits, insects, small vertebrates) |
| Social Behavior | Generally solitary, with variations among species |
| Reproduction | Mating season in late dry season, with males becoming more active and vocal |
| Predators | Owls, snakes, larger mammals |
| Lifespan (Wild) | Typically 6 to 12 years |
| Conservation Status | Endangered and vulnerable for some species |
| Notable Species | Madame Berthe’s Mouse Lemur, Gray Mouse Lemur, Golden-brown Mouse Lemur, and more |
| Unique Feature | One of the smallest primates on Earth |
| Role in Ecosystem | Seed dispersal and contributing to forest regeneration |
| Threats | Habitat loss and illegal pet trade |
| Conservation Efforts | Protected areas, research, and education initiatives |
Understanding Mouse Lemurs
Mouse lemurs, scientifically known as Microcebus, are among the smallest primates on Earth. These petite creatures belong to the Lemuriformes infraorder and can be found exclusively on the island of Madagascar, making them an endemic species.
What Makes Them Unique?
Mouse lemurs have some fascinating features that set them apart:
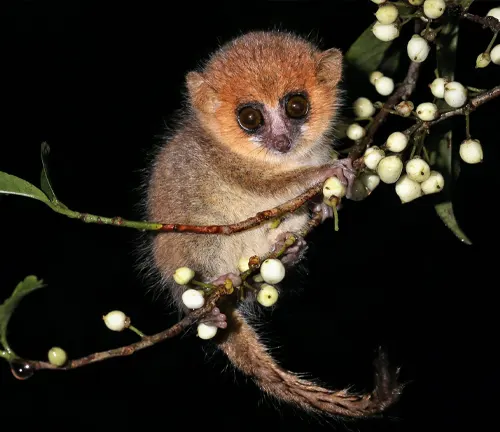

- Size Matters: They are incredibly small, with the smallest species, Madame Berthe’s mouse lemur, measuring just 9.2 cm (3.6 inches) in length.
- Nocturnal Wonders: Mouse lemurs are primarily nocturnal, which means they are most active during the night, making them masters of the dark.
- Big Eyes: Their large eyes are adapted for excellent night vision, helping them locate prey and avoid predators in the dark.
The Enigmatic Habitat
Mouse lemurs occupy a variety of habitats across Madagascar, including rainforests, dry deciduous forests, and even spiny forests. However, they prefer dense vegetation, where they can easily find food and take shelter from potential threats.
Where Can You Find Them?
These remarkable primates are distributed throughout Madagascar, but some popular spots for spotting mouse lemurs include Ankarafantsika National Park, Ranomafana National Park, and Andasibe-Mantadia National Park.
The Omnivorous Diet
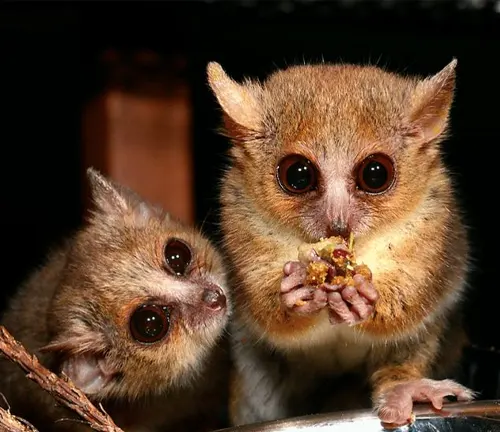
Mouse lemurs are omnivores, which means they have a diverse diet that includes fruits, flowers, insects, and small vertebrates. Their adaptability to various food sources allows them to thrive in different ecosystems.

A Glimpse into Their Diet
- Fruit Fanatics: Fruits are a staple in their diet, and they play a crucial role in dispersing seeds, contributing to the regeneration of forests.
- Insectivores by Night: During the night, they turn into expert insect hunters, preying on a variety of insects to meet their protein needs.
Social Structure and Behavior
Mouse lemurs are generally solitary animals, but their behavior can vary among species. Some are more social, while others prefer a solitary life.
Solitary Nomads
- Home Range: They establish a home range, usually marked with scent markings to communicate with potential mates and rivals.
- Mating Season: During the mating season, which typically occurs in the late dry season, males become more active and vocal to attract females.
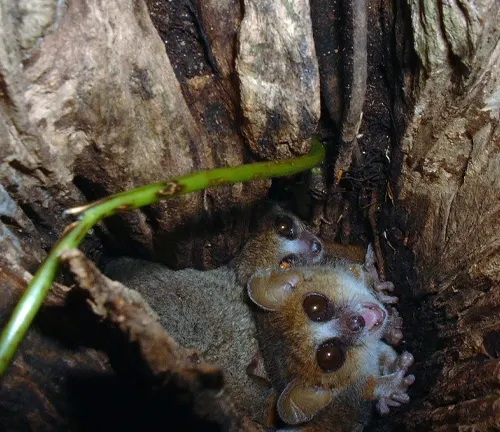

Mouse Lemurs in Peril
Despite their remarkable adaptations, mouse lemurs face various threats that endanger their survival.
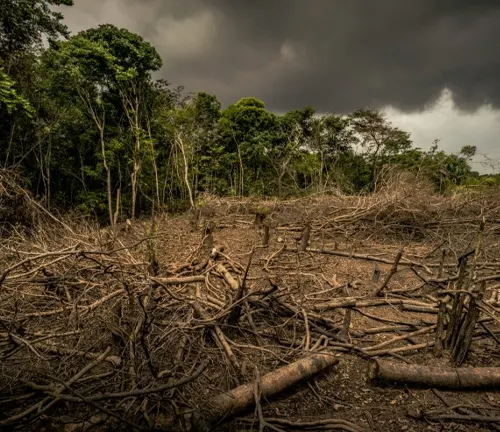
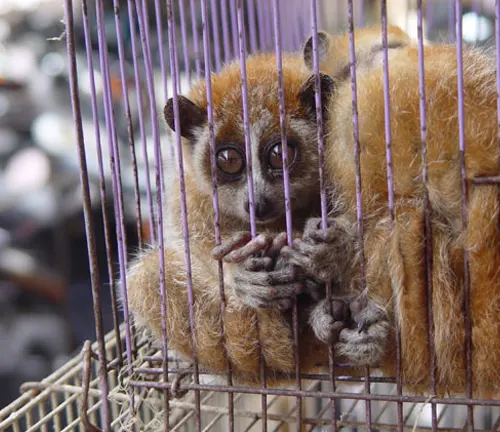


Threats to Their Existence
- Habitat Loss: Deforestation and habitat fragmentation are the most significant threats, as they reduce the available habitat for these tiny primates.
- Illegal Pet Trade: The capture of mouse lemurs for the illegal pet trade further exacerbates their population decline.
Conservation Efforts
Conservationists and organizations are working tirelessly to protect mouse lemurs and their habitats.
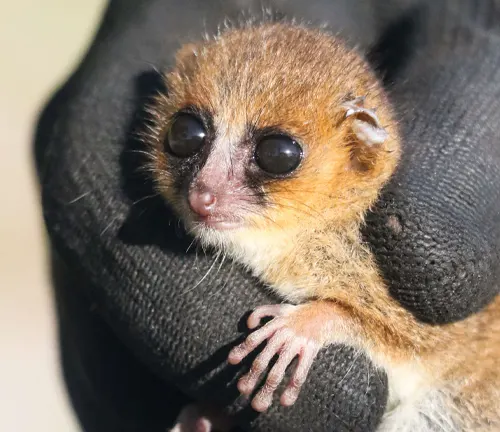


Protecting the Precious
- Protected Areas: Establishing and maintaining protected areas is vital for preserving their natural habitat.
- Research and Education: Ongoing research and educational initiatives help raise awareness and understanding of mouse lemurs’ importance.
Different Species
Madame Berthe’s Mouse Lemur
(Microcebus berthae)
This is the smallest primate in the world, measuring only about 9.2 cm (3.6 inches) in length. It is named after Madame Berthe Rakotosamimanana, a Malagasy conservationist.
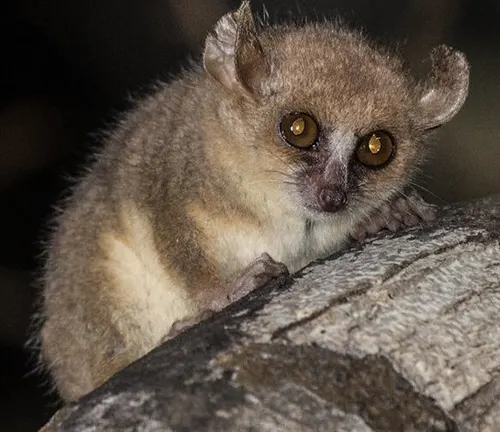
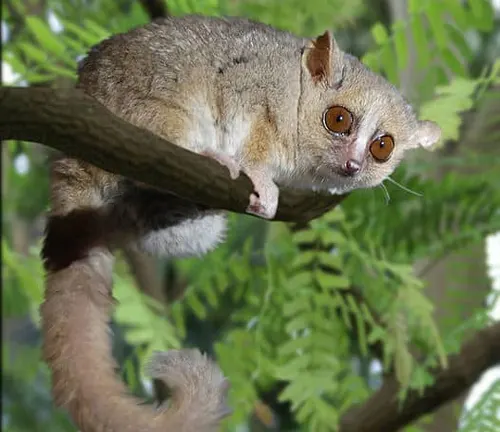


Gray Mouse Lemur
(Microcebus murinus)
The gray mouse lemur is one of the most common and widely studied species. It has a grayish-brown fur coat and is known for its adaptability to different habitats.
Golden-brown Mouse Lemur
(Microcebus ravelobensis)
This species is recognized by its golden-brown fur and large, expressive eyes. It is found in the dry deciduous forests of Madagascar.
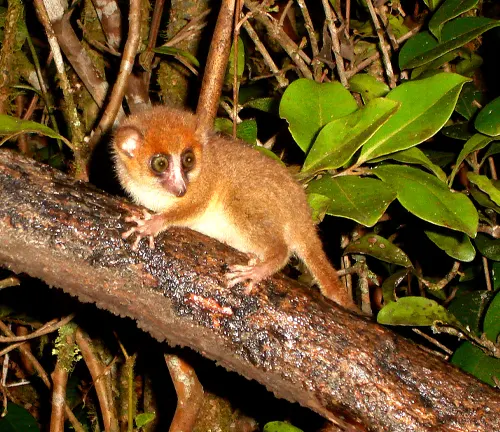
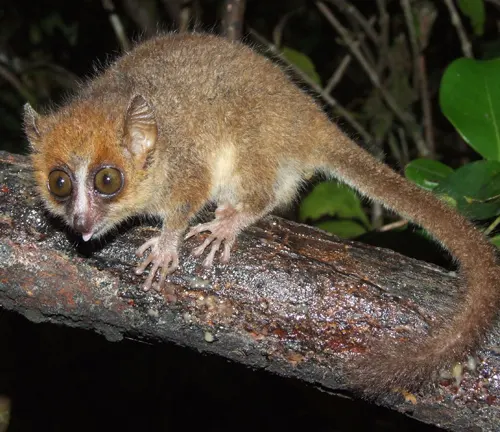


Dwarf Mouse Lemur
(Microcebus myoxinus)
The dwarf mouse lemur is a tiny species with a short tail and reddish-brown fur. It is known for its nocturnal behavior and insectivorous diet.
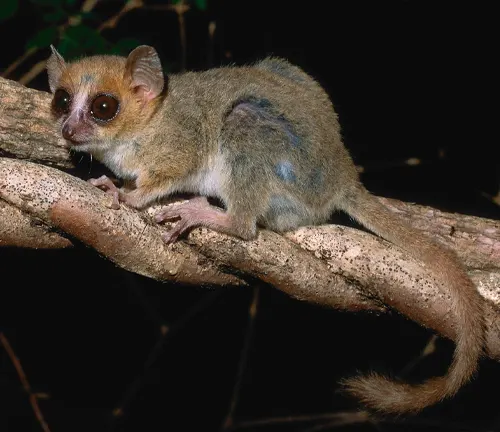
Fork-crowned Mouse Lemur
(Microcebus furcifer)
This species is distinguished by the forked crown of fur on its head. It inhabits the rainforests of eastern Madagascar.
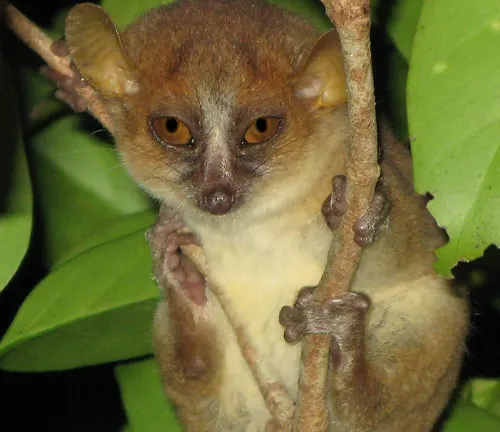


Mittermeier’s Mouse Lemur
(Microcebus mittermeieri)
Named after Dr. Russell Mittermeier, a primatologist and conservationist, this species is relatively newly discovered and found in central Madagascar.
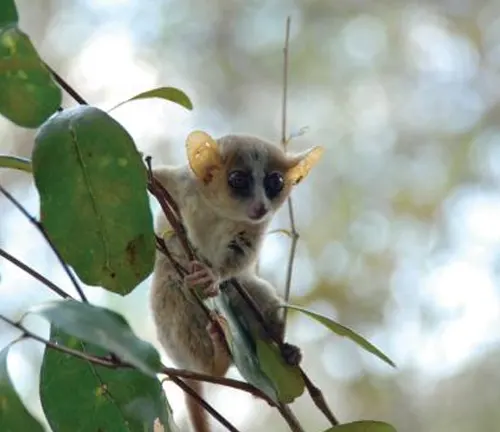
Bongolava Mouse Lemur
(Microcebus bongolavensis)
This mouse lemur is native to the Bongolava Massif in western Madagascar and is known for its small size and distinctive coloration.
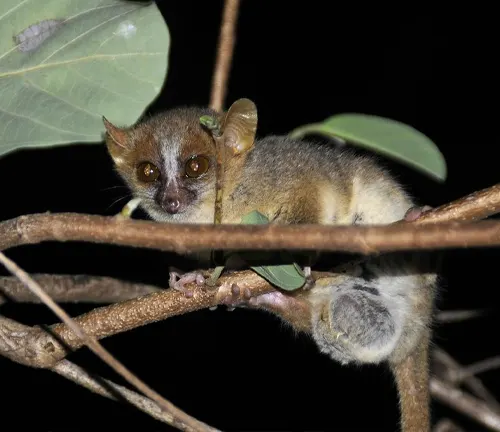


Northern Rufous Mouse Lemur
(Microcebus tavaratra)
This species has a reddish-brown fur coat and is found in northern Madagascar. It is known for its agility in tree-dwelling.
Sambirano Mouse Lemur
(Microcebus sambiranensis)
Found in the Sambirano region of northwestern Madagascar, this mouse lemur has a striking appearance with reddish-brown fur and large ears.
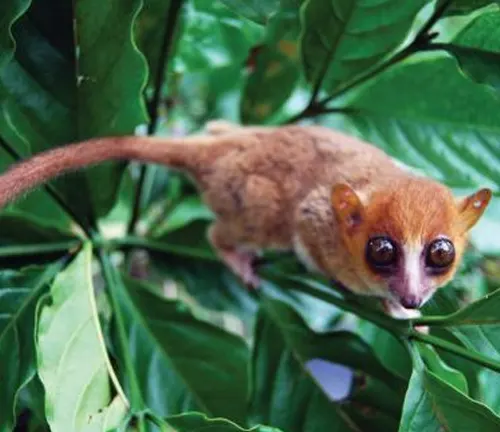
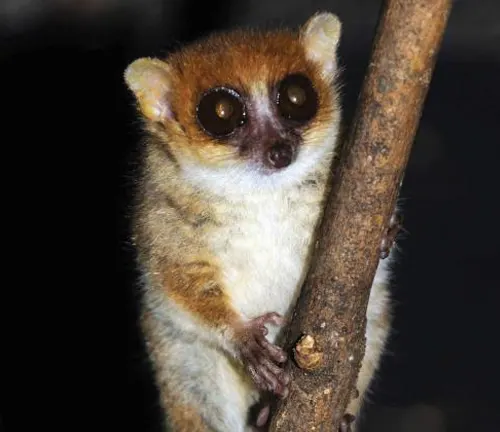


Simmons’ Mouse Lemur
(Microcebus simmonsi)
Named after the primatologist Lee Simmons, this species is found in the forests of eastern Madagascar.
Frequently Asked Question (FAQs)
1. What are mouse lemurs?
Mouse lemurs are small primates that belong to the Microcebus genus. They are known for their small size and are native to Madagascar.
2. How small are mouse lemurs?
Mouse lemurs are incredibly small, with some species measuring just around 9.2 cm (3.6 inches) in length, making them one of the smallest primates in the world.
3. Where are mouse lemurs found?
Mouse lemurs are exclusively found on the island of Madagascar, and they inhabit various types of forests and ecosystems across the island.
4. What do mouse lemurs eat?
Mouse lemurs have an omnivorous diet, which means they eat a variety of foods, including fruits, flowers, insects, and small vertebrates. Their diet varies depending on their habitat and the availability of food.
5. Are mouse lemurs nocturnal?
Yes, mouse lemurs are primarily nocturnal, which means they are most active during the night. They have adapted to hunting and foraging in low light conditions.
6. How many species of mouse lemurs are there?
There are over 20 recognized species of mouse lemurs, and more may be discovered as research continues.
7. Are mouse lemurs endangered?
Some species of mouse lemurs are endangered or vulnerable due to habitat loss and the illegal pet trade. Conservation efforts are in place to protect them.
8. Do mouse lemurs have predators?
Yes, mouse lemurs have natural predators, including owls, snakes, and larger mammals, which pose a threat to them, especially during their nocturnal activities.
9. What is the lifespan of a mouse lemur?
The lifespan of a mouse lemur typically ranges from 6 to 12 years in the wild, but they can live longer in captivity.
10. How can I support mouse lemur conservation efforts?
You can support mouse lemur conservation by donating to reputable organizations, spreading awareness about their conservation needs, and advocating for the protection of their natural habitat.














Leave your comment